Psychology
- The study of the human mind, mental states, and human development
- The purpose of psychology is to describe thinking and behavior, look at the relationships between them and try to explain the causes for them. A psychologist's intention is to understand, predict and/or influence behavior
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Psychologists seek .....
- to understand the brain and mind, and how is affects and directs human behaviour.
- Like other social sciences disciplines, insights gained from the efforts of early theorists and researchers contributes to and refines how we understand the human mind and behaviour
- Being able to describe how people feel, think, and act has been the mission for psychologists since the 19th century
Experiment
Line Experiment
Conformity
- General conformity for social approval or to fit in
- In group mentality
Psychologists Solomon Asch wanted to understand the nature of conformity on healthy, intelligent people and conducted a series of experiments in the 1950's on this topic
- His experiments consisted of six people per group
- they sat around a table and answered seemingly easy questions
- only one out of the six was an actual subject
- the rest were actors
- actors were carefully chosen
- the group had to make judgments about which line from a set of the three matched the standard line shown.
- the subject of the experiment was always the last to give a response
- At first everyone in the group gave the correct answer to ensure that there was no suspicion among the subject
- He discovered the people are often influenced by the responses of others.
- Only 24% percent of the subjects would not give the same answer as the others in the group
- 71 percent gave the same answer, even when they knew the groups answer was not incorrect
- Discovered that people are often influenced by the responses of others
Coping Strategies
6 Ways To Cope With High
Functioning Depression
Mindfulness
MENTAL HEALTH
What is Depression to Individuals?
A Student with Mental Illness
Sociopath vs Psychopath:
What's the Difference?
Borderline Personality
Disorder... What is it?
Mood
Depression:
- Long lasting and severe mood changes
2 types:
Major Depression:
- Deeply unhappy, finds little enjoyment/pleasures in life
- Often experiences anxiety, sleeping problems, changes in appetite
- Suicide attempts
Bipolar Affective Disorder (previously Manic Depression):
- Extreme mood changes
- Moods are both manic and depressive
- Manic state marked by confused/aggressive behaviour, unlimited energy & difficulty sleeping
- Depressive state marked by extreme fatigue, sadness, sense of futility and withdrawal (suicidal thoughts)
Schizophrenia:
- Distortion of reality, social withdrawal and disturbances of thought, perception, motor activity and emotions
- Several different forms
- Some withdraw completely, lose interest in the world and become totally apathetic
- Researchers still looking for cause/cure
- Recent evidence of a genetic component
- Drug therapy used in helping schizophrenics lead productive lives
Types:
Catatonic Schizophrenia:
- Become physically rigid and mute, holding one position for hours
Paranoid Schizophrenia:
- Delusions and hallucinations
- False beliefs, often of one’s importance or being persecuted
Personality
- Affect people’s ability to function in society/relate to others
- Often loners, suspicious and mistrustful of others
- Lie, break laws, feel persecuted and view their behaviour as normal
Antisocial Personality:
- No conscience
- No remorse/guilt after doing something immoral or criminal
- Total disregard for the rights and well-being of others
- Blame others for failures in life and failed relationships
- Organic Psychosis: physical damage to the brain (disturbance in brain function)
- Environment / socialization (ex. childhood full of abuse) may play a role
Substance
- Harmful use of substances such as alcohol, tobacco or drugs
- Leads to significant impairment or distress
- Classified as “abuse” or “dependence”
- Interferes with their ability to function in daily lives
- Dependence: users become addicted, requiring increasing amounts of the substance to achieve desired effect
- Experience severe withdrawal symptoms if substance not available (ex. physical reactions) Consequences vary (ex. organ/brain damage)
- Some people more vulnerable biologically, while others come to rely on a substance as a way of coping with problems, fear, anger or pain
- Dependence can also be result on close association with peers involved in similar substance usage
Anxiety
Generalized:
- anxiety with no obvious reason/cause
- person may not be able to function
- SYMPTOMS: fast beating heart, fainting, flushed skin
Phobias:
- intense, irrational fear of certain objects or situations
- interfere with daily life
- believed to have stemmed from bad experiences
OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder):
- Persistent, unwanted thought that comes from some sort of anxiety
- Compulsion: the need to perform an act that will relieve the anxiety OBSESSION→ANXIETY→COMPULSION→RELIEF
- Relief is temporary and the cycle repeats
Hysterical Reaction:
- When emotional conflicts are converted into physical symptoms
Disorders
- Can be caused by excessive negative stress.
- Mental illnesses are caused by psychological factors such as early childhood experiences or biological factors such as brain function, disease or genetic predisposition.
- Some psychologists refer to mental illness as abnormal behaviour
- behaviour that is out of the ordinary or does not conform to the behaviour of society.
- But “Normal” behaviour varies widely from person to person and from group to group so : What is abnormal behaviour?
