door Tyler Schulz 4 jaren geleden
1349
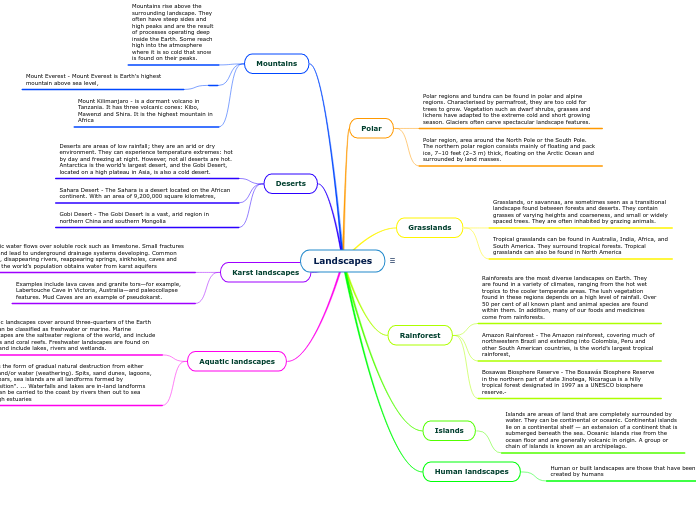
Landscapes
Arid deserts, like the Gobi and Sahara, experience extreme temperatures and vary from hot to cold, with Antarctica being the largest cold desert. Aquatic landscapes, covering three-quarters of the Earth, include both freshwater and marine environments, like lakes, rivers, oceans, and coral reefs.