HF/CA/IHD/HL/VT/PAD
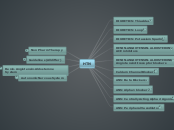
Peripheral Artery Disease
Cilostazol (pletal)
Improves exercise tolerance in intermittent claudication
"IC" is cramping, pain, and aching of legs that typically comes with walking and subsides at rest
Contraindicated
HF
decreased survival rates
phosphodiesterase inhibitor which suppress platelet aggregation and vasodilates
Clopidogrel (Plavix)
Prodrug
requires activation by CYP2C19 to activate drug
Effects platelets for entire lifespan
7-10 days
D/C 5 days before surgery
To pt:
prevents your platelets from sticking together to form a clot
blocks P2Y12 component of ADP receptors on platelets preventing activation of GPIIb/IIIa receptor complex reducing platelet aggregation
Chest Guidelines
For PAD refractory to exercise therapy and smoking cessation add cilostozal
For symptomatic PAD
use ASA or clopidogrel for 2ndary prevention
^ NO DUAL therapy
Aspirin is 1st line for asymptomatic PAD
moderatlely reduces cardiovascular events if taken over 10 years
NonPharm TX
exercise therapy
smoking cessation
Goals of Tx
reduce cardiovascular complications and death
improve quality of life
control comorbid conditions
improving walking distance, duration, pain
DM
cigarette smoking
Age >40
Risk of CVD morbidity and mortality
Progressive narrowing of arteries due to atherosclerosis
Hyperlipidemia
Bile Sequestrants
Poorly tolerated (Dead Drugs)
Lower TC, LDL, TG, and increase HDL
bind w/cholesterol in intestine
NOT metabolized by liver
promoting an increase in bile acid excretion they enhance conversion of cholesterol to bile acids by the liver and increase uptake of LDL
Ezetimibe (Zetia)
Better effects when used in combo with statins
recent data showed improved outcomes w/simvastatin for 2ndary prevention (IMPROVE-IT Trial)
Effects on cholesterol
reduces triglycerides (5-10%)
Increases HDL (1-4%) modest
Reduces LDL (19%)
works at cells in the brush border of the small intestine to inhibit dietary cholesterol absorption
also inhibits resorption of cholesterol secreted into bile
Niacin
Dosing is important:
1-3 grams
titrate slowly
avoid hot shower immediately after dose
take 30 min after aspirin 325mg w/snack
before bed
LA - hepatotoxicity
Immediate release:
flushing
Long-acting
Slo-niacin
Extended Release
Niaspan
Immediate Release
Niacor
Effects on Lipids
Increase HDL (modest)
Reduces Trigs (28-35%)
Reduces LDL (14-17%)
unknown
works in liver and adipose tissue to inhibit synthesis of triglycerides reducing VLDL and subsequently LDL
Fibrates
Administration
With food
Antara, lofibra
30 min prior to meals
Gemfibrozil
nausea, diarrhea, Gi upset
Myopathy
Hepatotoxicity
Fenofibrate (tricor, antara, lofibra, triglide, lipidil)
Genfibrozil (lopid)
Slightly elevate HDL
Slightly reduce LDL
Reduce triglycerides (40-50%)
binds PPAR alpha receptors in liver accelerating clearance of triglycerides
Effects on lipids
Elevate HDL 5-17% (modest elevation)
Lower triglycerides 10-40%
Atorvastatin and rosuvastatin
Lower LDL by >50%
HIGH INTENSITY STATINS
Lower LDL by 30-50%
MODERATE INTENSITY STATINS
drug interactions
rhabdomyolysis
Prevent Rhabdo
educate pts to hold statin for a few days if recieving interacting short term drug therapy
SEVERE INTERACTIONS:
clarithroycin, fluconazole, gemfibrozil, grapefruit, protease inhibitors, strong CYP 3A4 inhibs
may occur due to drug interactions or high dose statins
STOP STATIN
swelling of muscles, dark urine, fatigue, decreased urine output
breakdown of muscle tissue leading to accumulation of muscle fibers in blood
hepatoxicity
Diabetes (increase in A1C/BG)
cognitive dysfunction
myalgias
Plan: (if not rhabdomyolysis)
try 6 week statin free
Atorvastatin 10mg or Rosuvastatin 5mg dose every other day
Coenzyme Q10?