- Psychologists define behaviour as “abnormal” if it is characterized by one or more of the following:
-Irrationality
-Personal Suffering
-Interpersonal maladjustment (Difficulty with relationships)
- Additional criteria used in Canada:
-Persistent personal unhappiness
-Inability to function in society
-Antisocial behaviour that harms others
-If they pose a threat to themselves/others = kept in custody
Unethical Expiriments
Monkey Drug Trial
- C.R. Schruster and T. Thompson designed an experiment to help understand the effects of drug and alcohol abuse
- Monkeys and rats were trained to inject with a syringe and left with large stocks of alcohol , morphine, cocaine, codeince, and amphetamines
- some monkeys tore hair from their bodies, and broke their own fingers while attempting escape
- others died from drugs
David Reimer
- A botched circumcision when he was eight months old resulted in Bruce Reimers penis being burned off
- Psychologists John Money recommended his parents raise him as female -> "Brenda"
- Dr.Money claimed gender is a matter of socialization but failed to tell Bruce's mother that this theory had never been proven
- After years of feeling "wrong", Brenda discovered the truth and began to live as "David"
- He faced psychological issues (depression) and eventually committed suicide
Landi' Facial Expression Experiment
- Carey Landis studied hoe facial expression relates to human emotion and whether or not specific expressions where common to everyone
- participants had black lines drawn on their faces to make changes of expression easier to see
- at one point, participants where given a live rat and were told to behead it
- one-third did so , but because most people had no prior experience, the rats suffered
- Landis decapitated the animals of those who refused
- in the end, the study showed no proof that people have common facial expressions and the rats were killed for no reason
The Monster Study
- Wenbell Johnson conducted an experiment on 22 orphaned children with normal language development
- Half were placed in a negative speech therapy group, where they were belittled for each speech error
- many suffered negative psychological effects
- some actually developed speech problem that carried on throughout their lives
Little Albert
- John Watson attempted to understand the nature of fear
- exposed a nine month old boy named Albert to a variety of white objects (rabbits and cotton wool)
- Overtime Albert began to feel a sense of security while playing with white toys
- To create fear for little Albert, Watson started making loud noises behind Albert's back while he played specifically with white toys
- because of these experiences Albert soon began to associate fear with he colour white and furry things
- Albert did not receive therapy until after this experiment regarding fear
The Happiest Girl in the World
Approaches to Understanding Behaviour
Mary Ainsworth
- Infant-mother attachment
- “Strange Situation”
- Noted how child reacted when caregiver left and how much the child interacted with the stranger in the room with them, and with toys in the room during caregivers absence
- TYPES: secure, avoidant, resistant
Harry Harlow
- Rhesus monkey study
- Affection vs. nourishment
- Infants are dependent on caregivers for more than just physical needs, emotional needs are crucial for attachment
Leta Stetter Hollingworth
- Proved the belief that women had neither the same cognitive ability nor range of talents as men (and therefore would not achieve anything extraordinary) to be completely wrong
- Study: 1000 mens height and weight vs. womens
Erik Erikson
- Stages of psychosocial development theory
- Neo-Freudian in terms of child development and understanding of ego
- Believed humans developed over a lifetime rather than just childhood
- IN ORDER: trust vs. mistrust, autonomy vs. shame/doubt, initiative vs. guilt, industry vs. inferiority, identity vs. inferiority, identity vs. role confusion, intimacy vs. role confusion, generativity vs. stagnation, integrity vs. despair
Jean Piaget
- Stages of cognitive development theory
- Thinking ability, how someone thinks/problem solves
- IN ORDER: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational
- Psychosexual stages in development theory, based on observations of how children focus on pleasure as they mature
- Children can become fixated (continued focus on earlier stage of psychosocial development due to an unresolved conflict at the oral, anal or phallic stage)
- IN ORDER: oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital
Theories of Development
Elizabeth Loftus
Studied false memories and the flexibility/reliability of repressed memories. Devised the lost in the mall experiment to prove her hypothesis. 39 percent of people tested believed the false memory to be real.
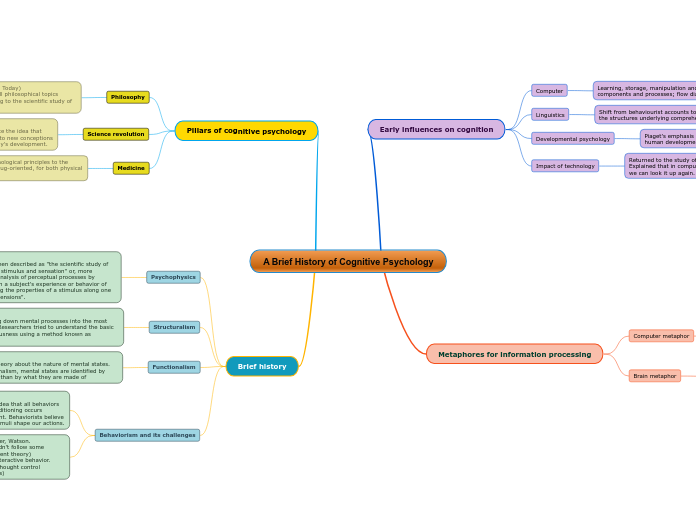
Cognitive Psychology
Albert Bandura
- Devised the Bobo Doll Experiment in order to prove his theory that people learn from watching others.
- Children use the actions of adults as a model on how they should act.
Cognitive Psychology
Carl Rogers
- Client-Centred Therapy (client plays an active role)
- Focuses on the potential of each person to realize their own growth in self-awareness and self-fulfillment
Humanist Psychologist
Viktor Frankl
- Logotherapy
- “What drives you to live?”
- Finding meaning and using it to continue to exist in even the worst situations
Humanist Psychologist
Abraham Maslow
- The pyramid lol
- Basic needs: physiological, safety
- Psychological needs: belongingness and love, self-esteem
- Self-fulfillment needs: self-actualization
Humanist Psychologist
B.F Skinner
- Operant conditioning
- Positive reinforcement (+-), negative reinforcement (--), positive punishment (+-), negative punishment (-+)
Behavioural Psychologist
Ivan Pavlov
Carl Jung
- Founded analytical psychology
- Analytical psychology: a branch of psychology based on the idea that balancing a person’s psyche would allow the person to reach their full potential
- Personal and collective unconscious
- Personality types, individual’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling and acting
Psychodynamic Theorist
Karen Horney
- Founder of feminine psychology, feminist look on Freud’s theories
- Highlights gender bias
- Promotes new thinking
- Neo-Freudian
Psychodynamic Theorist
Sigmund Freud
- Ego, superego and id
- EGO: rational part of the mind, reality
- SUPEREGO: moral centre of the mind
- ID: instinctual, operates on pleasure principle
Psychodynamic Theorist
Branches
Cognitive
Cognitive:
- Cognition refers to the mental processes in the brain.
- Cognitive Psychology is the study and application of how the brain learns.
- Believe in and consider mental states, such as beliefs, motivations, and desires.
- Founders: Jean Piaget, Noam Chomsky, Albert Bandura, Elizabeth Loftus, Leta Stetter Hollingworth
Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis:
- Belief that unlocked the unconscious mind is the key to understanding human behaviour and relationships
- All human behaviour is influenced by early childhood and that childhood experiences influence the unconscious mind throughout life
- Id (instinct), ego (reality), superego (morals)
- Includes defense mechanisms (denial, repression, displacement, etc.)
Founders: Sigmund Freud, Karen Horney, Carl Jung, Erik Erikson
Humanism
Humanism:
- Developed out of the patient relationship idea of therapy. Humanist psychologists believe that the client should be involved with their own recovery, rather than relying on the therapist's interpretations.
- Favoured qualitative over quantitative research to understand persons as a whole.
- Methods of data collection include diary entries, open ended questionnaires and unstructured interviews/observations.
- Founders: Abraham Maslow, Viktor Frankl, Carl Rogers
Behaviorism
Behaviourism
- Branch of Psychology common in the first half of the twentieth century.
