Learning Styles and Meeting the Needs of Learners
Multimodal representation
Students should always receive multimodal representation to ensure that they are learning the information as effectively as possible. By giving the students multiple access points for information, it will be clearer, memorized easier, and applied to future contexts better.
Representations can be in the form of: auditory, visual, kinesthetic, reading/writing, logical-mathematical, and more.
The more different representations I have included for every aspect of my lesson planning, the more effective the teaching and learner will be and I will be ensuring that I am meeting the needs of every learner and incorporating a universal design for learning regime.
Learning Styles
There is no creditable evidence that learning styles including multiple intelligences are fact, They are indeed myths and are more likely simply preferences of the students that are generated from their belief that one mode of representation will work greater for them
However, the reality is that everyone leans better when there is multimedia representation. Rather than giving a student only one representation, but multiple to help them think, memorize, and engage better
By making students believe that they have one intelligence that works better than the rest, you will be breeding fixed mindsets instead of growth mindsets
SEF
Ontario document that goes over the core components of reaching every student and meeting the needs of learners
Broken into different categories which are explained in detail to help identify means of carrying out the framework
Ensures that educators are taking every opportunity that they can to reach the needs of their learners. this well help the entire programming of the school to be more effective. This includes communication, assessment, curriculum knowledge, planning, pathways, student engagement, and much more.
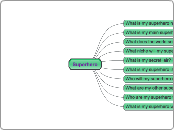
Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
Emotional: well-being, positive relationships, emotional regulation
Cognitive: Intellectual simulation, crticial thinking, curiousity and exploration
Motivational: autonomy, relevance, and goal setting
Special: individualized education plans, supportive services, accessibility
Physical: nutrition, health and safety, physical activity
Social: sense of belonging, peer relationships, communication skills
Academic: individualized instruction, clear expectations, differentiated instruction
Cultural: diversity, inclusion, culturally responsive pedagogy, multilingual supports