Check:
Vitamin D, TSH, CK
Assess:
Is it severe? limiting everyday activity? in a large muscle?
arthralgia
persistent elevation of LFTs
acute liver disease
pregnancy X
Reduce C reactice protein
Pleiotroic effects
anticoagulant effects
inhibit platelet aggregation
improve endothelial function
reduce inflammation or coronary plaque
explained to pt:
causes body to produce less cholesterol
inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, a rate limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis
As needed
repeat fasting lipid panel
repeat ALT
4-12 weeks
fasting lipid panel
Baseline
CK (if indicated)
ALT
Fasting Lipid panel
Benefits 4 groups
No ASCVD or diabetes, LDL 70-189, 10yr risk >7.5%
Diabetes, age 40-75, LDL 70-189
Primary LDL >190
Clinical ASCVD
HEART FAILURE
Classification
HFpEF (preserved EF)
use of beta blockers, ACEi, and ARBs reasonable in HTN
diuretics should be used for fluid overload
control BP based on current practice
Stage C HFrEF (reduced LVEF)
digoxin
Toxicity
blue/green auras, NVD, confusion, palpitation
electrolyte abnormalities may cause toxicity
super narrow therapeutic index
MOA: increases myocardial contractility
Hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate
can be used for pts with current or past sx who cannot tolerate ACE or ARB
rec'd for Black pts III-IV
Aldosterone receptor antagonists
rec'd to reduce morbidity and mortality followind acute MI
LVEF <40% or less or hx of DM
rec'd for LVEF <35%
potassium <5
creatinine <2.5 men, <2 women
Challenges: fatigue, edema, bradycardia, hypotension
Use of 1 of the 3 beta blockers proven to reduce mortality
Metorpolol succinate, carvedilol, bisoprolol
ARBS
Candesartan, Losartan, Valsartan preferred
can add ARB to ACE only if persistent sx and aldosterone antagonist indicated, but not tolerated
recommended for those w/ sx who could not tolerate ACEi
use caution in renal impairment and low BP
Recheck BMP in 1-2 weeks
recommended w/ current or prior sx to reduce morbidity and mortality
start low and increase
all equal in reducing death and hospitalizations
Diuretics
Adjust based on pt's weight
loop
may add metolazone to loop in renal impairment
supplement K+ if needed
eventually may need bumatanide d/t tolerance
1st line: furosemide
Stage B
Acei AND beta blocker in anyone with reduced EF to prevent sx HF (even w/o hx of MI)
Statin if hx of ACS or MI and reduced EF
Beta blocker if hx of ACS or MI
ACEi if hx ACS or MI and reduced EF
STAGE A
Control other contributors to HF
cardiotoxic meds
smoking
diabetes
obesity
Control HTN and lipids
Info
ACCF/AHA 2013 Guideline for management of HF
Tx based on EF
HFpEF
EF >50% (diastolic heart failure)
HFrEF
EF <40% (systolic heart failure)
Ejection Fraction (LVEF): measurement of how much blood is pumped out of the heart with each contraction
Mechanism
Activation of RAAS and SNS
Compensation
Tachycardia, LV remodeling, vasoconstriction
Myocradial injury
reduced contractility
Risk factors
Atherosclerotic disease (*MI*)
Metabolic Syndrome
50% mortality in 5yrs of dx (improvement!)
