av Mitchell Pape 4 år siden
421
Macroeconomics
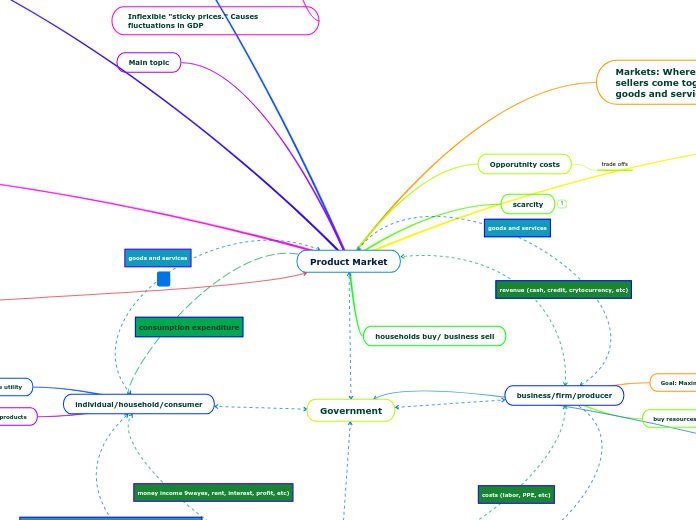
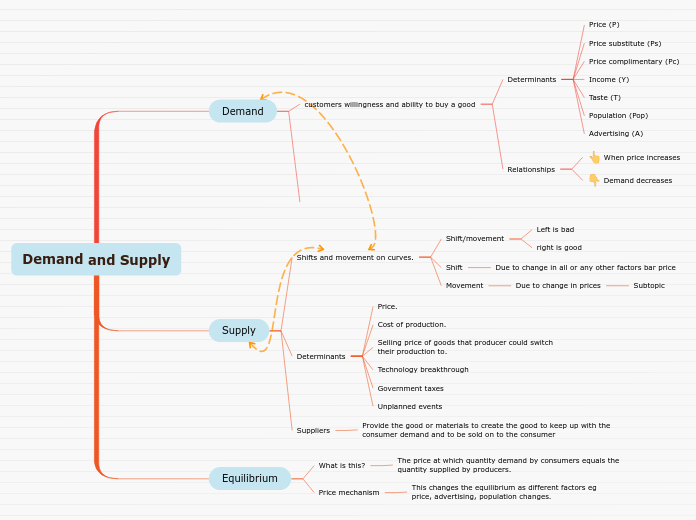
The interaction between supply and demand establishes market equilibrium, determining the optimal price level. The law of demand dictates that as prices decrease, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa.