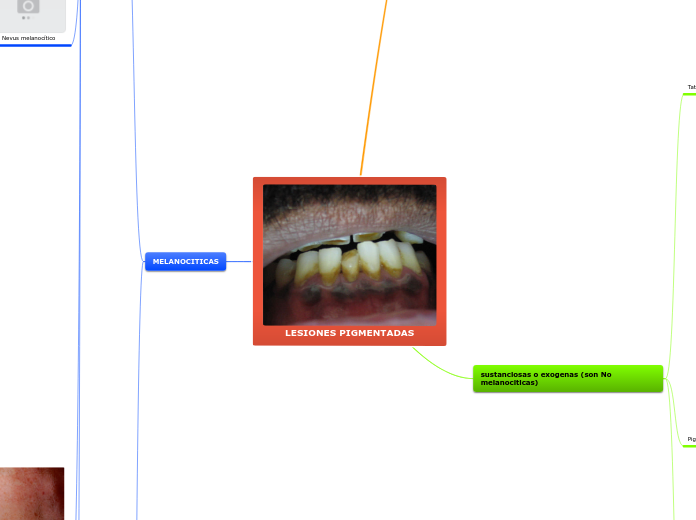
Lesiones pigmentadas de la mucosa oral
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
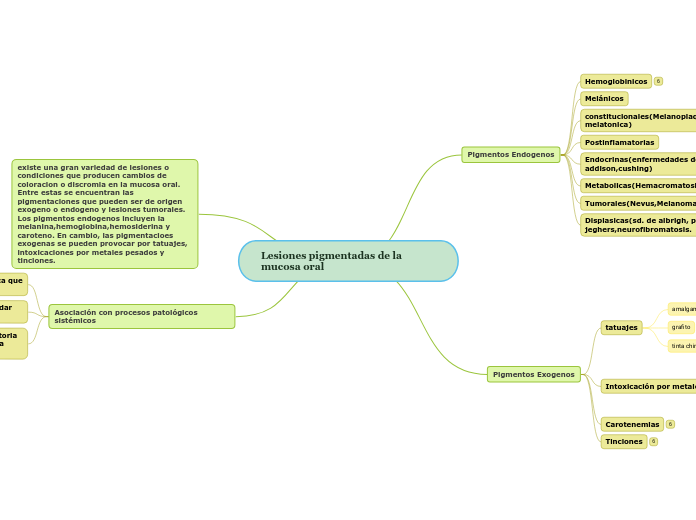
Asociación con procesos patológicos sistémicos
difteria que es una membrana inflamatoria resistente situada en las amígdalas y la retrofaringe.
La amigdalitis y faringitis que pueden dar lugar a una membranaexudativa.
El sarampion una enfermedad sistemica que presenta ampollas en la cavidad oral.
existe una gran variedad de lesiones o condiciones que producen cambios de coloracion o discromia en la mucosa oral. Entre estas se encuentran las pigmentaciones que pueden ser de origen exogeno o endogeno y lesiones tumorales. Los pigmentos endogenos incluyen la melanina,hemoglobina,hemosiderina y caroteno. En cambio, las pigmentacioes exogenas se pueden provocar por tatuajes, intoxicaciones por metales pesados y tinciones.
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
Pigmentos Exogenos
There are four Past tenses:
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple
- Past Perfect Continuous
Tinciones
Past Perfect Continuous is used:
- for an action that started in the past and continued up to another point in the past
- to show cause and effect
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Continuous:
- since (e.g. since yesterday)
- for (e.g. for 10 years, for 6 months)
Structure:
Had + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long had they been living in London before moving here?
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Had I been being?Had you been being?Had he/she/i been being?Had we been being?Had you been being?Had they been being?
Form of word "to have":
Had I been having?Had you been having?Had he/she/it been having?Had we been having?Had you been having?Had they been having?
