av Никита Самсонов 5 år siden
284
problems
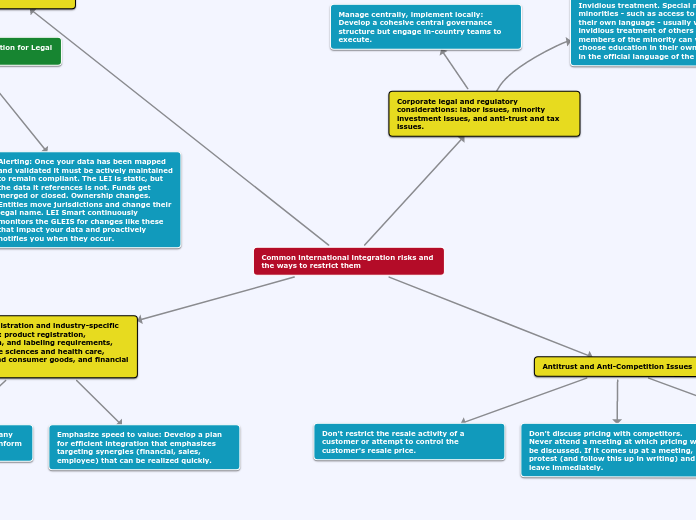
International integration poses numerous risks, necessitating a strategic approach to mitigate potential issues. Key considerations include addressing labor, minority investment, anti-trust, and tax concerns.