incidence increases with age
5.1 million ppl in US w/hf
Most common cause is impaired left ventricular function
Cardinal SX:
dyspnea, fatigue, fluid retention
Complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood
Venous Thromboembolism
Enoxaparin (lovenox)
Spinal or epidural hematomas
observe for neuro impairment
Risk of paralysis
Renal dose adjustments
Risk for HIT
Prefilled syringes for at home self admin
Longer half life than UF Heparin
Fixed dosing
does not require aPTT monitoring
caution in obesity
rapidly inactivate factor Xa
Unfractionated heparin
Antidote: Protamine
longer duration of action in renal impairment
Freq dose adjustment based on aPTT
Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
D/C heparin and do NOT rechallenge
Development of antibodies against heparin-plated protein
higher thrombosis risk
immune mediated disorder
reduction in platelets
Monitor
platelets
aPTT
MI
Disseminated intravascular coag
surgical prophylaxis
Evolving stroke
DVT/PE
do NOT use heparin for lock flush for parenteral anticoag
VTE and to flush lines
Large polysaccharide structure - unable to cross membranes
IV or SubQ
Does not cross placenta or into breast milk
rapidly acting anticoag, helps antithrombin inactivate clotting factors (Xa and thrombin)
rapid onset of action
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
Store in original container
do not place in pill box
expires in 4mo after opening
unstable when exposed to moisture
GI upset
consider use w/PPI
Take with food
Risk of bleeding
directly inhibits free thrombin and thrombin bound to clots
Factor XA inhibitors
INdications
DVT/PE tx
DVT/PR prophylaxis
Nonvalvular atrial fib
Does not require INR monitoring
ApiXAban (Eliquis)
RivaroXAban (Xarelto)
selectively inhibits factor Xa inhibiting the production of thrombin
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Safety
long term use:
risk of osteoporosis, alopecia
Bleed risk
Skin necrosis
usually within first several days
check for black skin on toes
Pregnancy Xd
Dosing
INR less than goal
assess for clots
increase dose by 5-20%
INR greater than goal
assess for bleeding
reduce by 5-20%
>4 consider holding a dose
start 5mg/day
2.5 for elderly, Asian, hepatic impairment, poor nutrition
Drug-Drug interactions
Many herbals increase bleed risk
ginseng, ginger, garlic
Avoid NSAIDs, increase bleeding
metabolized by CYP450 2C9
more freq INR checks with dose changes
MANY INTERACTIONS
statins, fluconazole, FQs, SSRIs, levothyroxine
Vit K can reduce effect of warfarin
smoking may reduce INR/ increase clot risk
alcohol may increase bleeding risk
kale, spinach, broccoli, collard greens, brussel sprouts, fried food
assess diet each visit
therapeutic levels measured by INR
Testing frequency depends on stability of INR
low INR = clot risk
elevated INR = bleeding risk
Goal varies
could be increased if pt had clot while on wafarin/APLS
mechanical mitral valve 2.5-3.5
General 2-3
INR about 1 for pts not on warfarin
No effect on clotting factors that are already circulating
also inhibits Protein C and Protein S:
body's natural anticoags = bridging
takes longer for the body to form clots
Vit K "antagonist" which inhibits vitamin k dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, X
Risk Factors
Meds:
estrogen, SERMSs, Chemo
pregnancy
malignancy
disorders of hypercoaguability
post surgery
immobility
clot in venous circulation resulting in DVT or PE
Angina
(Ischemic Heart Disease)
TX
Aspirin and statins in angina
reduction in LDL cholesterol levels play a signiificant role in decreasing the formation of athersclerotic plaque
preventative
aspirin decreases platelet aggregation to prevent cycle of vasoconstriction and platelet buildup
ACEis reduce the secretion of aldosterone
reducing extracellular fluid volume and preload
decreased sodium and water retention
decreased peripheral vascular resistance
decreased afterload
Subtopic
act on RAAS system
Calcium Channel Blockers in angina
CCBs may cause coronary vasodilation
