by arianna cutaia 6 months ago
102
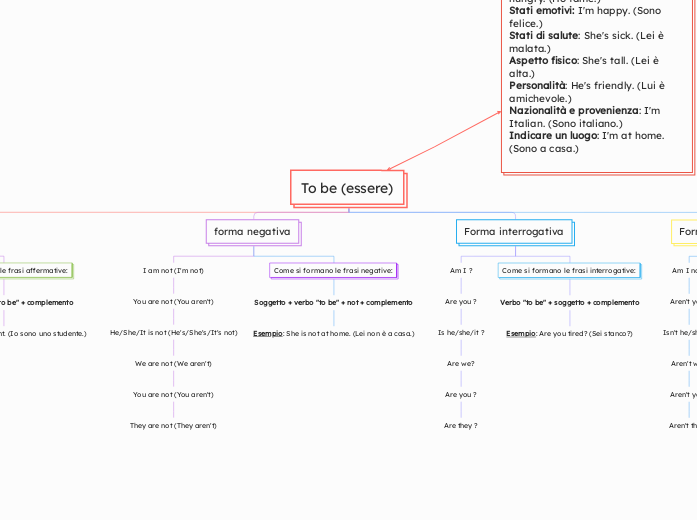
To be (essere)
Il testo spiega come esprimere diversi stati fisici, emotivi e di salute utilizzando il verbo "essere". Include esempi come "Ho fame" per la fame, "Sono felice" per la felicità, e "
by arianna cutaia 6 months ago
102

More like this
Esempi: Aren't you coming to the party? (Non vieni alla festa?) Isn't she beautiful? (Non è bellissima?)
Isn't he/she/it?
Aren't we?
Aren't they?
Esempio: Are you tired? (Sei stanco?)
Is he/she/it ?
Are we?
Are they ?
Esempio: She is not at home. (Lei non è a casa.)
He/She/It is not (He's/She's/It's not)
We are not (We aren't)
They are not (They aren't)
Esempio: I am a student. (Io sono uno studente.)
He/She/It is
We are
They are