- Based on the belief that psychologists need empirical evidence, obtained through experimentation, to understand and change human behavior.
- Emphasize importance of observable behaviour and phenomena.
- Founders: John Watson, Ivan Pavlov, B.F Skinner
Key Terms...
Analytical Psychology
- A branch of psychology founded by Carl Jung, based on the idea that balancing a person's psyche would allow that person to reach his or her full potential
Archetypes
- Universal symbols that tend to reappear over time; includes models of people, behaviours, and personalities
Cerebrum
- The largest and most developed portion of the brain, which is responsible for controlling memory, understanding, and logic
Classical Conditioning
- A type of learning where a once neutral stimulus comes to produce a particular response after pairings with a conditioned stimulus
Client-Centered Therapy
- A humanistic therapy developed by Carl Rogers in which the client plays an active role
Cognition
- The mental processes in the brain associated with thinking, knowing, and remembering
Collective Unconscious
- The shared, inherited pool of memories from our ancestors
Conditioned Response
- The learned response to previously neutral stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus
- An originally neutral stimulus that comes to trigger a conditioned response after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus
Conscious
- Information that we are always aware of; our conscious mind preforms the thinking when we take in new information
Correlation
- A measure that indicates a relationship between two factors but does not indicate causation; in positive correlation, one variable goes up precisely as the other goes up; in a negative correlation, one variable goes up precisely as the other goes down
Defense Mechanism
- The ego's way of distorting reality to deal with anxiety
Denial
- A defense mechanism whereby a person refuses to recognize or acknowledge something that is painful
Displacement
- The shift of an emotion from its original focus to another object,person, or situation
Ego
- Freud's term for the rational part of the mind, which operates on the reality principle
Extinction
- In operant conditioning, the diminishing of a conditioned response due to a lack of reinforcement
Fixation
- The continued focus on an earlier stage of psychological development due to an unresolved conflict at the oral,anal, or phallic stage
Free Association
- A method used in psychoanalysis where a patient relaxes and says whatever comes to mind
Id
- Freud's term for the instinctual part of the mind, which operates on the pleasure principle
Identity Crisis
- A time in a teenagers life filled with extreme self-consciousness as he or she attempts to test and integrate various roles
Logotherapy
- A form of psychotherapy that tries to help the patient find the aim and meaning if his or her own life as a human being without accessing the medical aspect of mental health
Neo-Freudians
- Psychologists who modified Freud's psychoanalytic theory to include social and cultural aspects
Neuroscientists
- A scientist who specializes in the study of the human brain
Neurotic Disorder
- A mental disorder involving anxiety and fear
Operant Conditioning
- A type of learning that uses rewards and punishment to achieve a desired behaviour
Personality
- An individuals characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
Projection
- A defense mechanism whereby a person attributes their own threatening impulses onto someone else
Psychoanalytic Theory
- Sigmund Freud's theory that all human behaviour is influenced by early childhood and that childhood and that childhood influence the unconscious mind throughout life
Psychodynamic Theory
- An approach to the therapy that focuses on resolving a patient's conflicted conscious and unconscious feelings
Repression
- A process in which unacceptable desires are excluded from consciousness and left to operate in the unconscious
Self-actualization
- Reaching one's full potential; occurs only after basic physical and psychological needs are met
Superego
- Freud's term for the moral centre of the mind
Unconditioned Response
- The natural response to an unconditioned stimulus
Unconditioned Stimulus
- A stimulus that naturally triggers a response
Unconscious
- Information processing in out mind that we are not aware of; according to Freud, it holds our unacceptable thought, feelings, and memories ; according to Jung, it includes patterns of memories, instincts, and experiences common to all
Social Identity
and
The Life Style
*** Changes and grows along with the individual throughout his or her life and is influenced by life experiences***
- Life stages is a key determinant of social roles and identities
- Sociologists assume that individuals will pass through different stages in their life and while doing so. The individuals are meant to accomplish certain developmental tasks
***Stages of the life cycle refer to developing social skills and abilities that form your behavior in society***
Sociology
*The study of human behaviour, including, individuals, groups , and societies*
- Looks at society as a whole (not the individual)
- what are the shared values of a whole society
- in depth parts of a culture (teenagers, elders, young adults)
- studies : perspective, number or group, backed up by facts, theories, and statistics
Conformity
NOTE
- The various factors that affect the individual will conform
Status of Members
Source: Solomon Asch
Influence on Conformity: If a group member is knowledgeable, as a teacher or has a high status , such as a workplace superior , other participants are likely to conform to that person's views. There is also higher conformity to a group that has high status
Ambiguous Situation or Difficult Situation
Source: Muzafer Sherif, Solomon Asch
Influence on Conformity: When a task is difficult or ambiguous participants look to each others in the group for cues as to how to react, assuming the others will know what to do. More difficult the task, the greater the conformity
Self-Esteem
Source: Solomon Asch, Phillip Zimbardo
Influence on Conformity: Those with lower self-esteem are more likely to conform because they want to belong. Conversely, participants are less likely to conform when they are confident in themselves or their abilities
Public vs Private
Source: Muzafer Sherif, Solomon Asch
Influence on Conformity: When participants are able to give answers privately, conformity is decreased
Group Unanimity
Source: Muzafer Sherif, Solomon Asch, Philip Zimbardo
Influence on Conformity: When everyone in a group appears to agree, participate conformity is high, Even one person voicing disagreement decreases the conformity of participants
Group Size
Source : Solomon Asch
Influence on Conformity : Larger groups tend to have higher rates of conformity; however, that rate does not change much after groups reach four or five members
Culture
What Do Cultures Have
In Common?
Individual cultures can vary greatly, but all cultures share some common characteristics
--------------------------------------------
Culture is learned
- Parent teaches a child --> beliefs, values, traditions
Culture is shared (have subcultures)
- Teenagers
- Individual heritage group
Culture defines nature
- How things are done, best practices
Culture shapes how e perceive and understand the world
Culture has patterns
Where does culture come from?
- There has been an ongoing debate about the factors that influence human behaviours, attitudes, beliefs and other factors associated with culture.
- This debate is called that Nature-Nurture Debate
---------------------------
- At one time, it was believed that inherited characteristics , or "nature" directed all human behaviour (i.e. people behaved a certain way because they inherited that behaviour from their parents
- As anthropology studies evolved, people began to believe that culture is based, not on inherited characteristics, but on the way people learn to adapt to their environment in order to survive.
