door Prisha Singh 9 maanden geleden
61
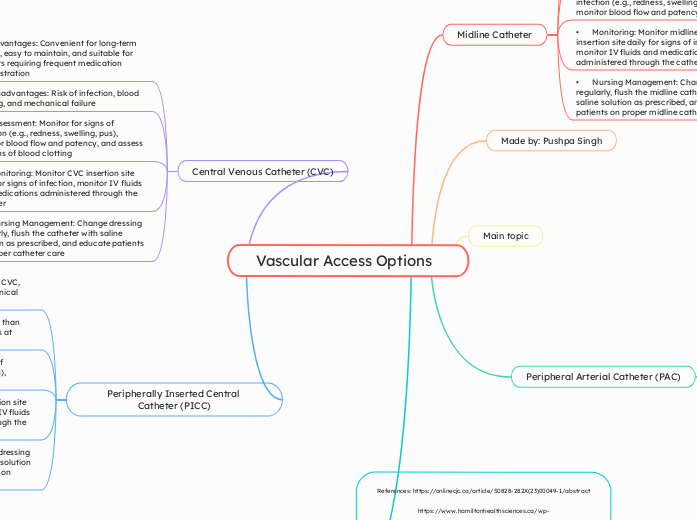
Vascular Access Options
Vascular access options for patients include Peripheral Arterial Catheters (PAC), Central Venous Catheters (CVC), and Midline Catheters, each with distinct benefits and drawbacks. PACs are easily inserted and removed, reducing infection risks but can cause discomfort.