Gayatri Spivak:
'Can the subaltern speak?'
Spivak and Deconstrucyion (Derrida)
Of Grammatology
The word "writing" is a practice
"only within the historical closure
that is to say within the limits of
science and philosophy
Awareness of the itinerary of the
discourse of presence in one's own
critique
3 kinds of prejudices--constituted a
symptom of the crisis of European
consciousness (p.292-p.293)
3. Hieroglyphist prejudice
2. Chinese Prejudice
1. Theological prejudice
The limitation: The appropriate
ideological self-justification of an
imperialist project
The question is how to keep the
ethnocentric Subject from
establishing itself by selectively
defining an Other--Recognition
and Assimilation (Third World)
Prejudice between Derrida and
Foucault (p.291)
Derrida is "probably" most
significant --Dismantling
Eurocentrism p.292 (hard to read
yet less dangerous)
"Can the Subaltern Speak?" is notable for its bold criticism of Western scholars who study the poor and excluded, and its concern for gender* in postcolonial* studies (inquiry into the various effect and legacies of colonialism, particularly through the study of language and culture).
Discussed how scholarship, and particularly Western scholarship, always misrepresents so-called "Third World" people (those from the developing countries), and show why subaltern women are doubly marginalized (first as the colonized, then again as women)
Epistemic Violence (violence inflicted through thought, speech, and writing, rather than actual physical harm).
Example of epistemic violence is when accounts of history leave out subalterns. When oppressed people are not allowed to speak for themselves, or to have their contributions recognized, they are in effect erased from their place in the world. This is especially common for subaltern women.
"If, in the context of colonial production, the subaltern has no history and cannot speak, the subaltern as female is even more deeply in shadow".
Hindu Law of Indian Education
the narrative of the stabilization
and codification of Hindu law is
less well known than the story of
indian education,
Quoted from Macaulay's famous
program "Minute on Indian
Education" (1835) "We must at
present do our best to form a class
who may be interpreters between
us and the million whom we
govern; a class of person, Indian in
blood and colour, but English in
taste, in opinion, in morals, and in
intellect."
one effect of establishing a version of the British
system was the development of an uneasy
separation between disciplinary formation in
sanskrit studies and the native, now alternative,
tradition of sanskrit "high culture". within the
former, the cultural explanations generated by
authoritative scholar matched the epistemic
violence of the legal project.
Epistemic Violence and Hindu Law
4. Vyavahara (the performed-in-exchange)
3. Sastra (the learned-from-another)
the second two texts-the learned and the performed-were
seen as dialectically continuous. legal theorist and
practitioners were not any given case certain if this
structure describe the body of law or four ways of
settling a dispute.
2. Smiriti (the remembered)
the origins what have been heard and
what was remembered were not necessarily
continuous or identical. every in vocation of
sruti technically recited (or re-opened) the
even of originary "hearing" or revelation.
1. Sruti (the heard)
What does "Can the subaltern speak?" Say?
-Whether subaltern can speak, it is more interested in whether they can be heard.
There are a number of factors preventing this: the most powerful people- academics, religious leaders, or people who are otherwise privileged in society- always speak for them.
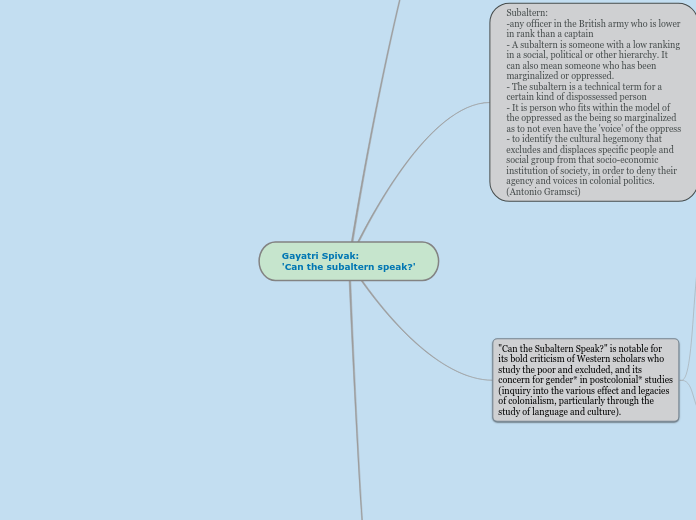
Subaltern:
-any officer in the British army who is lower in rank than a captain
- A subaltern is someone with a low ranking in a social, political or other hierarchy. It can also mean someone who has been marginalized or oppressed.
- The subaltern is a technical term for a certain kind of dispossessed person
- It is person who fits within the model of the oppressed as the being so marginalized as to not even have the 'voice' of the oppress
- to identify the cultural hegemony that excludes and displaces specific people and social group from that socio-economic institution of society, in order to deny their agency and voices in colonial politics. (Antonio Gramsci)
In postcolonial studies and in critical theory, the term subaltern designates and identifies the colonial populations who are socially, politically, and geographically excluded from the hierarchy of power of an imperial colony and from the metropolitan homeland of an empire
Antonio Gramsci (was an Italian Marxist philosopher, journalist, linguist, writer, and politician)
Gayatri Chakravory Spivak
- India, February 24, 1942 (80 years)
- an Indian scholar, literary theorist, and feminist critic.
- a university professor at Columbia University and a founding member of the establishment's institue for Comparative Literature and Society
Spivak combines ideas from Marxism* (here an approach
critical of capitalist economic exploitation), feminism* (promotion of equality between the sexes), and deconstruction. These specialties help her make an argument about the oppression caused by differences in power, gender, and access to knowledge
Her essay offers a perspective on many key postcolonial concerns:
5. The relationship between colonialism and other systems of
oppression, including patriarchy and, to her mind, capitalism*
(a social and economic system in which trade and industry are
exercised for the sake of private profit).
4. How history might be told from
the point of view of the
colonized, rather than the colonizer.
3. How to restore indigenous (so-called
“native”) cultures that were systematically pushed down under colonialism.
2. The ethical issue that arise when representing and speaking for others.
1. The dangers of believing that
Western thinking can be used in
non-Western contexts without
causing problems.