- In other words culture was a result of "nurture"
What is culture?
- Culture is the learned behaviours, beliefs, attitudes, values and ideals of a particular society or population
Important Sociologists
Margaret Mead
- One of the most widely known anthropologists who studied cultural anthropology
- Her findings supported that - nurture rather than nature - largely determines human behaviour
---------------------------------------------------------
- One of Mead's studies involved comparing gender riles across three different cultures.
- Here her findings were revolutionary
- She concluded that most of the personality traits we associate with "masculinity" and "femininity" are the result of early learning , not heredity
Charles Cooley
- Studied relationships between, the individual and society in great depth
- Believed, that the two are interconnected and their functions cannot be separated (influence on another constantly)
- Believed, the constant interaction with members of one's primary group is crucial to developing a social identity
- The individual becomes a reflection and representative for the primary group
Looking-Glass
Self Idea
The way in which the individual's sense of self is mirrored and reflected by others
Example ---> An Avatar
- People create an avatar , a customized symbol, to represent themselves online
- This symbol can represent what someone actually looks like as well as represent how a person would like to be seen by others
Max Weber
- 1864-1920
- German scholar
- Believed that social life is rife with examples of conflict and cohesion
Weber's Theory
Rationalization
- Social actions motivated by efficiency or benefit, rather than morality, custom, or emotion
- According to Weber, Rationalization helps society to function more efficently
- Thought that people could be liberated through bureaucracy rather then revolution
- Envisioned a society in which the bureaucracies would improve social problems
--------------------------------------------
Weber's idea of a bureaucracy VS. sociological bureaucracy
Weber
- An organization where people are given specialized tasks and where each role is supervised in hierarchy
- A person holds a job based on his or her competence
- People are treated impersonally so that everyone is treated the same
Sociology
- A form of administration that is found in organizations pursuing a ide variety of goals
Example of Modern
Bureaucracy
Canadian Civil Service
- Weber believed , social inequalities and disparities could not be explained in only economical terms as suggested by Marx
- Government bureaucracies could better manage these resources by ensuring that all essential social services, such as education, would be available to all
- Bureaucracies could theoretically lessen the tensions in society and potentially eliminate existing inequality
Mysore Narasimhachar
Srinivas
- 1916- 1999
- One of the most noted scholars on Indian sociology in the 20th century
- His work focused on the Caste system in India
-----------------------------------------
Caste System
- A complex social system that organizes people in social classes that determine status, occupation, culture, marriage partners, and political power
- Caste-based discrimination is outlawed by Indian constitution, Caste-based barriers still exist in rural communities
Srinivas Work
- His work challenged colonial and western assumptions about Indian society
- His field work proved that the Caste System was a fluid and dynamic social institution that had a tremendous imapct on society
- Studied the importance of Caste in the electoral Process as democracy developed in India, moving researches away from classical texts and into contemporary world they were studying
- Encouraged his students to look a society in raw, to get out into villages, hospitals and trade unions
- Developed new ways of understanding Indian society
William Foote
- 1914-2000
- An economist who, through study of a poor Boston neighborhood in the 1930's
- Created the model for urban ethnography and set the standard for this methodology in sociology
- Known as a pioneer in participant observation
--------------------------------------
The Street Corner
Society Experiment
- For more than three and a half years in the 1930's, Whyte lived in a poor Boston neighborhood
---> Inhabited by 1st and 2nd generation Italian immigrants
the neighborhood ---> High crime rates, considered dangerous refereed to as a slum
- While living in there (Cornerville) whyte
---> observed/ recorded tensions between different groups from withing the neighborhood
Two Groups Studied -->"Corner Boys" and "College Boys"
Corner boys
- Hung out on the street corners and around shops
College Boys
- Wanted an had means to get as education
- Ambitions to get out of the slums
- Enjoyed the position of privilege
- Viewed the Corner Boys negatively
-----------------------------------------------
- Whyte was more interested in the Corner Boys and their relationship to other groups
- He was able to peer into their daily lives and make sense if their world
- In his study Cornerville, Whyte demonstrated that a poor community had the capability to be socially organized
- His research changed the was societies could be and are studied
- Revolutionized the way sociologists conduct their research in the filr and how sociology is studied today
Herbert Spencer
- 1820-1920
- British philosopher/sociologist
- Influential figure during the Victorian era (1837-1901)
- Supported Darwin's evolutionary theory
- Applied and compared Darwin's theory to Spencer's study of society
- Applied the notion of natural selection to society
- Known as what he called "survival of the fittest"
Social Darwinism
- Used to justify colonialism and slavery
- People claimed that because white people were superior to to other races and cultures --> that they were justified in taking over other countries or enslaving people
- Connected to concepts of Eugenics
- A movement that advocated for the "improvement" of the species by either selective breeding or the sterilization or killing of "undesirable" humans
- This concept was also used in Canada by Helen Macmurphy
- She led the national council of women to endorse sterilization as means of preventing mothers from "filling cradles with degenerate babies"
- Alberta sexual sterilization act was passed in 1928
---> Led to the creation of a eugenics board
---> Board had the power to order the sterilization of individuals
---> Between 1929 and 1972 ---> 2822 individuals were sterilized
Spencer's Theory
- The fittest people in society should survive and flourish while the weak (or unfit) wither deserve to live in unfortunate circumstances or be allowed to die
Example
- Under social Darwinism, the poor elderly or disabled should not receive any financial assistance since they aren't fit enough to survive on their own.
Prejudices
The
Competition
Theory
- To give themselves a competitive edge, a dominant group may try to exploit another less powerful group in order to control these resources
(To justify this to exploit another group, the dominant group may choose to see the group they are exploiting as inferior)
- This opens the door to prejudice and discrimination
Social Conditions
- Rapid social change increases prejudice and discrimination
- Whenever a country experiences economic hardship, some citizens assume-incorrectly-that immigration is responsible
- unemployed people believe their jobs have been taken by newcomers.
- Other believe that an influx of people strains our social and health services and contributes to the country's deficit.
