RSS
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
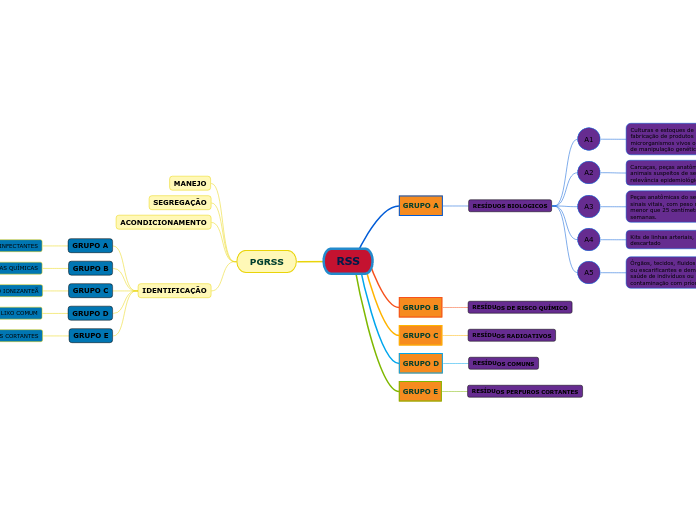
PGRSS
IDENTIFICAÇÃO
Solar energy begins with the sun. Solar panels are used to convert light from the sun, which is composed of particles of energy called 'photons', into electricity that can be used to power electrical loads.
Write down the benefits of using solar panels.
LIXO COMUM
RADIAÇÃO IONIZANTEÃ
SUBSTÂNCIAS QUÍMICAS
SUBSTÂNCIAS INFECTANTES
ACONDICIONAMENTO
Nuclear energy originates from the splitting of uranium atoms – a process called fission.
This generates heat to produce steam, which is used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Because nuclear power plants do not burn fuel, they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Nuclear Energy.
SEGREGAÇÃO
MANEJO
GRUPO E
RESÍDUOS PERFUROS CORTANTES
GRUPO D
RESÍDUOS COMUNS
GRUPO C
RESÍDUOS RADIOATIVOS
GRUPO B
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
RESÍDUOS DE RISCO QUÍMICO
Motion energy or mechanical energy is the energy stored in objects; as objects move faster, more energy is stored.
Examples of motion energy include wind, a flowing river, etc.
Give more examples.
GRUPO A
RESÍDUOS BIOLOGICOS
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Write down the main components of a typical flywheel.
A5
Órgãos, tecidos, fluidos orgânicos, materiais perfurocortantes ou escarificantes e demais materiais resultantes da atenção à saúde de indivíduos ou animais, com suspeita ou certeza de contaminação com príons
A4
Kits de linhas arteriais, endovenosas e dialisadores, quando descartado
A3
Peças anatômicas do ser humano; produto de fecundação sem sinais vitais, com peso menor que 500 gramas ou estatura menor que 25 centímetros ou idade gestacional menor que 20 semanas.
A2
Carcaças, peças anatômicas, vísceras e os cadáveres de animais suspeitos de serem portadores de microrganismos de relevância epidemiológica com risco de disseminação
A1
Culturas e estoques de microrganismos; resíduos de fabricação de produtos biológicos; descarte de vacinas de microrganismos vivos ou atenuados; resíduos de laboratórios de manipulação genética.