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t been/had not been + Verb-ING
e.g. I was tired because I hadn't been sleeping.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I had not been beingYou had not been beingHe/She/It had not been beingWe had not been beingYou had not been beingThey had not been being
Form of word "to have":
I had not been havingYou had not been havingHe/She/It had not been havingWe had not been havingYou had not been havingThey had not been having
Structure:
Subject + had been + Verb-ING
e.g. They had been talking for over an hour before I arrived.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I had been beingYou had been beingHe/She/It had been beingWe had been beingYou had been beingThey had been being
Form of verb 'to have':
I had been havingYou had been havingHe/She/It had been havingWe had been havingYou had been havingThey had been having
Carotenemias
Past Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that began in the past and is still going on at the moment of speaking
- an action that continued before and after another action
- a change of mind
- an action happening repeatedly in the past
The Past Perfect tense is not normally used alone. It is used to denote the earlier of two past actions. We use Past Simple for the latter action.
Some adverbs used with Past Perfect Simple:
- already, before, ever, never
- once, twice, yet
- just, up to then
- for, since
Interogative form
Structure:
Had + Subject + Past Participle?
e.g. Had they met Sarah before the party?
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Had I been?Had you been?Had he/she/it been?Had we been?Had you been?Had they been?
Form of word "to have":
Had I had?Had you had?Had he/she/it had?Had we had?Had you had?Had they had?
Structure:
Subject + hadn’t (had not) + Past Participle
e.g. They hadn’t met Julia before the party.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I had not beenYou had not beenHe/She/It had not beenWe had not beenYou had not beenThey had not been
Form of word "to have":
I had not hadYou had not hadHe/She/It had not hadWe had not hadYou had not hadThey had not had
Structure:
Subject + had + Past Participle
e.g. They had already met Julia before the party.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I had writtenYou had writtenHe/She/It had writtenWe had writtenYou had writtenThey had written
Form of verb 'to have':
I have hadYou have hadHe/She/It has hadWe have hadYou have hadThey have had
Intoxicación por metales pesados
Past Continuous is used for:
- an action that happened before another action in the past
- an action that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past
- an action done several times up to a point in the past and continued to do after that point
- an action that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting
Some adverbs used with Past Continuous:
- always, only, never, ever, still, just
Bismuto
Structure:
Was/ were + Verb-ING?
e.g. Were you studying when she called?
Mercurio
Structure:
Subject + wasn’t (was not)/ weren’t (were not) + Verb-ING
e.g. You were not studying when she called.
Plomo
Structure:
Subject + was/ were + Verb-ING
e.g. You were studying when she called.
tatuajes
Past simple expresses:
- an action that happened in the past and has no connection with the present
- an action that happened once in the past
- an action that happened regularly in the past
- an action that was true for some time in the past
- an event or action that already occurred
- an action that is finite - has both a starting and a stopping point
Some adverbs used with Past Simple:
- yesterday
- last month, last year
- ago (e.g. two days ago)
- in (e.g. in 1997)
- never, always, seldom, often, frequently, occasionally, once, twice
tinta china
Structure:
Subject + did not/didn’t + Base Form of the Verb
e.g. They didn’t like my food.
grafito
amalgama
Structure:
Subject + Verb in Past Simple (2nd form)
e.g. They lived in Spain three years ago.
Pigmentos Endogenos
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Displasicas(sd. de albrigh, peutz-jeghers,neurofibromatosis.
Tumorales(Nevus,Melanoma)
Metabolicas(Hemacromatosis)
Endocrinas(enfermedades de addison,cushing)
Postinflamatorias
constitucionales(Melanoplaquia,macula melatonica)
Melánicos
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
Hemoglobinicos
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
Interrogative form
Structure:
Do + Subject (I, You, We, They)+ V1 (First Form of Verb)?
Does + Subject (He, She, It)+V1 (First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Where does he work?
Type in your own examples or choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
Am I?Are youIs he/she/it?Are we?Are you?Are they?
Form of word "to have":
Have I?Have youHas he/she/it?Have we?Have youHave they?
Negative form
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + do not / don’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
Subject (He, She, It) + does not / doesn’t + V1 (First Form of Verb)
e.g. He doesn’t work in a bank.
Type in your own example or choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I am notYou are notHe/She/It is notYou are notWe are notThey are not
Form of word "to have":
I do not haveYou do not haveHe/She/It does not haveWe do not haveYou do not haveThey do not have
Affirmative form
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.
Examples
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb "to be":
I amYou areHe/she/it isWe areYou areThey are
Form of verb "to have":
I haveYou haveHe/she/it hasWe haveYou haveThey have