- These false assumptions may lead some people to resent immigrants, which in turn leads to prejudice and discrimination
The
Frustration-Aggression
Theory
- People being to blames others for their personal frustration
- It is easier for an individual to put the blame on someone else. Using the other person as a "scapegoat", rather then to blame themselves
- leading to prejudice and to discrimination
Ignorance
- Lack of personal experiences can cause people to make incorrect assumptions about others
- Caused by lack of education
- When we refuse to learn about others, we prejudice our thoughts because we are incapable of seeing all sides of a situation--- Thus we discriminate against the unknown
The Learned
Prejudice Theory
- Prejudice and the willingness to discriminate are attitudes that are learned
- The learning of prejudice begins in early childhood
- Prejudice parents may prevent their children from associating with groups that are viewed as inferior
- where the children are NOT allowed to have positive experiences with these groups and only hear of negative opinions (that of their parents)
- Teachings may be passed down from generation to generation
Agents of Socialization
- The sources we use to learn about society and ourselves
Agents of Socialization
- Family
- Peers
- Media
- Schools
- Religious Groups
- Voluntary Associations
Effects of the Agents
Over Time
- Agents of socialization affect an individual or group and an entire population
Life Cycle Effect
- Causes an individual or group to alter their beliefs/behaviour
Example: Political revolution (military coup, etc.)
Period Effect
- Affects entire society and usually occurs due to disease, depressions or wars
Cohort Effect
- A social event that creates a major impact on a specific group of people (e.g. Atomic Bomb)
Social Classes
- These agents divide individuals into categories within society
- Socioeconomic classes include lower class, working middle class, aswell as the working elite (wealthy)
Secondary Agents of
Socialization
- Secondary agents are those institutions or places that help an individual find their place in society
Examples: school, work,religion
- These agents help an individual improve their social skills and integrate them into society
Primary Agents of
Socialization
- Includes the agents that are closest to an individual; family and friends
- Most important because that play a critical role in shaping the life and behaviour of an individual within society at a child's earliest age
Meet the Agents of Socialization
Family
- (Most important) Moulds values, beliefs, religious/political views, etc.
School
- (2nd most important) Teaches important knowledge from society including acceptable behaviours -- forces children to engage socially.
Peers
- (Social contact is a major influence) Behaviour patterns are shaped by what peers feel are acceptable.
Media
- Portrays norms and reinforces views by repeated exposure.
Culture
- Passes religious, nationalistic traditions, allows to meet other members of society.
What is Socialization?
The way people think and act
- Done though encounters with other people/groups (social contact)
**Allows new members to learn accepted ways of behaving within a certain culture
Socialization
- Takes place through the interaction with others
- Can be intentional or unintentional
** Various types of social contact are called the agents of socialization
Socialization
- The process by which people learn from other people how to think, feel and act, along with the knowledge and skills needed to participate in society
Subtopic
7 Ways Alcoholic Parents Affect their Children
The Process of
Socialization
In our everyday relationships with people we learn different knowledge and skills, When we start to use these skills and knowledge ourselves this is called internalization .
Symbolic Interactionism
(Microsociology)
- Is more interest in the process of socialization then the result.
- "how does internalization happen?"
- Cooley's the Looking Glass Self :
"I am not what I think I am; I am not what you think I am; I am what I think you think I am"
Explanation
Cooley is talking about the process of developing The Self
This is done in three stages:
- The imagination of our appearance to the other person
- How we imagine the person judges our appearance
- How we feel about the other person's judgment (as we have imagined it)
Structural Functionism
(Macrosociology)
- Sees primary socialization as the means whereby children are integrated into society, coming to take their allotted role and learning to fulfill socially necessary functions
- children are viewed as a "blank slate"
- survival of society
Social Identity
Allows a person to interact with a number of people in a variety of different situations
- The greater the number of interactions, the more a person is able to develop his or her approach to social interactions or social identity
Elements Include...
- Gender
- Culture
- Social Class
- Age
*Aide in formation of social identity*
When Studying The
Emergence of Social Identity
- It is important to acknowledge the elements that work together to establish identity
Macro and Micro Sociology
- Life stages is a key determinant of social roles and identities
- Sociologists assume that individuals will pass through different stages in their life and while doing so. The individuals are meant to acomplish certiain developmental tasks
***Stages of the life cycle refer to developing social skills and abilities that form your behaviour in society***
Microsociology
Concerned with the role and interactions an individual or small group of people may have in society
- Microsociologists are interested in understanding the bases of social action and interaction among individual members and their place in society
Example
A microsociologist would study a religious worship by looking at role and beiefs of a single worshipper or small group of worshippers in a religion
Macrosociology
Takes a wide perspective and is concerned with studying society as a whole
- Macrosociologists analyze social systems and populations on a much larger scale
- Examine larger social institutions that individuals belonging to, such as a country or a place of worship
Example
A macrosociologist studying a religion would try to learn a great deal about religious worship as a large structure or institution in society.
Life Strategies
and
Developments Tasks
- A guide for the major life stages through which many people pass and the possible connections to an emergent social identity for individuals.
6. Family in Later Life
- Adjusting to retirement and possible changes in social status and class
- Maintaining love, sex, and marital relationships
- Reintegrating important agents of socialization (for example, religion)
- Passing along cultural traditions to future generations.
5. Family in Mid Life
- Launching grown children (sometimes relaunching them more than once)
- Incorporating new members through social institutions such as marriage
- Maintaining cultural traditions of the family while expanding traditions to include new members
- Agingand possibly developing alienation between older and younger generations
4. Family With Adolecents
- Further integrating agents of socialization (for example peer groups)
- Establishing balance of autonomy and control for adolescents
- Coping with strong social influences on the family (for example, media)
- Ensuring cultural traditions are maintained by all members of the family
3. Family With Young Children
- Fully integrating gender roles and expectations of parenthood
- Acting as the primary agent of socialization for children
- Passing along cultural traditions to offspring
- Confirming social class and status
- Integrating important agents of socialization ( for example, school, religion)
2. Newly Married Couple
- Determining social and gender roles
- Further establishing social class and status
- Developing conflict -resolution strategies
- Deciding on parenthood
- Teaching cultural Traditions of one's family to spouse
1. Young Single Adult
- Establishing one's independence as an individual and setting life direction
- Planning and obtaining an appropriate education
- Establishing one's social class and status
- Developing love relationships in connection to one's identity
- Acknowledging cultural traditions of the family
Sociological School of Thought
Symbolic Interactionalism
Studies human interaction at the micro level
- This approach emphasizes the individual living within a larger society
-----------------------------------------------------
To study the individual's social role and peace within a wider society and how people create their world through social interactions
To examine how a physical environment and social structures determine individual behavior
- Believe people have unique interpretations of symbols based on meanings they learn from others
- People base their interaction with others on their interpretation of symbols (i.e. Musical groups learn that people don't like the music they hear or the performance if boos are heard)
---------------------------------------------------
Theory
- The individual is at the center of understanding society, since social values and roles are formed by individual interpretation
- The individual creates a sense of self by the reactions of others
- Social life depends on our ability to imagine ourselves in our social roles but also the ability to see ourselves reflected in experiences of those around us
Behaviour of others in a society is deeply rooted in our response and reactions to it
*influencing the way an individual may...
