Comprensión de Lecturas
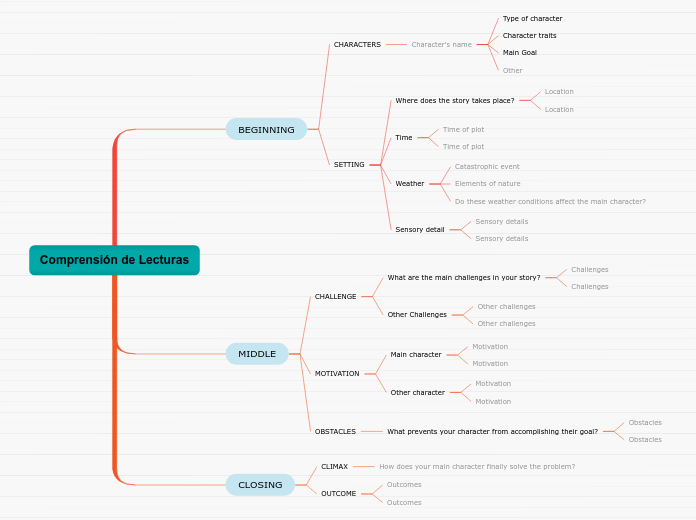
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
Propósitos
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
Evaluación Critica
Formular una opinión acerca del contenido del texto.
Ideas Generales
Para examinar un libro.
Información Especifica
Lectura de investigación para elaborar un trabajo o exposición.
Aplicación Practica
Ofrece conocimiento de algo.
Función Formativa
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
Deberes y valores éticos.
Try answering these questions in order for you to come up with a closure:
- Have all problems been solved?
- Is it clear what happens with all your characters in the story?
- Has the challenged transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Placer
This is the moment when the main character surpasses the last obstacle and finally faces their greatest challenge.
The climax usually follows one of these patterns:
- realization
- resolution
- choice
Type in your answer.
Funcion recreativa de la lectura.
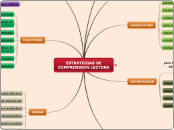
Estrategias
Hacer mapas conceptuales.
Ordenar las ideas principales en cuadros que se relacionarán por
medio de flechas con las ideas secundarias encontradas.
Realizar síntesis.
Reduce la información de un texto, pero utilizando
palabras propias.
Hacer resúmenes.
Ordena y reduce la información del texto leído, de manera tal que dejes sólo
aquello esencial.
Niveles
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Lectura Intertextual
Este modo de lectura se refiere a la posibilidad de poner en relación el contenido de un texto con el de otros textos.
Lectura Critica
There wouldn't be any tension and excitement in your story if there weren't any obstacles in your character's way.
En esta lectura el lector debe de proponer un punto de vista documentada y sustentada sobre el texto.
A story is nothing more than a character overcoming a series of difficulties to reach the desired goal. Obstacles usually create suspense and conflict. In overcoming obstacles, there is growth: weak becomes strong; hatred turns into love; sadness into happiness; wrong into right; lies into truth; or evil becomes good.
See a few examples below:
- stopping a meteor
- finding a killer
- finding love
Lectura Inferencial
Your character(s) need(s) motivation in order to solve the challenge(s).
Se explora la posibilidad de relacionar información del texto para dar cuenta de una información que no aparece de manera explicita.
Secondary characters also might have motivs beacuse of which they may cross path with main character or which might trigger them to help the main character.
Each story has a main character and that character usually needs to solve a problem or challenge. The character's challenge is the one that creates tension throughout the story.
Es cuando se explora la superficie del texto, osea lo que dice el texto de manera explicita.
Type in any other challenges which other characters in the story need to face.
La comprensión lectora es un requisito básico para la sobre-vivencia de cualquier persona.
Ciclos
Ciclo Semántico
Es cuando el lector procesa la información, se imagina el escenario y construye un nuevo significado.
Ciclo Gramatical
Procesar la información contenida mediante estrategias de predicción.
Ciclo Perceptual
Cuando la lectura se guía en conformidad con expectativas con miras a los conceptos del texto.
Ciclo Óptico
Es cuando con los ojos se rescata a información mas útil.
Tipos de Lecturas
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
Escaneo
Se basa en la búsqueda de palabras o conceptos en un texto.
Lectura Diagonal
Esta es realizada solo buscando cosas llamativas de la lectura ya sea como el titulo, o cosas especificas que te den información de lo que leerás.
Lectura Rápida
Solo el lector lee lo que le parece interesante-
Lectura Denotativa
En esta se realiza una comprensión literal de lo escrito o se efectúa una descomposición del texto en piezas estructurales.
Lectura Fonológica
The setting (time & place) of a story can change throughout the plot.
Consiste en la perfección de la pronunciación de vocales y consonantes, la modulación de la voz, etc.
Lectura Mecanica
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
Es aquella en que se identifican los términos sin la necesidad de contar con el significado de ellos.
The time of the story can also change. It can describe the event of a single day or can include an entire year's plot. Anyway, don't forget to mention it.
Lectura Literal
Se refiere a leer conforme a lo que dice el texto.
Literal en profundidad
Se penetra el a comprensión de lo leído.
Literal primario
Se da hincapié en la información y datos específicos del texto.