av Aqilah Nordin 3 år siden
239
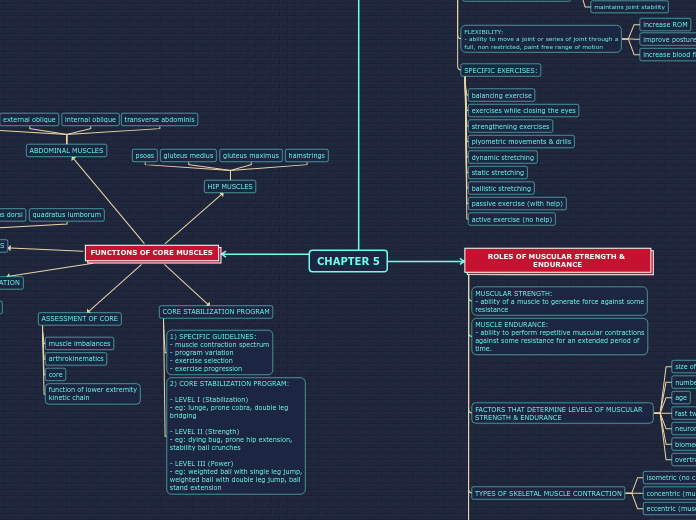
CHAPTER 5
The text delves into the multifaceted roles and functions of core muscles, highlighting their significance in various physical activities and overall body stability. It emphasizes the different muscle groups involved, including hip muscles like the gluteus medius and maximus, hamstrings, and psoas, and the lumbar spine muscles such as the erector spinae and quadratus lumborum.