}-------------->This dependent relationship is what
allows a society to function smoothly
----------------------------------------------
- Does NOT focus on social system
Focus
- The way that individuals, through their interpretations of social systems and behaviours negotiation with others, give meaning to social interaction
Charles Cooley,
George Herbert
and Max Weber
Feminist Theory
To examine conflicts created by gender
- Is an extension of Feminism that aims to understand the nature of gender inequality
- Examines social role, experience, and interests
- Believe that men have held power in society unjustifiably and that women's interests must be promoted
- Branch of conflict theory
- Differences in opportunity (jobs,sports, advertisment)
Research based on two premises;
- Shouls focus on the condition of women in society
- Must be grounded on the assumption that women generally experience subordination
Dorothy Smith
Conflict Theory
To study how power forms the basis of the relationships between different groups and creates conflict
- Believes society expirences inconsistency and change everywhere (i.e. technology is important - need it to learn to get ahead- but high tech is not accessible to all therefore poor cannot get ahead)
- All societies involve control and coercion of some members by others (some people have power over others - and have the ability to constrain or limit those with less power)
Karl Marx
Strucural Functionism
To study how social structure functions serve the needs of society
- Believes every structure in society has a vital function (the whole is made up of parts such as family, economy, religion)
- Society seeks stability (after every upheaval society will return to a normal stable or normal state)
- Most aspects of society contribute to its wellbeing/survival (families contribute by reproducing and taking care of its members)
- Society works in a logical manner to protect most of its members (makes laws and punishes those that break them)
Emile Durkhiem
Forms of Child Abuse
Emotional Abuse
- May include repeatedly critizing child or subjecting the child to an unhappy or disturbing enviroment
Neglect
- The failure to provide physical or emotional necessities of life
Physical Abuse
- Involves assult or inflicting physical harm
Sexual Abuse
- Occurs when an adult , the sibling or peer touches a child sexually or inappropriately
Gender Identity
One's personal experience of one's own gender. This is generally described as one's private sense of being a man or a woman, consisting primarily of the acceptance of membership into a category of male or female, and into the following identities:
- Heterosexual
- Homosexual
- Inter-sexed (having both sexual characteristics)
- Transgender (having a different gender identity from the physically assigned sex)
How are genders constructed?
- Clothing
- Symbols
- Classifications of "male" and "female" characteristics/roles
- Relative values of genders (how are they valued when compared with each other)
- What behaviours are expected or acceptable
Gender Roles
A set of societal norms dictating what types of behaviours are generally considered acceptable, appropriate or desirable for a person based on their actual or precieved sex :
- The way someone looks
- The things someone does
- The things someone says
- Who someone spends times with
- (stereotypes)
- (social assumptions)
Gender
Culturally Constructed
- Symbols connected to gender
- Concepts of gender ( what it means to be male or female)
- Relative values between genders (power relationships)
- Patterns of behaviour , and appropriate actives
Culturally Defined
- Roles
- Expectations
- Image and appearance
Sex
Visibly Identifiable
- Genitalia
- Sex-linked-features
- Biological
Genetically defined
- x x chromosomes (female)
- x y chromosomes (male)
Introduction to Sociology
Agents of Socialization
- People and institutions that shape an individual's social development
Anticipatory Socialization
- The process of learning how to plan the way to behave in the new situation
Bureaucracy
- A large administration that pursues a wide variety of goals
Empiracle
- Base on facts, statistics, and data
Feral
- Unwanted child deserted at a young age and raised by animals
Functional Differentiation
- Divisions that are created to help deal with a complex environment; these divisions operate independently but are connected to one another
Isolate
- A child raised in near isolation within a human household
Macrosociology
- An approach to sociology that analyze social systems on a larger scale
Microsociology
- The study of small groups and individuals within a society
Norms
- Expectations about how people should behave
Positivism
- The application of the scientific method to obtain quantifiable data in order to understand society
Primary Group
- A set of people with whom an individual has strong emotional and personal connections
Primary Socialization
- In the process of learning the basic skills needed to survive in society
Rationalization
- Social actions motivated by efficiency or benefit, not custom or emotion
Resocialization
- The process by which negative behavior is turned into society acceptable behavior
Role
- Expected behavior of a person in a particular social position
Secondary Socialization
- The process of learning how to behave appropriately in group situations
Social Influence
- Effect of other people on a person's thought and actions
Socialization
- Continuing process where an individual learns appropriate behavioral patterns, skills, and values for his/her social world
Survey
- Set of questions used on a sample of the population study about opinions, values, or actions
Values
- Shared ideas and standards that are considered acceptable and binding
Sociology and Me
Acting Crowd
- A group of people fueled by a single purpose or goal
Altruism
- Principle of unselfish regard for the needs and interests of others
Casual Crowd
- A group of people in the same time but who do not have a common goal
Census
- Official periodic count of a population including, such information as sex, age, education, and occupation
Chaperone
- Older or married women who accompanies or supervises young unmarried women on social occasions
Classism
- A systemic or personal actions that discriminate against persons according to their social socio-economic level, which leads to human needs being unmet
Compliance
- Social behavior by an individual that may be contrary to his/her beliefs but is exhibited nonetheless in order to achieve rewards and avoid punishment
Conformity
- The process by which one changes one's thoughts, feelings, and behavior to meet the expectation of a group or authority figures
Conventional Crowd
- A large group of people gathered for a clear purpose who behave according to expectation
Dehumanize
- To deprive people of their human qualities; to degrade or deny the humanity of another person
Demography
- The study of the structure and development of human population
Differential Association
- The theory that individuals learn the values, attitudes, techniques, and motives for criminal behavior through interaction with others
Discrimination
- The act of treating groups or individuals unfairly based on their race, gender, or other common characteristic; can be overt or systemic
Dyad
- A group consisting of two members\
Expressive Crowd
- A large number of people at an event who display emotion or excitment
Groupthink
