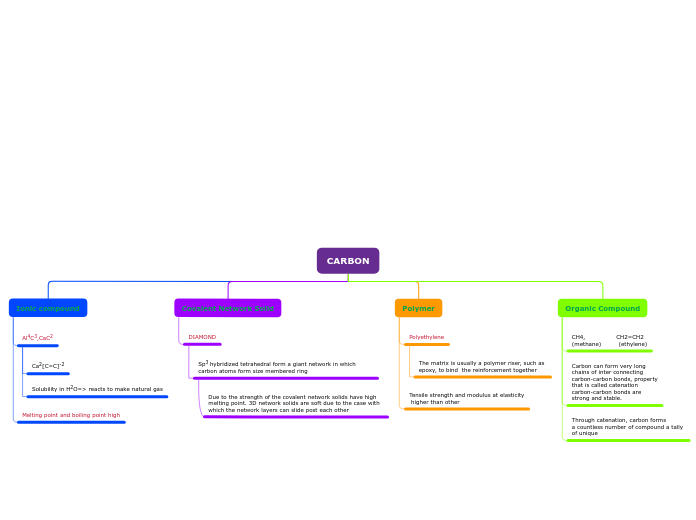
CARBON
Organic Compound
Through catenation, carbon forms
a countless number of compound a tally
of unique
Carbon can form very long
chains of inter connecting
carbon-carbon bonds, property
that is called catenation
carbon-carbon bonds are
strong and stable.
CH4, CH2=CH2
(methane) (ethylene)
Polymer
Tensile strength and modulus at elasticity
higher than other
Polyethylene
The matrix is usually a polymer riser, such as
epoxy, to bind the reinforcement together
Covalent Network Solid
DIAMOND
Sp3 hybridized tetrahedral form a giant network in which carbon atoms form size membered ring
Due to the strength of the covalent network solids have high melting point. 3D network solids are soft due to the case with which the network layers can slide post each other
Ionic compound
Melting point and boiling point high
Al4C3,CaC2
Solubility in H2O=> reacts to make natural gas
Ca2[C=C]-2