av Gabriela Gutierrez 5 år siden
245
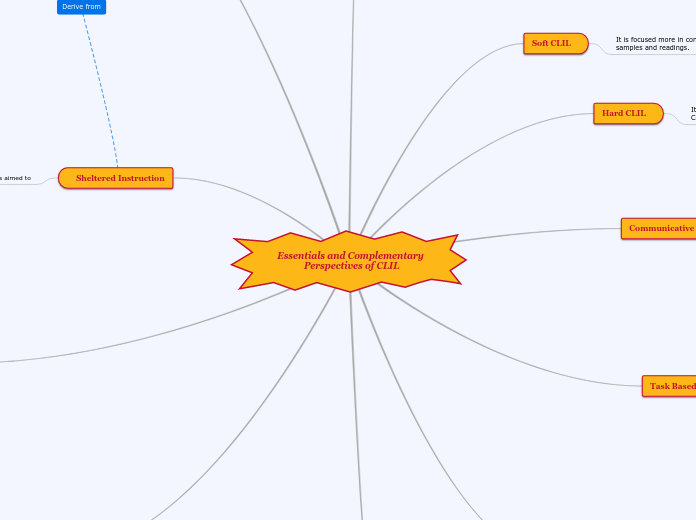
Essentials and Complementary Perspectives of CLIL
Various approaches to language teaching and learning are designed to address the multifaceted needs of students in multilingual and multicultural classrooms. Content and Language Integrated Learning (