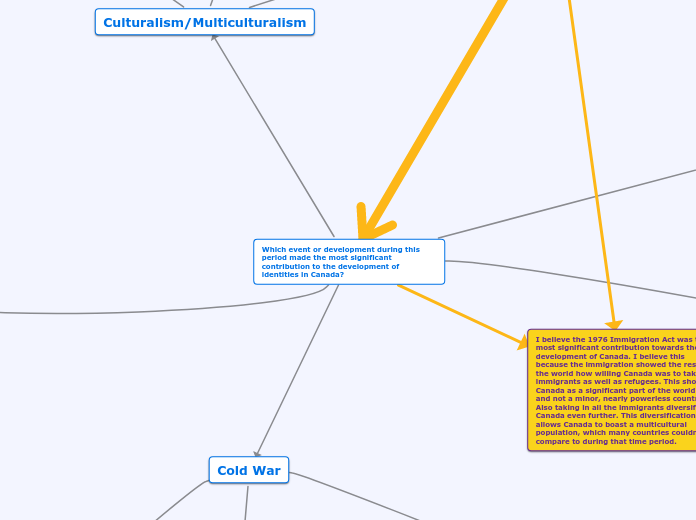
by Raeed Zafar 5 years ago
154
Post War Canada
In 1962, the Cuban Missile Crisis marked a pivotal moment in the Cold War, as Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba posed a direct threat to North America. The tense standoff between the United States, led by President John F.