av Cara Browdy 11 år siden
502
AIS Ch 3
Internal control is a process that involves the entire organization and is subject to continuous improvement and analysis. It aims to reasonably assess situations despite not providing absolute assurances.
av Cara Browdy 11 år siden
502

Mer som dette
FOREIGN CORRUPT PRACTICES ACT (1977)
addresses issue of bribery and other illegal (in the U.S.) activities by requiring multinational organizations to implement sound internal controls
SARBANES-OXLEY ACT (2002)
enacted in response to wave of financial fraud in 1980s-90s.
makes mgmt accountable for assessing and maintaining internal controls
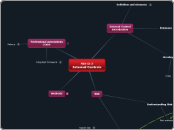
Internal Control:
-is a process, subject to improvements and analysis
-involves members of the organization and must take into consideration effects of behavior on the execution of the process as well as effects of the process on behavior
-cannot provide absolute assurances, but with ongoing ananlysis and improvements, can reasonably assess situations
-operates over a variety of departments and processes
1. safeguard assets
2. ensure reliability of financial stmts
3. ensure operating efficilency
4. ensure compliance with mgmt's directives
Financial Executives Institute
Institute of Internal Auditors
institute of Management Accountants
American Institute of CPAs
American Accounting Association
-control environment (executive support)
-control activies
(preventive, detective, corrective)
-risk assessment
-monitoring (ongoing assessment of IC performance)
-information and communicaiton
-adequate documentation (changing rapidly in an increasingly paperless atmosphere)
-backup of electronic files
-bank rec
-document matching
-edit checks
-insurance & bonding
-limit checks
-physical security
-preformatted date entry interface
-separation of duties
many others
taxonomy = organizational structure for knowledge
Fianacial Risk
-market risk (stock prices, investment values, interest)
-credit risk (nonpayment)
-liquidity risk (too much $$ tied up in long-term assets)
Operational Risk
-Systems risk (IT)
-human error
Strategic Risk
Concerned with executive & director behavior
-legal/regulatory risk (breaking laws, failing to comply with regs)
-Business strategy risk (poor decision making)
Hazard Risk
-directors' and officers' liability
(idiocy on the executive level)
-strategic risk
-decision risk
-operating risk
-financial risk
-information risk
Risk professionals organize risks involved in running the company to make better use of historical and forecasted information.
Different structures probably allow for specialization of risk management, depending on the industry/activity of the organization.