- The effects of collective pressure on the decision-making abilities of individual members of a group
Homophily
- The tendency to associate with those who are similar to us
Informal group
- A less intimate gathering of people in which member interaction is not governed by explicit rules
Islamaphobia
- Prejudice against and fear of Islamic beliefs and Muslms
Mass Hysteria
- The widespread irrational reaction to precieved danger
Mob
- A disorderly crowd of people
Obedience
- The act or habit of doing what one is told or submitting to authority
Panic
- A highly emotional and irrational response on the part of an individual or a group to a dangerous or harmful social event
Prejudice
- An individual judgment about or active hostility toward another social group
Prosocial Behavior
- A form of altruism in which individual or groups demonstrate empathy toward and car for the welfare of others without themselves
Racism
- Erroneous judgment,assumptions, opinions, or actions, toward a person or group, based on the belief that one race is superior to another
Review of Literature
- A search for an examination of credible, reputable studies conductible by others
Riot
- Civil Disorder stemming from a social grievance, caused by disorganized crowd exhibiting agression, who may turn to acts of violence, vandalism, and destruction of property
Sanction
- Informal or formal penalty or reward to ensure conformity within a group
Scapegoat
- A specific person or group of people who become the target of hatred or blame for the hardships of others
Secondary Group
- A large impersonal gathering of people in which member' roles are measured by their contributions to a common goal or purpose
Sexism
- Attitudes or behaviors based on predetermined ideas of sexual roles that discriminate against others because of their sex
Smart Mobs (flash mobs)
- A large group of strangers who use electronic media to organize and stage a surprise public gatherings
Social Identity
- (sociology) The way you define yourself to the world and to yourself
Social Role
- Expectations attached to particular social positions
Solidarity
- The ties that unite members of a group
Stereotype
- An exaggerated view or judgment made about a group or class of people
Threshold
- A level or point at which something would or would not happen; a tipping point
Upstander
- A person who takes action, particularly when the easiest or most acceptable course is to do nothing, when the believe something is right
Virtual Community
- A group of individuals who communicate online
Prejudice's
Discrimination's
and Other "Ism's"
Ethnocentrism
- The strong tendency to view other races or cultural groups in terms of the standards of one's own race or group.
- The belief that one's own ethnic group or culture is superior
Xenophobia
- Excessive or unreasoning fear or hatred of foreign people or things
Intergration
- The abolition of racial separation or segregation, esp. as occurring in the United States (cultures blended to become one)
Separatism
- The separation of a political, religious. or racial group from a larger group to which it had belonged
Pluralism
- A national policy favoring the coexistence of a variety of cultural, ethnic, or religious groups (cultural mosaic)
Racism
- The theory or opinion that a certain race or races of people usually one's own, are superior to others because of certain inborn characteristics
Prejudice
- An opinion, judgment, preference, or conception formed without knowing or examining facts (the thought)
Unequal
- Not equal, as two or more persons, things, or numbers
Expulsion
- An act or instance of expelling or forcing out, ot the state of being explelled
Annhiliation
- To destroy completely ; reduce to ruin
Genocide
- The intentional attempt to exterminate all members of a certain race, nationality, or ethnic group
Segregated
- Practicing or characterized by segregation, especially racial or ethnic segregation (residential schools)
Cultural Influence
Art and Entertainment
Enviroment
- Availability of resources influences who does what in a society
Values/Religious/Beliefs
- Provide a set of guidelines on what is acceptable within a culture, for both roles and expression of identity
Education/Insitutions
- Determines what people learn, which then informs who they "should be"
Laws/Customs
- Laws and customs determine what people should or should not do, some roles and expressions of identity are controlled by law
Divisions of Labour/Power
- Labour and power are an expression of who has more value in society
- An imbalance in labour/power leads to a "Master-Servant" like scenario whereas a balance in labour/power leads to an equilateral
Deviance and Social Control
Key terms......
Social Norms
- Social expectations that guide people's behaviors
Folkways
- Informal practices, based on tradition or accepted group behavior
Mores
- Norms involving moral or ethical judgments... some so important made in laws
Degrees of conformity
- Freedom of thought and expression important to be individuals
- Same time, society needs people to conform to social norms in order to function
- Need balance between two
Social Roles
- Set of expected behaviors and beliefs related to the part one plays in society
Deviant Behaviors
Behavior that differs from social norms of the group and is judged as wrong by members of that group
Biological Theories
- Based on brain function or genetics
Psychological Theories
- Looks at early experiences : i.e. children.
- Criminals learned to think and act in certain ways and were rewarded for deviant behavior
Sociological Theories
- It's a learned response due to the environment
Motivational
- Some people are encouraged to achieve but do not have the tools to succeed, so they use deviant ways to reach their goals
Learning
People learn deviant behavior from people that they know really well
Control
- People display deviant behaviour if they experience as absence of social control and if the rewards for such behavior are more certain than the punishment
Labeling
- Looks at how definitions define people in certain ways and how people react to that label
Anthropology
The study of humans, including their origins; behaviors; and physical, social and cultural development.
- Studies attitudes, values, beliefs, and norms within a culture
Otzi
Known as......
- The man found within the ice

Found in 1991
Found.....
- Otz Vally ( between Austria and Italy)
- Approximately 5100-5350 years old
- Body presented along with clothes, tools, ect.
Gives an insight to diet, climate, clothes, tools, and weapons of our early ancestors that walked the earth.
Important Anthropologists
Dian Fossey
Studied....
Met Louis Leaky in 1966
First trip to Africa under Louis Leaky in 1967
Other information...
- Protected gorillas
- Murdered in 1985 by poachers while protesting for the protection of the gorillas
- popularized by the movie "Gorillas in the Mist"
Research and findings
- Learned to imitate the gorillas to gain their trust
- Believed that gorillas shared much in common with our earliest ancestors
- Observed gorillas displaying highly structured social systems, as well as affection
Birute Galdikas
- Studied orangutans
- Met Louis Leaky on collage campus
Findings/Research
- Discovered orangutans are vegetarians who rarely killed one of their own for meat
- Have highly developed social structure
- Added knowledge: towards early humans
- Orangutans, chimpanzees : bear much in common with our early ancestors
- Similar to Goodall's research
Studied.......