atherosclerotic vessels do not dilate
cause arterial smooth muscle relaxation leads to peripheral vasodilation and decreased preload
Beta Blockers
decrease force of myocardial contractility and decrease HR and conduction velocity
1st line
Nitrates
ADRs: HA, Bradycardia, orthostatic, hypotension
Pregnancy C
Transdermal patches, allergy to adhesives may limit use
Contraindicated: hypersens
Nitrate prep - prophylaxis
Isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil)
to maintain nitrate free period
TID: 8am 1pm, 6pm
BID: 8am, 1pm
sustained release 1-2 times daily
immediate release dosed 2-3 times daily
Isosorbide mononitrate (Imdur)
extended release dosed once daily
immediate release dosed twice daily 7 hours apart
TAPER DOWN! DO NOT DC ABRUPTLY
NTG patch
apply in AM and leave on for 12-24 hours
apply once daily to hairless area, rotate
NTG ointment
cover with plastic
best to rotate sites
Apply to skin of chest, back , abdomen, or thigh
Nitrate preparations - acute
Take at first signs of chest pain, may repeat after 5 minutes for a total of 3 doses
If CP not relieved 5 min after 1st dose, call 911
Translingual spray
DO NOT INHALE
spray onto oral mucosa
0.4mg sublingual tablets
educate pts: SL only! do not swallow
store in original bottle
used for immediate relief or prophylaxis
Nitrate free period to prevent tolerance
Some dilation of coronary arteries
ATHEROSCLEROTIC VESSELS DO NOT DILATE
Higher doses dilate arterial vessels
DECREASED VASCULAR RESISTANCE (afterload)
low doses of NTG dilate veins decreasing venous return to heart
DECREASES PRELOAD
coronary vasodilators
Statins
ACEi
Calcium channel blockers
beta-blockers
nitrates
Aspirin
lifestyle changes: smoking cessation
Unstable
SX occur at rest or as worsening sx of stable angina
Sx occur as result of severe CAD with
transient coronary thombi or emboli
vasospasm
platelet aggregation
Medical emergency
Chronic Stable
TX goal
reduce risk of MI and death
reduce intensity and frequency of attacks
partial restriction of arteries results in angina
underlying cause is CAD (plaque in arterial wall)
triggered by physical activity, stress, or large meal
Oxygen demand
afterload
arterial pressure that the left ventricle must overcome in order to contract
preload
amount of tension from ventricular filling
myocardial contractility
heart rate
Cardiac Arrest
Vasopressin
vasoconstricts w/o effects on HR and contractility
increases water permeability at the renal tubule resulting in reduced urinary output of water
ADH analog
Epinephrine
Also used in anaphylaxis
increases blood pressure to perfuse the heart and brain
Alpha1 is majority of action in cardiac arrest
Agonizes alpha and beta receptors leading to vasoconstriction, increasing inotropy and increased chronotropy
Sympathomimetic
Tx
Electrical Defib
ACLS
CPR
main tx is nonpharm
HTN
Autonomic Nervous System
Beta actvity
Beta 2 receptor stimulation
bronchial dilation
Beta 1 receptor stimulation
increased heart rate/contractility
uterine relaxation
bronchial relaxation
vasodilation of arterioles supplying skeletal muscle
cardiac acceleration and increased contractility
Alpha activity
Alpha 2 receptor stimulation:
Vasodilation
Alpha 1 receptor stimulation:
Vasoconstriction
relaxation of gut
Pupil dilation
vasconstriction of arterioles (=HTN)
Parasympathetic
Acetylcholine
SLUDGE
Emesis
Gastric Distress
Digestion
Urination
Lacrimation
Salivation
Rest and digest
Sympathetic
AntiSLUDGE
No emesis
No gastric distress
No digestion
No urination
No lacrimation
No Salivation
dopamine
fight or flight
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Angiotensin II
activates Aldosterone and ADH
lead to Sodium& water retention, vasoconstrictor
vasoconstrictor
Guidelines (All differ)
JNC 8 (not endorsed)
Recommendation 8
18yo+ with CKD
Regardless of race or diabetes status
ACEi or ARBs to improve kidney outcomes
Recommendation 7
Black +those w/diabetes
thiazide or calcium channel blocker
Recommendation 6
NonBlacks <60 including diabetes
