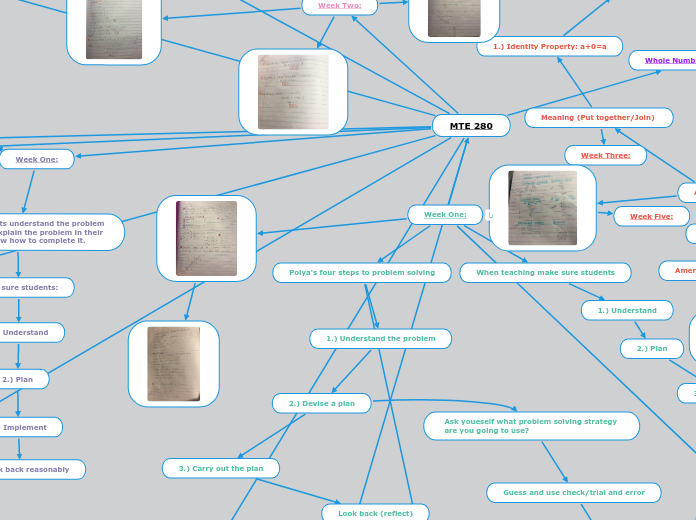
Week One:
MTE 280
Week Ten
Problem Solving with Fractions
Fraction word problems with models
Problem examples
Week Nine
Addition and Subtraction (common denominators)
Week Eight
Fractions
Models
1.) Surface Area
2.) Length
3.) Sets (groups of things)
1.) Part-whole
3 divided by 4=3/4
Ratio
Week Seven
GCF (Greatest Common Factor) LCM (Least Common Multiple)
Prime Factorization
The "Fingerprint"or "DNA" of every composite number: always the same factoraztion tree.
Number Theory
Prime numbers 1-60 2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47,53,59
-Types of Numbers
-Divisibility
-Factors-multiples>Fraction work
Divisibility Rules
Week Six
*Last Digits
-By 4: Last two digits are divided by 4
*Ending
-By 2: 0,2,4,6,8
-By 5: 0,5
-By 10: 0
*Sum of Digits
-By 3: Sum of digits is divided by 3
Make sure students understand the problem by having them explain the problem in their own words or show how to complete it.
Make sure students:
4.) Look back reasonably
Week Two:
Numeration Systems
-Base-10 System
-The Value of the number depends on the place
-The numbers get bigger by 10 times (1/10) x (1/10)= (1/100)
Numbers to the right of the decimal are part of the unit
Whole Number Operations
Division
Week Four:
Multiplication
Subtraction
Week 5:
Meanings
1.) Take Away 5-2=3
2.) Comparison
3.) Missing Add End
7-3=4
7 is the Minuend
3 is the subtrahend
4 is the Difference
Intager Subtraction
Left to Right Algorithm
Reverse Indian
European Mexican
Addition
Meaning (Put together/Join)
Week Three:
1.) Identity Property: a+0=a
2.) Commutative Property: a+b=b+a
Associative Property: (a+b)+c=a+(b+c)
Lattice
Expanded Notation
Place Value Explicit
Left to Right
Left to Right Algorithom
Right to Left
Partial Sums with Place Value
Partial Sums
American Standard
When teaching make sure students
1.) Understand
2.) Plan
3.) Implement
Look back to check if results are reasonable
Polya's four steps to problem solving
1.) Understand the problem
2.) Devise a plan
Ask youeself what problem solving strategy are you going to use?
Guess and use check/trial and error
Draw a picture or a diagram
Act it out
Make the problem simpler
Look for the pattern
Work backwards
Make an organized list
3.) Carry out the plan
Look back (reflect)