door ANDREI RUSAN 3 jaren geleden
218
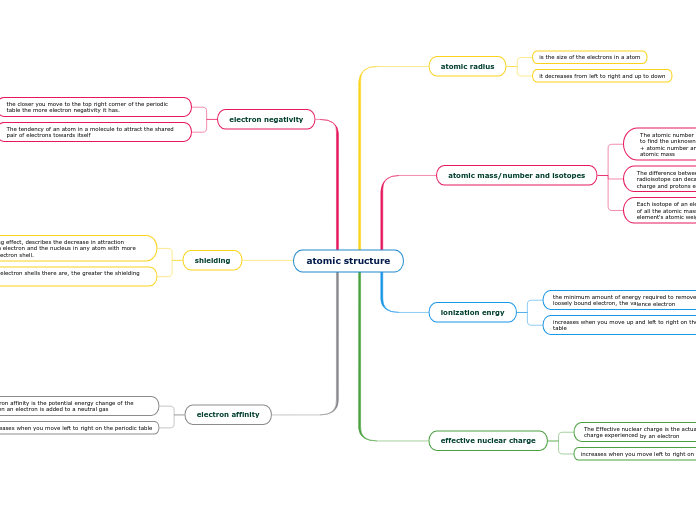
atomic structure
The text delves into various concepts related to atomic properties and behaviors. It begins by explaining atomic structure and the differences between isotopes and radioisotopes, noting that radioisotopes can decay due to lower nuclear charge.