door saudith padilla berrio 5 jaren geleden
476
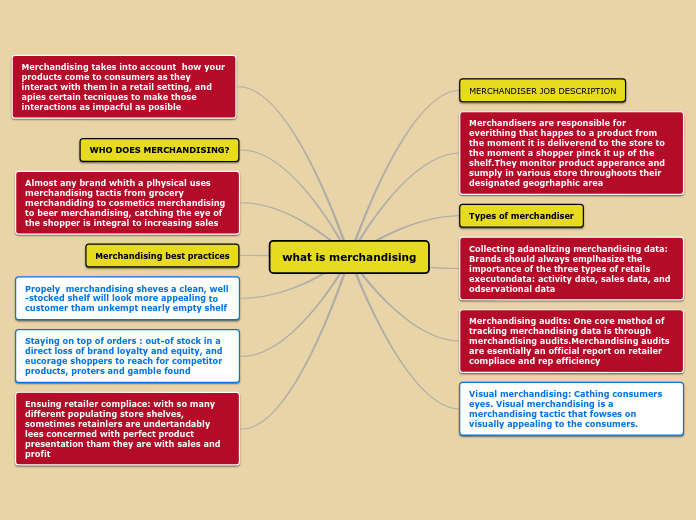
what is merchandising
Merchandising involves the strategic presentation and management of products in a retail environment to enhance appeal and drive sales. It encompasses a variety of practices, with merchandising audits playing a critical role in assessing retailer compliance and efficiency.