Motor Skill
Classifications
Fine
Examples:
-Throwing a Dart
-Writing
-Typing
Precise smaller movements
Uses small muscle groups
Gross
Example:
-Jumping
-Sprinting
-Throwing a ball
Generates large power/force
Uses large muscle groups
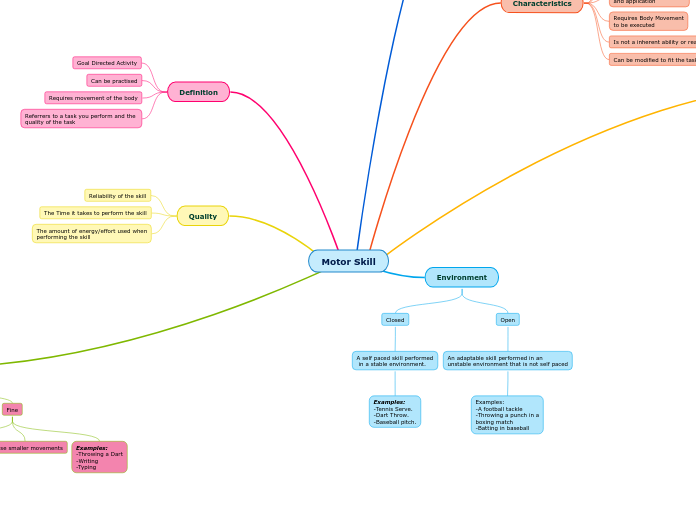
Quality
The amount of energy/effort used when
performing the skill
The Time it takes to perform the skill
Reliability of the skill
Definition
Referrers to a task you perform and the
quality of the task
Requires movement of the body
Can be practised
Goal Directed Activity
Environment
Open
An adaptable skill performed in an
unstable environment that is not self paced
Examples:
-A football tackle
-Throwing a punch in a
boxing match
-Batting in baseball
Closed
A self paced skill performed
in a stable environment.
Examples:
-Tennis Serve.
-Dart Throw.
-Baseball pitch.
Organisation
Continuous
A repeated movement with an
unclear beginning and ending.
Longer in duration
Examples:
-Running
-Swimming
Serial
Several individual discrete
actions linked together in
a specific order
Examples:
-A drive into a shot in
basketball
-A 1-2 punch combination
-Dribbling and kicking the
ball into a net
Discrete
A movement with a specified
beginning and ending. Short
in duration
Examples:
-Shooting a basketball
-Throwing a punch
-Kicking a soccer ball
Characteristics
Can be modified to fit the task required
Is not a inherent ability or reaction
Requires Body Movement
to be executed
Learned through practise
and application
Voluntarily and deliberately
performed
Performed for the sake of achieving
a specific goal
Types
Fundamental Motor Skills
Foundational skills learned through
the lived experience
Specialised Motor Skills
Advanced/combinations of the fundamental
skills that can be applied to a specific sport/task