- Behaviour and social structure of the orangutans
Jane Goodall
Studied Chimpanzees
Findings/ Research
- Discovered that chimps had tools : retrieving termites
- Discovered chimpanzees NOT strictly vegetarian
- Discovered highly developed social structures within chimpanzee tribes....
- An alpha male wins supremacy over the other males : aggression and strength
- Alpha male : rite to mate with any/ every female
- Other males are not aloud to mate while alpha is in charge
- old/overthrown males: treated as a respected grandparent
- Insight to what the human kingdom might have been like a million years ago
- Ancestors vegetarian: until they learned to cooperate and hunt together
- She gained the trust of the chimpanzee tribe
Conclusion...
- Her research has given valuable insight into the human kingdom and provided a window into the ancient past.
What did she do?
- Recorded and documented information that has never yet been documented
- Lived among chimpanzees
- Recorded/ Documented behaviours, traits, patterns and relationships of the chimpanzees
The Leaky'
Mary, Louis, and Richard
- Reconstructed ancient civilizations dating from 100 00 to 2 million years ago
- uncovered two of anthropology's greatest finds
- Australopithicus
- Homo Habilis
Conclusions...
- Violence was partly instinctive; but, could be changed into constructive behaviour
- Left over from primitive times when hunting was necessary for survival
Konrad Lorenz
Best known for
- His work on imprinting birds
Also studying...
- Human aggression and violence
- animal studies led Lorenz to conclude that violence was partly instinctive , left over from primitive times when hunting for food was necessary for survival
Founder of...
- Ethology ( the comparative study of biology of behaviour in animals)
Fields of Anthropology
ETHNOLOGY
Study and compare of past and contemporary cultures
Interested in knowing about......
- Cultural beliefs : practices and patterns of thought and behaviours.. i.e: marriage customs, family, relationships, politics, religion, music
- often gather info through interview or observation and published research
ARCHAEOLOGY
Studies/ analyze material and human remains left by ancient culture
- Creates ideas on how our ancestors once lived
ANTHROPOLOGICAL LINGUISTICS
Studies languages
- Use of documents, existing research or tape recorded interviews to study different things
- Study the changes in language over time
- How different languages may be related
- Meaning language has for the people who speak it
PRIMATOLOGY
Study the anatomy and behaviours of primates
- Branch of zoology dealing with primates
- Investigate what makes us similar to and different from other primates
FORENSIC ANTHROPOLOGY
Studies/ examines human skeletal remains for law enforcement agencies.
- Determines the identity of unidentified bones
- Sent out after mass disasters, wars, homicides, suicides, and or accidental deaths occur
PALEOANTHROPOLOGY
The study of human ancestors based on evidence from the distant evolutionary past
- human-like ancestors together with living humans called hominins
Evolutionary Theories/Theorists
Gregor Mendel
- 1822-1884
- Considered to be the founder of modern genetics (the study of heredity in plants and animals
- Mendel experimented with a variety of flowers and plants in order to gain a better understanding of the nature of species
- He concluded that characteristics are passed from generation to generation by genes, or hereditary factors
- Half of these genes come from one parent and half from the other
- establishes the laws of heredity
- Characteristics are passed from generation to generation by genes, or hereditary factors, and half of these genes came form one parent and half from the other
Jean Baptist Lemarck
- 1744-1829
- Was a French Zoologist
- He developed a number of theories about how animal species are developed
- His theories stated that complex animal forms , such as whales and elephants were developed over time from simple ones, such as worms and insects.
Theory
- Complex animal forms, such as whales and elephants, were developed over time from simple ones.
Charles Darwin
- 1809-1882
- A British scientist
- perhaps the worlds most famous biologist
- He developed the theory of Evolution (gradual change over many generations)
- This theory revolutionized contemporary thinking
- began his research on a round-the-world voyage on the H.M.S Beagle
Theory : Evolution
- A gradual change over many generations.
Key Terms
Key Terms.......
Bipedalism
- Trait of habitually walking on two legs
- Walking on two legs
Culturally defined
- Created or shaped by a culture
Culturally Constructed
- Created or shaped by culture
Culture
- The total system of ideas, values,behaviors, and attitudes of a society commonly shared by most members
- All learned behaviours, beliefs, attitudes, values and ideals of a particular society or population
Ethnically
- To so no harm, cannot manipulate data, respect the research
Ethnocentric
- Believing that one's own culture is superior to all others
Ethnography
- The written account of a culture
- In depth description of a particular culture
- infield work done through observation
- Rely on informant or teacher who explains the meaning of event and helps ethnographer integrate into the community
Ethnology
- The study of the origins and cultures of different races and peoples
Fossils
- Preserved remains of biological matter
Hominin
- A human or human ancestor
Hominid
- A member of a group of primates that includes orangutans, gorillas, chimps, and humans
Hypothesis
- A tentative assumption made from known facts as the basis for investigation
Informant
- A reliable and knowledgeable person who provides specific information to an anthropologist studying his or her community
Kinship
- The relationship between two or more people that is based on common ancestry, marriage or adoption
Objective
- Type of conclusions based on facts and data and uninfluenced by personal perspective, prejudices, or emotions
Participant observation
- The careful watching or a group, in some cases living with its members and participating in their culture
Radio metric dating
- A process that is used to determine the age of an object, based on measuring the amount of the radioactive material it has
Reflextivity
- The practice of reflecting on your own world view, biases, and impact on the culture you are studying
Subculture
- A small group within a larger group who shares a common system of values, beliefs, attitudes, behaviours, and life styles distinct from those of the larger group
Subjective
- Type of conclusions shaped by a person's cultural and personal perspective, feelings, and beliefs.
Social Science Inquiry Model
- Formal process that structures social research
- Steps to follow when conducting research to investigate a question
STEP 1 : Question
- Create a research with questions that can be answered throughout your investigation
STEP 2 : Focus
- Takes notes about what you already know, and research what has been previously learned
STEP 3 : Formulate a Hypothesis
- Turn your question(s) into (a) hypothesis
STEP 4 : Collect Your Data
- Use various methods that will provide the most relevant information
STEP 5 : Assemble and Analyze Data
- Organize your data into charts, graphs, or another format that best communicates your main ideas
STEP 6 : Stop and Check
- Have you collected enough data to confirm research hypothesis
STEP 7 : Present Results
- Draw conclusions, identify limitations, make recommendations
STEP 8 : Reflection
- What went well? What would you make done differently?
Introduction to Anthropology, Psychology, and Sociology