initial tx: thiazide diuretic, calcium channel blocker, ACEi or ARBs
Recommendation 5
18yo+ with DIABETES
treat & target <140/90
Recommendation 4
Any age with ALBUMINURIA (>30mg albumin) at any GFR
18-70 with GFR <60
18yo+ with CKD, target <140/90
Recommendation 3
<60yo, initiate pharm to lower SBP >140 mmHg
goal SBP <140
Recommendation 2
18-29yo: expert opinion
30-59yo: strong evidence
<60yo initiate drug tx to target DBP of <90
Recommendation 1
If a lower BP is achieved without adverse effects, no modification necessary
>60yo initiate pharm to treat and target <150/90
Main Objective
to reach and maintain a goal BP
DO NOT USE ACEi and ARB together
If goal is not reached w/2 agents, titrate a 3rd med
Continue to assess BP and adjust tx until goal BP is achieved
If goal BP not reach w/n 1 mo, consider increasing dose or adding 2nd agent
ASH/ISH
Heart Failure
(w/ or w/o HTN)
(ACEi or ARB) + beta blocker + diuretic +spironolactone
StrokeHx
CAD
Beta blocker + ACEi or ARB
CKD
ACE or ARB
Diabetes
ARB or ACE
(acceptable to start with CCB/thiazide in Black pts)
Essential HTN first line
Non Black >60: CCB or thiazide
Non Black <60: ACEi or ARB
Black: CCB or Thiazide diuretic
Non Pharm Therapy
Smoking cessation
Reduce alcohol
2 drinks M, 1 drink F
2-4 mmHg
Exercise
30 minutes/day
4-9 mmHg
Salt Reduction
DASH diet
8-14mmHg
Weight loss
For every 10kg lost
5-20 mmHg SBP
ANS: Peripheral Vasodilators
minoxidil
hirtsuism
fluid retention
use w/ beta blocker
hydralazine
drug-induced lupus
tachycardia
use w/ beta blocker
Not first line
Directly relax smooth muscles causing vasodilation
ANS: Centrally Acting Alpha 2 Agonists
Rebound HTN - taper dose down
methyldopa (Aldomet)
preferred agent in pregnancy
guanfacine (Tenex)
clonidine (Catapress)
stimulate alpha 2 receptors decreasing cardiac output, peripheral resistance, and sympathetic outflow (reduced HR)
ANS: Alpha1 blockers
dry mouth
drowsiness
palpitation
First does phenomenon
caution in elderly
start at low doses
take first dose at night/in bed
syncope
ANS: Beta Blockers
Monitor heart rate
DO NOT abruptly discontinue
ischemic events
Rebound tachycardia/HTN
fatigue
sexual dysfunction
Contraindicted
Severe bronchospastic disease
AV node dysfunction
acebutolol (Sectral)
pindolol (Visken)
nebivolol (Bystolic)
labetalol (Trandate)
propranolol (Inderal)
carvedilol (Coreg)
bisoprolol (Zebeta)
atenolol (Tenormin)
metoprolol
tartrate (Lopressor)
dosed twice daily
succinate (Toprol XL)
dosed once daily
Indicated
Arrhythmias
Migraine prophylaxis
Angina
Post MI
HF
NOT first line for hypertension
Negative inotropes and chronotropes
MOA:
selectively or non selectively inhibit beta1 receptors
Calcium Channel Blockers
2 Classes of CCBs
NON Dihydropyridines (Non-DHP)
CAUTION: if concomitant use with Beta-blocker and in HF w/reduced ejection fracture
Benefit in atrial fibrillation and stable angina
bradycardia
Sick sinus syndrome
Heart block
MOA: potent vasodilator of coronary vessels increasing blood flow and reducing heart rate by reducing AV node conduction
diltiazem (Cardizem)
verapamil (Calan)
Dihydropyridines (DHP)
Good first line option for HTN
benefit in Black pts
Side effects
flushing
palpitations
peripheral edema
constipation
MOA: relax smooth muslce vasodilating arterial walls which lowers total peripheral resistance and increases blood flow to the heart muscle
nifedipine (Procardia)
felodipine (Plendil)
amlodipine (Norvasc)
RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE:
Angiotensin II receptor blockers
hypotension
Contraindicated in pregnancy
Alternative to patients who cannot tolerate ACEi
less incidence of angioedema and cough
ACE not inhibited = normal breakdown of bradykinin
Valsartan (Diovan)
Temlisartan (Micardis)
Olmesartan (Benicar)
Irbesartan (Avapro)
Candesartan (Atacand)
Losartan (Cozaar)
angiotensin II receptor antagonist inhibting the RAAS system
Reduces peripheral resistance
RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE
ACE inhibitors
First Line if....
