What are the possible solutions ?
(Further Investigation)
- renewal energy sources
- solar, wind, hydro etc
- Change to electric cars
- Ride bikes
- Reduce/ Reuse/ Recycle
- Political cooperation (i.e. Paris Agreement)
- to cut fossil-fuel use in half in less than 15 years and eliminate use almost entirely in 30 years (IPCC)
- convert land to grow bioenergy crops & plant about 10 million square km of forests by 2050 (IPCC)
- Reduce consumption of meat
Links
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/12/climate-geoengineering-series-intro/
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/10/ipcc-report-climate-change-impacts-forests-emissions/
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/global-warming/global-warming-solutions/
Who is involved ?
- Governing bodies
- Industrial companies
- Global citizens
What is their responsibility?
Every person, in some form, is responsible for CO2 emissions and climate change.
- Governments and other political administrations have a responsibility to make policies in order to reduce CO2 emissions and remain within the carbon budget
- Industrial companies have a responsibility to reduce their carbon footprint as much as possible
- Global citizens have a responsibility as consumers and citizens to support and influence politicians to make laws and policies which limit their carbon footprint. They also have a responsibility to limit their own carbon footprint
Where does it come from ?
In Canada, greenhouse gas emissions are sourced from:
- 45% - burning fuels for heat & electricity
- 28% - transportation
- 8% - leaks & unintended emissions
- 8% - Agriculture
- 7% - Industrial Activity & Manufacturing
- 4% - Garbage & Wastewater
Who is Affected? (Further Investigation)
- poor people are more underprivileged than the rich because they will not have resources to combat the effects of C2 emissions
- Rich people will still be affected by changes in climate and landscape however, they will be at an advantage in terms of access to resources
- 'people who contribute to climate change the least, are those who be affected by it the most'
- Politicians have the power to create policies that will regulate and reduce CO2 emissions however, in a short-term perspective they view these policies as 'costly'
- However, if we exceed the carbon budget, costs of repairs, infrastructure, and aid will have an immense increase and affect on economies and quality of life
- Industrial companies which are profiting from the fossil fuel industry could have strict regulations in order to reduce waste & emissions as much as possible however, they too see it as costly
- Inhabitant of coastal regions/ islands can potentially suffer from extreme flooding making regions uninhabitable
- Global citizens who use cars for transportation, waste gas and fossil fuelled electricity create carbon footprints
- Everyone: The effects of climate change are permanent and will effect every region a
Links
http://prairieclimatecentre.ca/2018/03/where-do-canadas-greenhouse-gas-emissions-come-from/
http://onlineborders.org.uk/community/carbonreduction/carbon-emissions-carbon-footprints-explained
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014098831830272X
References
What is CO2? http://onlineborders.org.uk/community/carbonreduction/carbon-emissions-carbon-footprints-explained
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/12/climate-geoengineering-series-intro/
What is Climate Change?
https://school.eb.com/levels/high/article/climate-change/384741
Consequences of climate change?
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/10/ipcc-report-climate-change-impacts-forests-emissions/
Who is involved:
http://prairieclimatecentre.ca/2018/03/where-do-canadas-greenhouse-gas-emissions-come-from/
https://www.nature.com/news/politics-is-biggest-factor-in-climate-uncertainty-1.12138
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S014098831830272X
What are CO2 emissions?
CO2: "A minor but very important component of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide is released through natural processes such as respiration and volcano eruptions and through human activities such as deforestation, land use changes, and burning fossil fuels" (NASA)
- The term 'CO2 emission' often refers to the release of Carbon Dioxide (CO2), which is a greenhouse gas that traps heat from the Sun into the atmosphere, warming the Earth.
- When carbon based fuels such as coal, oil, and gas are burned, Carbon dioxide is released
- These fuels are used in homes, power stations, cars, airplanes, etc.
- An excess of CO2 emissions in the atmosphere causes climate change
How much is 'too much' ?
