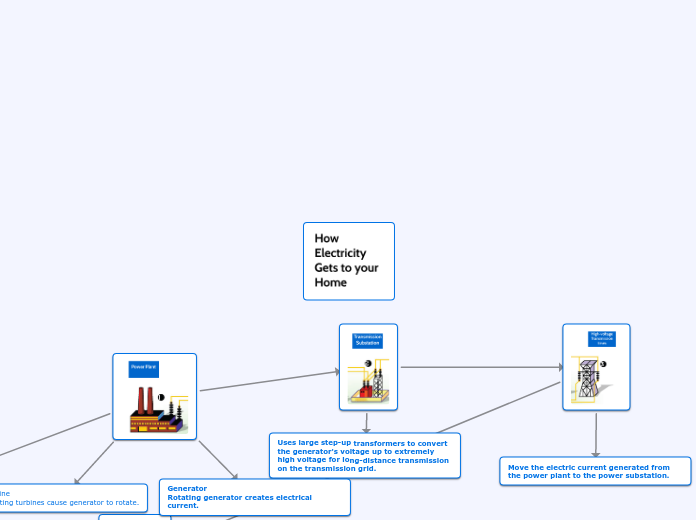
Current Electricity
Add the starting statement or claim.
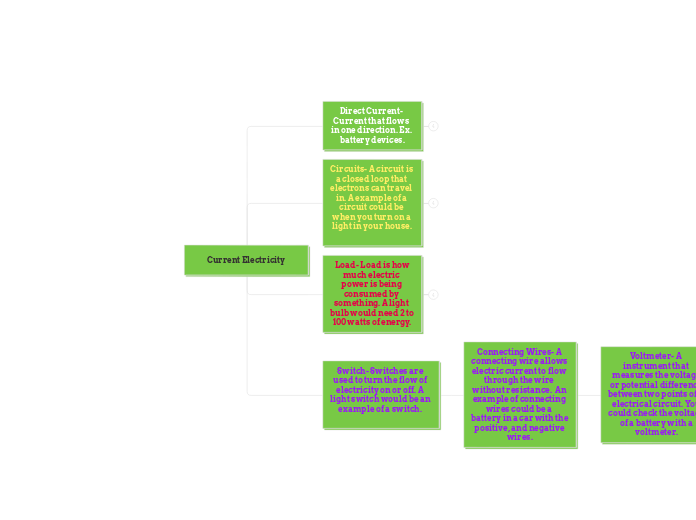
Switch- Switches are used to turn the flow of electricity on or off. A light switch would be an example of a switch.
Write an argument or an objection that is against the statement.
Connecting Wires- A connecting wire allows electric current to flow through the wire without resistance. An example of connecting wires could be a battery in a car with the positive, and negative wires.
Voltmeter- A instrument that measures the voltage or potential difference between two points of a electrical circuit. You could check the voltage of a battery with a voltmeter.
Ammeter- An ammeter measure how may amps are going through a circuit. Amps are how much electricity is going through a circuit. You could measure the current of a car.
Resistor- A resistor is an electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in a circuit. Some led lights have resistors. A resistor is measured in ohm's.
Load- Load is how much electric power is being consumed by something. A light bulb would need 2 to 100 watts of energy.
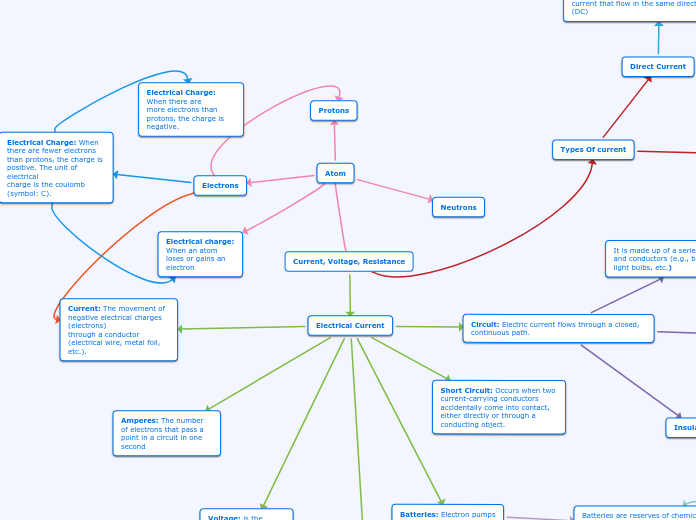
Battery- A battery is a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. You could use 2 AA batteries to power your TV remote.
Do you have an assumption regarding this reason? Write it here.
Voltage- Voltage describes the “pressure” that pushes electricity. The more voltage the quicker electricity flows. A normal outlet has 120 volts of electricity.
Support the assumption you've made by writing an argument.
Resistance- Resistance is trying to stop something. In circuit terms, resistance regulates the flow of current. Resistance is measured in ohm's.
Add additional information.
(this is optional)
Potential Difference- How much voltage is in a specific spot of a circuit. There is a potential difference that the voltage is lower or higher in some areas of the circuit. An example of potential difference could be a outlet. Someone could plug in a charger. One prong could have 59 volts going through it. And one could have 61 volts going through it.
Circuits- A circuit is a closed loop that electrons can travel in. A example of a circuit could be when you turn on a light in your house.
Series Circuit- A series circuit is all elements are in a single path. If you cut a series circuit wire in half, everything would turn off, and no electricity would flow through.
Parallel-A parallel circuit has two or more paths for the electricity to flow, the loads are parallel to each other. A washing machine has a parallel circuit. If you cut a parallel circuit wire in half there is a chance that some things would stay on.
Open Circuit- A open circuit is not complete. Most of the time the current has been opened by a switch. A open switch example could be when you turn off a light switch.
Short Circuit- A short circuit is a circuit with no close. The electrons would be flowing so quickly and the electrons wouldn't have anywhere to go, and it would eventually heat up the wire. Sometimes a short circuit can create sparks.
Direct Current- Current that flows in one direction. Ex. battery devices.
Write a reason that supports the statement.
Alternating Current- Current that changes periodically. Ex. Homes, Industry, Power plants.
Current- A measure of electrons/charge that passes in a given point in a circuit each second.
Kirchoff's Law- Kirchofff's law states that the sum of all currents entering a junction must equal the sum of all currents leaving the junction. You can use this law is used to calculate the unknown values of current and voltages in the circuit.
Ohm's Law- Ohm's law states that V=IR, where V=voltage, I =current, and R=resistance. Voltage equals resistance multiplied by current. You can use ohm's law to make sure the current of something isn't too high or two low.