by Brynn Bondy 6 years ago
414
Theories Explained HSB4U
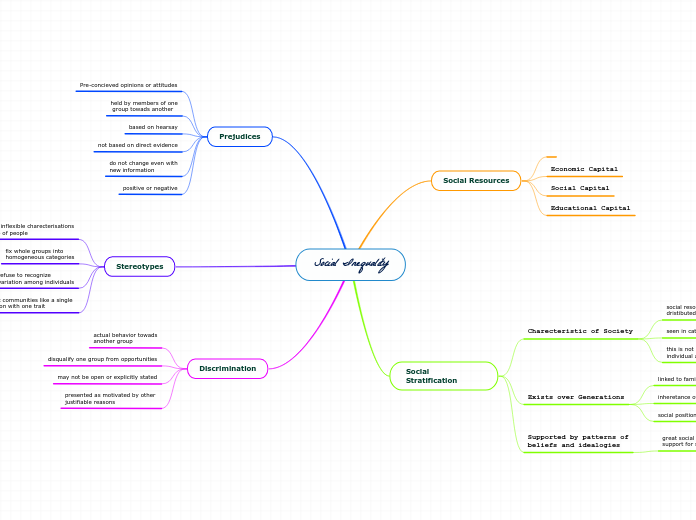
The structural functionalist perspective views society as a complex system with interdependent parts working to maintain stability and order. Intersectionality highlights how facing multiple forms of discrimination can motivate individuals to seek equality and social change.