by instrumentales sin copy 4 years ago
397
Organigrama
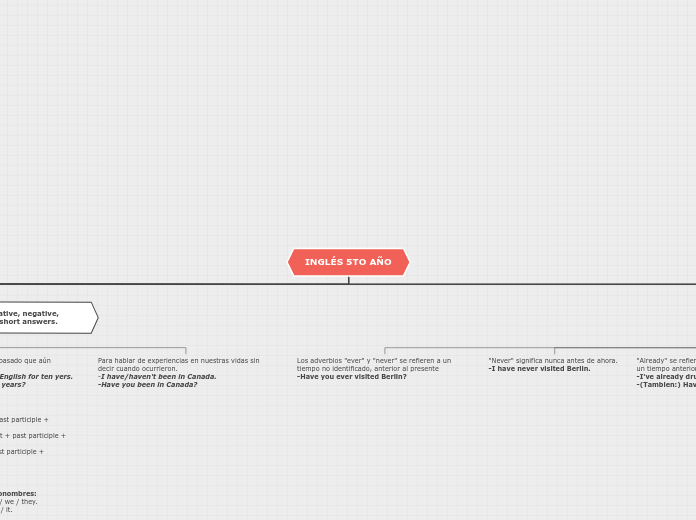
El present perfect en inglés se usa para hablar de acciones que comenzaron en el pasado y continúan en el presente o tienen relevancia en él. Se emplean expresiones como "for" para indicar periodos de tiempo y "