by Luke Movius 6 years ago
338
Movius Macromolecules
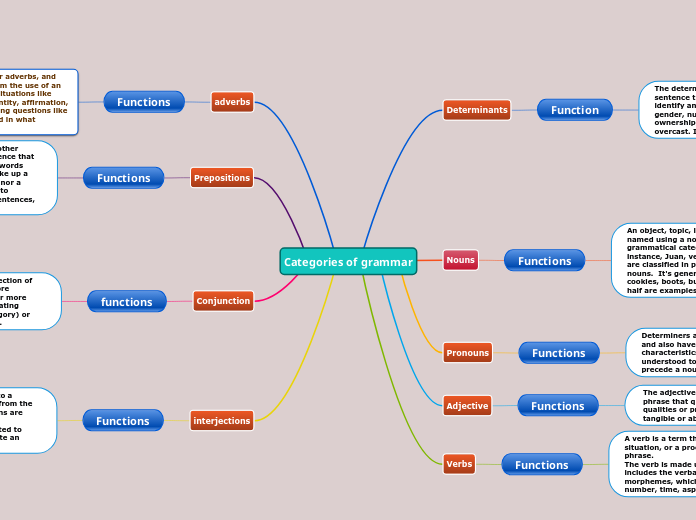
Biological macromolecules are essential components of all living organisms, each serving distinct and critical functions. Proteins are composed of amino acid chains linked by peptide bonds and are vital for movement, hormonal activity, immune responses, and transport of substances within the body.