(Further Investigation)
- In order to avoid dramatically changing the climate by warming the Earth more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, we must stay within the limits of the 'carbon budget'
- The carbon budget determines how much CO2 emissions we can emit to avoid reaching an extensive level of global warming temperatures
- The carbon budget is set at 2.8 trillion metric tons of carbon emissions
- Only one fifth of the carbon budget remains (5.8 billion metric tons)
- In the past decade, 398 billion metric tons of CO2 was emitted
- if we continue at this rate, we will surpass the carbon budget in less than 15 years
Where does it come from?
"On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse. Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO2. To a lesser extent, the clearing of land for agriculture, industry, and other human activities has increased concentrations of greenhouse gases" (NASA)
Links
http://onlineborders.org.uk/community/carbonreduction/carbon-emissions-carbon-footprints-explained
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/12/climate-geoengineering-series-intro/
https://school.eb.com/levels/high/article/climate-change/384741
https://climate.nasa.gov/causes/
Background Information
What is Climate Change?
Climate change is the "...periodic modification of Earth's climate brought about as a result of changes in the atmosphere as well as interactions between the atmosphere and various other geologic, chemical, biological, and geographic factors within the Earth system" (Britannica)
What are the consequences of climate change?
- Earth's average temperature will rise
- Warmer conditions may lead to increased evaporation & precipitation -- some regions will become wetter & others will be dryer
- Warmer oceans & partially melted glaciers will increase sea level & expansion of ocean water
- Some crops & other plants may increase more vigorously.
- natural plant communities and areas in which certain crops can grow may be altered
How are we currently being affected?
(Further Investigation)
Current impacts (1.0 degrees Celsius global warming temperature)
Record breaking;
- Storms
- Forest Fires
- Droughts
- Rates of coral bleaching
- Heat waves
- Floods
on a global scale.
Examples:
- 3 consecutive high-level hurricanes devastated Dominica, the Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico, & Florida (USA)
- dying coral in the great barrier reef
- Droughts in USA
etc.
As the global warming temperature rises, the irreversible consequences will only progress and become increasingly dangerous.
Links:
https://climate.nasa.gov/causes/
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/10/ipcc-report-climate-change-impacts-forests-emissions/
https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/drought/201901
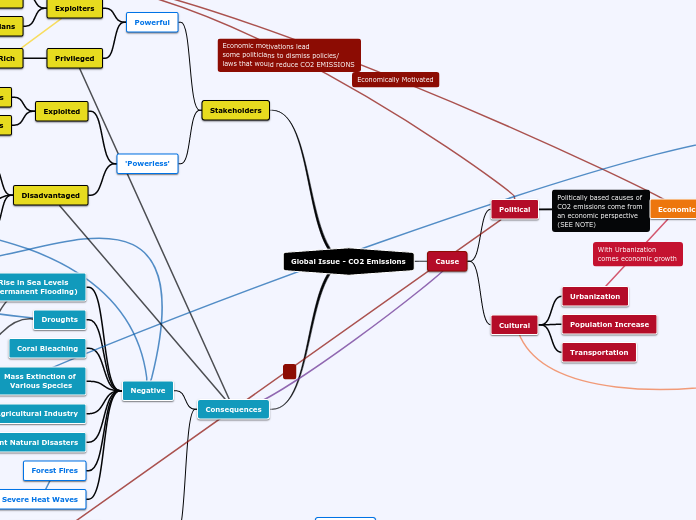
Global Issue - CO2 Emissions
Consequences
Positive
Possible Political/
Global Cooperation
Negative
Severe Heat Waves
Forest Fires
Frequent Natural Disasters
Disruption in Agricultural Industry
Mass Extinction of
Various Species
Coral Bleaching
Droughts
Rise in Sea Levels
(Permanent Flooding)
Stakeholders
'Powerless'
Disadvantaged
Poor
All Species on Earth
Coastal Regions/
Islands
Exploited
Global citizens
Politicians
Powerful
Privileged
Rich
Exploiters
Governing bodies/Politicians
Industrial companies
that are profiting
Cause
Cultural
Transportation
Population Increase
Urbanization
Political
Economic
Industrial Companies
Use of Fossil Fuels
Lack of Policy
Deforestation
Agriculture