Cell Growth and Divison
Section 4
Frontiers in Stem Cell Research
Ethical Issues
Would be killing a human being
Some humans argue that embryo is already living
Embryonic mus be taken from a new embryo
Embryonic cells are Very controversial
Very few issues with Adult cells
Potential Benefits
One way may be to put bone marrow cells into the heart
Researchers hope to reverse effects of heart attacks
Repair/Replace damaged cells and tissues
Repair damaged organs
Make new organs
Stem Cells and Developement
Stem Cells
Adult is Multipotent
Embryonic is Pluripotent
Make Different cells
Unspecialized Cells
2 TypesEmbryonic and Adult
Human Developement
Inner cells for the embryo
Outer cells form tissue to attach to mother
Blastocyst- Hollow ball of cells with a cluster of cells inside
Human embryo forms a blastocyst after 4 days
Multipotent- Can make a FEW kinds of cells
Pluripotent- Can make ANY type of cell
Section 1
Cell Division and Reproduction
Comparing Asexual/Sexual Reproduction
Asexual- Can't adapt to conditions Sexual- Adapts to conditions
Asexual- Genetic Clones
Sexual- Genetically Diverse
Asexual- Fast
Sexual- Slow
Some organisms can reproduce both ways
Both are survival strategies
Sexual Reproduction
Genetically Diverse
Takes time
Inherit DNA from both parents
Two cells fuse to make one cell
2 Parents
Asexual Reproduction
Child is genetically identical to parent
Population increase quickly
Simple, Efficient, Effective
One cell splits to form Two cells
One Parent
Limits to Cell Size
Divison of the Cell
Solves "Information Overload" and "Cell Volume" problems
Before division, cell replicates DNA
Reduces cell volume
Process is called Cell Division
Cell divides to form two "daughter" cells
Exchanging Materials
Surface Area= l x w
Volume= l x w x h
SMALL Surface Area: Volume is bad for cell
Rate of food, oxygen, and waste exchange depends on surface area
Waste needs to be removed quickly
Information Overload
Causes cell to divide
Too much DNA to handle
Happens when cell is too big
DNA does not increase with cell size
Critical Info stored in DNA of cell
Section 3
Cancer
Treatments
New advances have cured some cancers
Chemotherapy also corrupts some normal cells
Chemotherapy (Chemicals)
Targeted Radiation
Surgery
Causes
Sun Tanning
Viral Infection
Defective Genes
Chewing/Smoking Tobacco
Too much Radiation
Section 2
Cytokenesis
Plant Cells
Forms two new plant cells
Cell Plate forms a Cell Wall
Cell Plate forms between the 2 nuclei
Cell Wall isn't flexible enough to pinch
Animal Cells
If done correctly, Cells are genetically identical
Each new cell contains a nucleus and organelles
Cell splits into 2 closely equal parts
Cell Membrane is pinched together
Cytokinesis- Splits cell into two
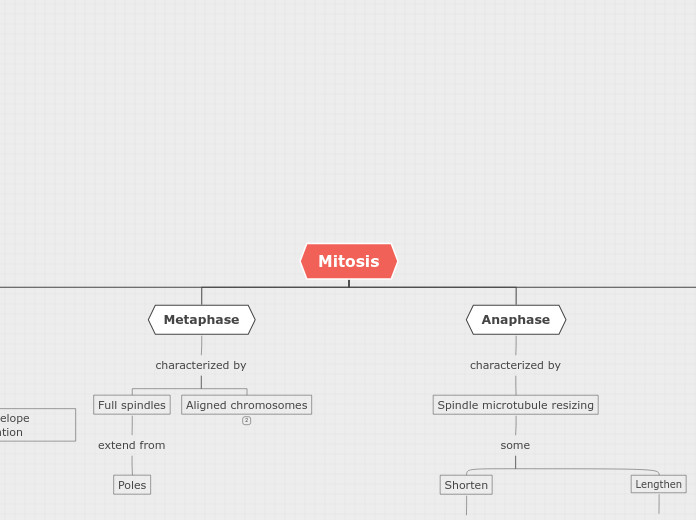
Mitosis
Telophase
Mitosis is Done
Spindle Fibers break apart
Nuclear Envelope re-forms
Chromosomes untangle into a ball of chromatin
Last Phase
Anaphase
Ends when chromosomes are separated and are in 2 groups
Chromosomes move along spindle fibers to opposite sides of cell
Each half (Chromatid) considered a Chromosome now
Chromosomes are Ripped Apart
3rd Phase
Metaphase
Spindle Fibers attached to each end of chromosomes
Middle of chromosome(Centromere) lined up with each other
Chromosomes Lined Up in Middle
Shortest (Least time)
2nd Phase
Prophase
Spindle Fibers extend from centrioles
Nuclear Envelope Disappears
Chromosomes Appear
Longest (About half of time)
1st Phase
The Cell Cycle
Eukaryotic Cell Cycle
M Phase- Mitosis and Cytokinesis
G2 Phase- Preparation for Mitosis
S Phase- DNA Replication
G1 Phase- Cell Growth
4 Cycles- G1, S, G2, M
Prokaryotic Cell Cycle
Begins when cells have grown to a certain size
Results in Genetically Identical cells
Binary Fission
Form of Asexual Reproduction
Rapid in ideal conditions
Chromosomes
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Chromosome in Nucleus
Chromosomes are made of coils
Contains Histones and Chromatin
Multiple Chromosomes
X Shaped Chromosome
Prokaryotic Chromosomes
Loop Shaped Chromosome
Single Chromosome holds DNA
Chromosome in Cytoplasm
No nucleus for DNA
Chromosomes- Packages of DNA