by Lira Karen 2 years ago
236
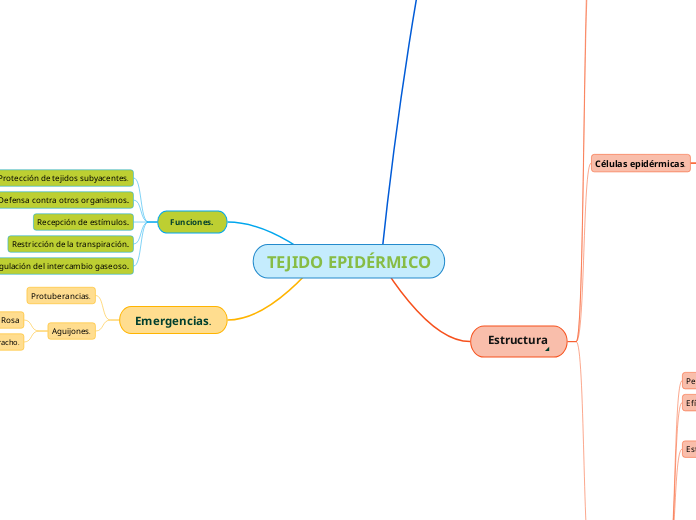
TEJIDO EPIDÉRMICO
El tejido epidérmico de las plantas se caracteriza por su estructura sin espacios intercelulares y la presencia de tricomas, que son apéndices con diversas funciones, formas y estructuras.
by Lira Karen 2 years ago
236

More like this
Global warming is the ongoing rise of the average temperature of the Earth's climate system which has various negative effects.
Overpopulation creates an increased demand for energy as well as having negative effects on our environment and ecosystems.
Water is essential for agricultural production and food security. It is the lifeblood of ecosystems, including forests, lakes, and wetlands.
Overpopulation affects our water and this has negative outcomes.
Over-cultivation is the practice of excessive farming on a piece of land to the point of degradation of the soil as well as the land itself.
Climate change is likely to both increase electricity demand for cooling in the summer and decrease electricity, natural gas, heating oil, and wood demand for heating in the winter.
New infrastructure investments may be necessary to meet increased energy demand.
e.g.: nuclear power plants
How will climate change affect the production of clean energy?
e.g.: solar, wind, water
Finding reusable energy sources can be our first step towards conserving our environment.
Healthy ecosystems and rich biodiversity are fundamental to life on our planet.
Even small changes in average temperatures can have a significant effect upon ecosystems.
The inter-connected nature of ecosystems means that the loss of species can have knock-on effects upon a range of ecosystem functions.
e.g. bees go extinct
Pluricelulares.
Glandulosos.
Escamosos.
Unicelulares.
Ramificados.
Simples.
Absorción de agua.
Secreción de sustancias o enzimas digestivas.
Protección contra la radiación o frío.
Reducen la transpiración.
Retención de agua.
Defensa.
Apéndices epidérmicos.
Diversa función.
Diversa estructura.
Diversa forma.
Órganos florales.
Tallos.
Aparato estomático.
Células anexas.
Dos células oclusivas.
Paredes engrosadas.
Con cloroplastos.
Regular
Transpiración.
Intercambio gaseoso.
Cutícula.
Función.
Evita perdida de agua por transpiración.
Evitas daños mecánicos.
Usos industriales.
Bulnesia retama.
Lisa o no.
Cubierta grasosa.
Cutina.
Con pared primaria.
Climate change is affecting the habitats of several species, which must either adapt or migrate to areas with more favorable conditions.
e.g.: natural habitat disappearing
Climate change will affect mountain and lowland ecosystems, the diversity of wildlife, and the distribution of freshwater.
e.g.: forest fires
Climate change is supported by scientific evidence.
Write down the consequences caused by the melting of the ice-caps and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of polar bear habitat
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of land surface
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: flooding, rainfall increase