door Michael McGlue 13 jaren geleden
398
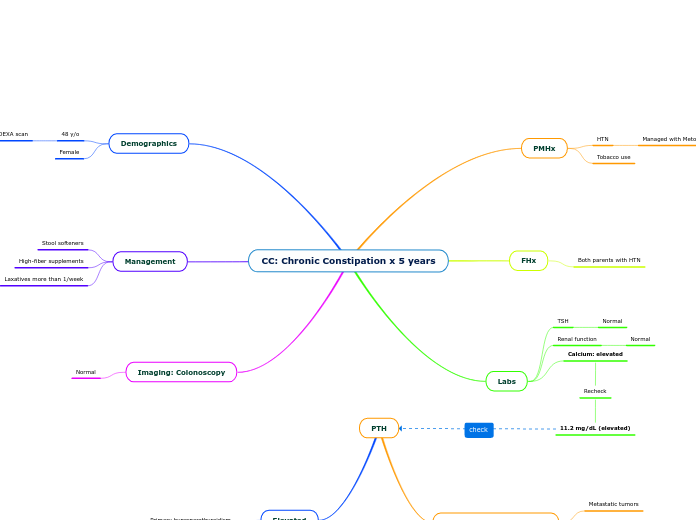
Congenital kidney anomolies
Various kidney disorders, both congenital and acquired, can lead to a range of complications including the development of cysts and renal cell carcinoma. Dialysis-associated cysts, often filled with clear fluid, can increase the risk of carcinoma in long-term dialysis patients.