by Jamie Gilliam 9 years ago
459
Poetic Techniques Assignment
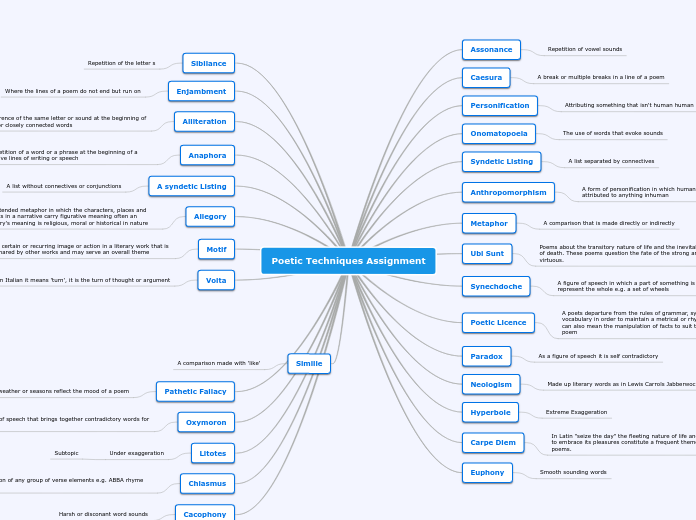
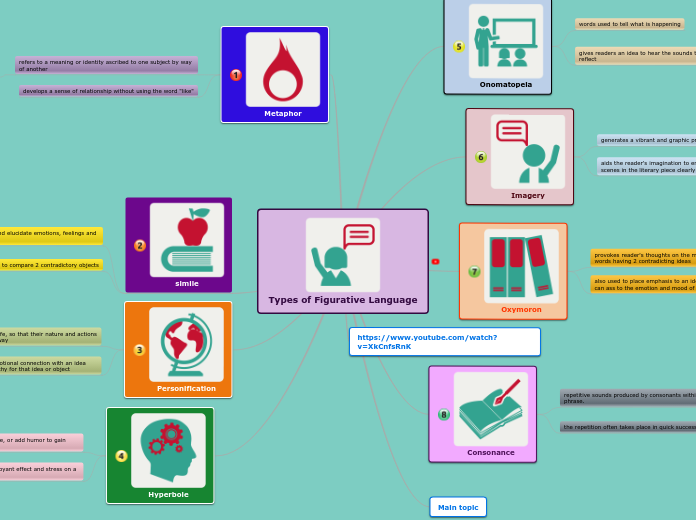
This text outlines various poetic techniques and literary devices often used in writing. It begins by describing euphony, which involves smooth-sounding words, and continues to explain anaphora, the repetition of words or phrases at the beginning of successive lines.