authentic
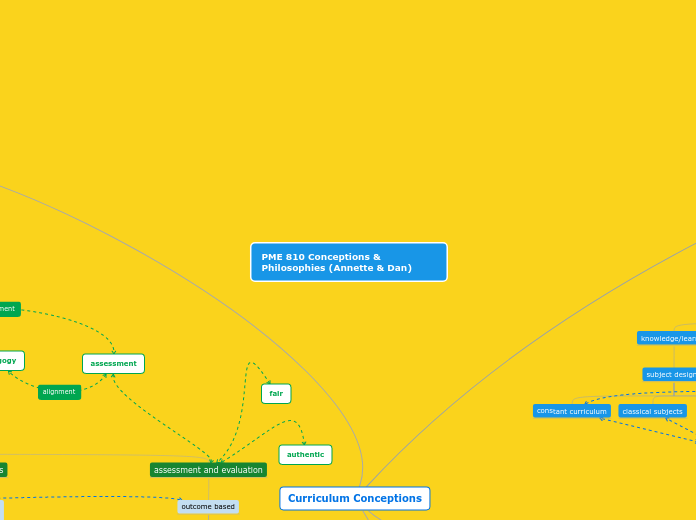
fair
Technology Driven Curriculum
Alignment
curriculum
pedagogy
Fair
assessment
authentic
fair
continuous
summative
formative
For student:
-Mid-unit reflection and assessment
For teacher:
-shows how much knowledge students
have taken in
-lets teacher know if students are
ready to move on to next step in
progression of topic
Generally summative:
self assessment
-rubrics
-evaluation forms
-checklist
-reflective tasks
peer assessment
-rubrics
-evaluation forms
-checklist
teacher assessment
-test/quizzes/homework/etc
-rubrics
-written feedback
-oral feedback
Formative or Summative:
-questioning
-feedback
-from peers
-from self
-from teacher
Subject Centered
Curriculum Conceptions
Technology/Cognitive Processes
evaluation and assessment
-facilitated
-can be tech based
-provides growth through
feedback and reflection
-logical
-concise
teaching to the test
most valuable outcomes are learned
teaching to an ends
how vs what
specific
Cognitive Process objectives:
-refinement of intellectual skills
and processes
-develop cognitive skills
concentrates on developing
intellectual processes by
sharpening students' intellectual
and cognitive skills (Al Mousa, p. 30)
use technology to communicate knowledge and facilitate learning (Al Mousa, p. 23)
use technology to communicate learning
use technology to learn theory
efficient
concise/to the point
logical
experiences
real life situations
growth oriented
personalized
problem centered
Learner
learning how to learn
self-awareness
intellectual autonomy
Science
programmed
science/knowledge based
student driven/paced
predictable
systematic
task by task completion
working towards a goal
Social Reconstruction
philosopy
reconstructionism
Problem Centred/Society-cultural based
Authentic
*Alternative assessments—authentic (journals, demonstrations, portfolios)
*working cooperatively with others
*performance tasks—products
*oral questioning
*self-assessment
*many correct answers
*teacher observations
*peer assessments
*open-ended
*ongoing feedback
*conceptualized tasks
*broad range of tasks
*access prior knowledge
*co-created criteria
develop critical consciousness
group--active learners
*real-world significant
*learning through errors
*teacher facilitates learning--
*creating and being a community of learners
*connected knowledge
*democracy
*social justice
*spirit of inquiry
*critical thinking
integration
social problems exist
in other disciplines
content relevant
to learners
liberal
conservative
radical
Humanistic/Self-Actualization
consciousness
guided fantasy and meditation
confluent
existentialism/reconstructivism
Design
Learner Centred
assessment and evaluation
of learning
*self-assessment
*student ownership
*many correct answers
*open-ended
*alternative assessments
*performance tasks
*portfolios
as learning
*self-assessment
*ongoing teacher feedback
*self-monitoring
*interviews
*informal oral questioning
*variety of applications
for learning
*understanding how each student learns
*planning with students
*co-created success criteria
*access prior knowledge
exploratory, puzzling,
playful, spontaneous
*holistic
*inquiry based
*flexible
*individual needs
*teachers provoke,mentor,
stimulate, and engage
*authentic tasks
*real world context
*cooperative learning
personal growth;
break bonds; change
students be what they
want to be
self-awareness
development of skills and
conceptual knowledge
through physical movement
and expressing feelings
Dimensions
content varies
balance
articulation
Integration
action
intellectual
affective
sequence/continuity
not well defined
Source
Participation, integration,
relevance, self, goal
existing subject matter
infused with affect
Academic Realism
also known as
cumulative tradition of
organized knowledge
philosophy
essentialism
perennialism
objectives
design
evaluation
outcome based
This
skill based
synthesize
hypothesize
question
learning experiences
"curriculum is seen as the vehicle by
which learners are introduced to subject
matter...and organized fields of study"
(Al Mousa, p. 27)
Pedagogy
organized knowledge building
undisciplined
flexible
eg. home economics
disciplined
rigid
prescribed
subject matter
academic disciplines
backwards mapping or
backwards design
setting goals that dictate
instructional methods and
assessment tools
forward mapping
start at beginning and move
towards specified end goal
scope and sequence of outcomes
Introduces students to subject disciplines
and to organized studies of knowledge.
Teaches students to think, question, hypothesize
and draw conclusions.
Engages students in critical thinking, problem solving, and inventive activities
descriptors
scholarly
cultivating
generality
precision
acquire tools for Western society
preparation for life
develop rational minds
"cultivate cognitive achievement and
intellect by helping students understand
knowledge" (Al Mousa, p. 29)
content
Curriculum Based
source
political
influence on curriculum
society
dimensions
scope
horizontal
continuity/sequence
vertical
knowledge/learner
subject designs
single subject
broad based
generalized
classical subjects
constant curriculum
PME 810 Conceptions & Philosophies (Annette & Dan)