Post MI/Stroke
Diabetes - prevent nephropathy
Heart Failure
CKD - reduce progression
Proteinuria
Up to 30% bump in Scr normal
50% stop ACE inhibitor
> 30% reduce dose
becomes new baseline
Less effective in black patients
renal function deterioration
cough and angioedema
likely d/t bradykinin accumulation
Contraindications
Bilateral renal artery stenosis
Angioedema due to ACEi
Pregnancy
Not a great choice for women of childbearing age
Trandolapril (Mavik)
Ramipril (Altace)
Quinapril (Accupril)
Moexipril (Univasc)
Fosinopril (Monopril)
Benazepril (Lotensin)
Captopril (Capoten)
Enalapril (Vasotec)
Lisinopril (Zestril)
competitive inhibitor of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
causes increase in plasma renin activity and reduced aldosterone secretion
DIURETICS: Potassium Sparing
WARNINGs
anuria
hyperkalemia
Uses
HYPERKALEMIA
CAUTION using w/ACE-I and ARBs
use in combo w/another diuretic (commonly thiazide)
mostly used in edema/HF sx management
Not very potent in BP reduction/diuresis
Triamterene (Dyrenium)/ (Dyazide w/HCTZ)
Amiloride (Midamor)
Eplerenone (Inspra)
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
WARNING: gynecomastia
STOP if any sign of
aldosterone receptor blocker
Magnesium, calcium, and hydrogen excretion
Potassium retention
Not as potent as other diuretics
decreases function of the Na/K ATPase
block distal sodium channels in distal convulted tubule (DCT) inhibiting sodium resorption from the lumen.
DIURETICS: Loop
hyperglycemia
HA
dizziness
Diuretic resistance
Ototoxicity
Electrolyte imbalance
BUN
Renal function
VERY potent diuretics
may need K+ supplements
NOT generally used for BP
Agents
Torsemide (Demadex)
Ethacrynic Acid (Edecrine)
Does not have sulfa group
Bumetanide (Bumex)
Furosemide (Lasix)
interferes with cholride-binding cotransport system causing increased excretion of water, sodium, chloride, potassium, magnesium, and calcium
Inhibits resorption of sodium and chloride in ascending loop of Henle and distal renal tubules
DIURETICS: Thiazides
Warnings
MAY INCREASE CALCIUM
electrolyte disturbances
gout
Sulfa allergy
Side Effects
skin rash
orthostasis
dizzness
urinary frequency
Photosensitivity
Monitoring
renal function
electrolytes
BP
Administer in morning
AGENTS
Metolazone (Zaroxolyn)
EFFECTIVE even if eGFR <30ml/miin
Indapamide (Lozol)
Chlorthalidone (Microzide)
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)
ineffective if eGFR <30ml/min
MOA
inhibits sodium resorption in distal tubule leading to increased excretion of sodium and water, potassium and hydrogen ions (reducing blood volume)
reduces vascular resistance