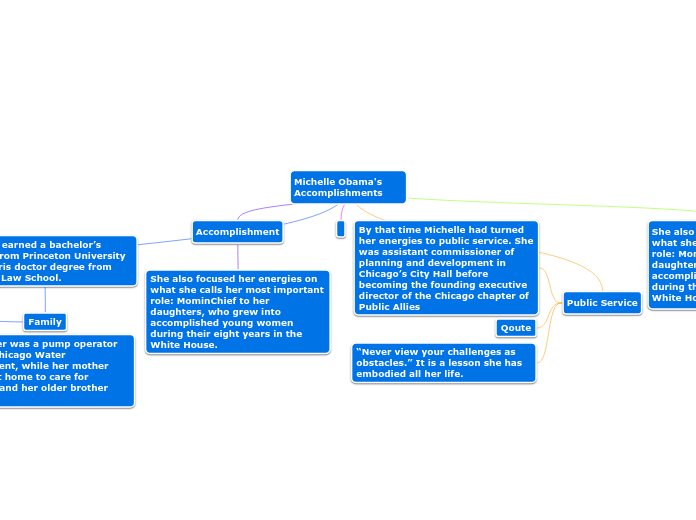
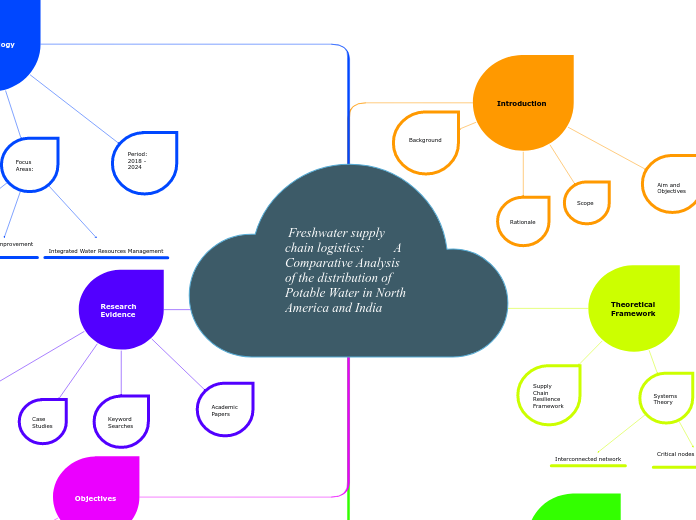
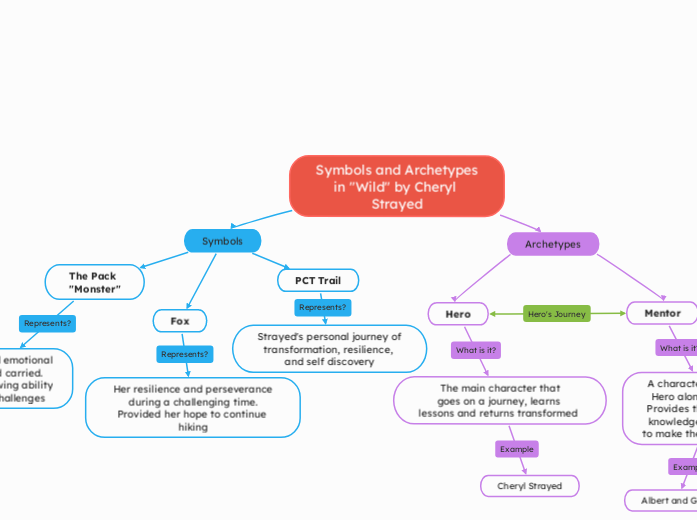
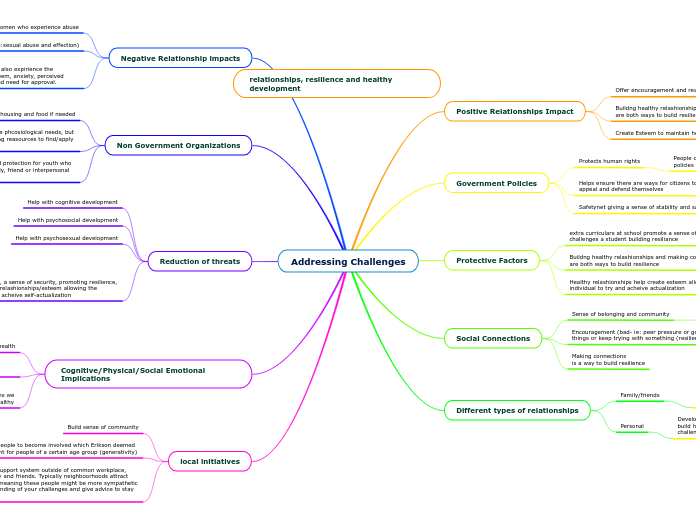
An ecologigal property is any
property that refer to the enviroment.
A technological is any property
that can be used for making
scientific investigation, also they
are used for solving some problems.
A chemical property is any of a
material's properties that becomes
evident during, or after, a chemical
reaction.
A physical property is any
property that can be mesured
whose value is in a physical
system.
properties of materials
Ecological
BIODEGRADABLE
Something that is biodegradable breaks down or decays naturally without any special scientific treatment, and can therefore be thrown away without causing pollution.
TOXIC
A toxic substanceis a someone that
is poisonous.
RESICABLE
Is a material that can be
usedd more than on time.
Technological
RESILIANCE
The property of a material that enables it to resume its original shape or position after being bent, stretched, or compressed; elasticity.
PLASTICITY
The ability of a material to be
change in shape permanently
ELASTICITY
The ability of a material to absorb force and flex
in different directions, returning to its original position.
DUCTILITY
The ability of a material to change shape (deform) usually by stretching along its length.
MALEABILITY
The ability of a material to be reshaped in all directions without cracking
BRITLENESS
An object that is easy to break, snap, or crack, as when subjected to pressure.
TROUGHNESS
A characteristic of a material that does not break or shatter when receiving a blow or under a sudden shock.
HARDNESS
The ability of a material to resist scratching, wear and tear and indentation
Chemical
CORROSION
Is the damage that is caused when something is corroded.
OXIDATION
Is a process in which a chemical substance changes because of the addition of oxygen.
Physical
MECHICAL
Flexion
Is the act of bending or the condition of being bent.
Compression
Is the increase of pressure in an engine cylinder as the piston travels toward top dead center.
Tension
The ability of a material to stretch without breaking or snapping.
Subtema
Torsion
Is a twisting effect on something such as a piece of metal or an organ of the body.
Shear
A strain in the structure of a substance produced by pressure, when its layers are laterally shifted in relation to each other.
Strengh
The ability of a material to stand up to forces being applied without it bending, breaking, shattering or deforming in any way.
OPTICAL
Transparent
Translucent
If a material is translucent, some light can pass through it.
Opaque
If an object or substance is opaque, you cannot see through it.
THERMAL
Welding
Welding is the process of joining two plastic or metal parts by melting them, with or without using a further molten material.
Fusibility
A material that can be fused or easly melt.
Expansion/ Contraction
Contracion is the process of becoming smaller in size, number,
or amount.
Expansion is the process of becoming greater in size, number, or amount.
The property of transmitting heat, electricity, or sound
ELECTRICAL
Semiconductivity
A semiconductor is a substance that can act as an electrical conductor or insulator depending on chemical alterations or external conditions.
Insulator
A substance or device which does not readily conduct electricity.
Conductivity
The ability of a material to conduct electricity.
DENSITY
Density is a scalar quantity referred to the amount of mass in a given volume of a substance.