by Gagandeep Ram 2 years ago
143
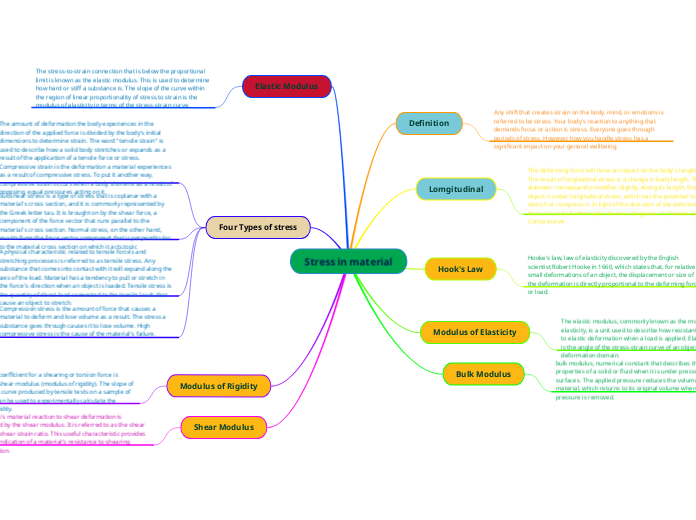
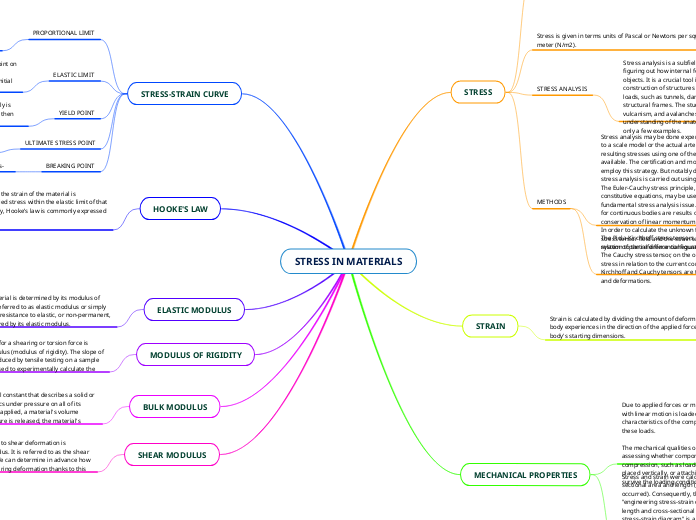
Stress in material
The modulus of rigidity, also known as the shear modulus, is crucial for understanding how materials respond to shearing or torsion forces. This property can be experimentally determined through tensile tests, offering insights into a material'