av Alexander Refsum Jensenius 7 dager siden
165
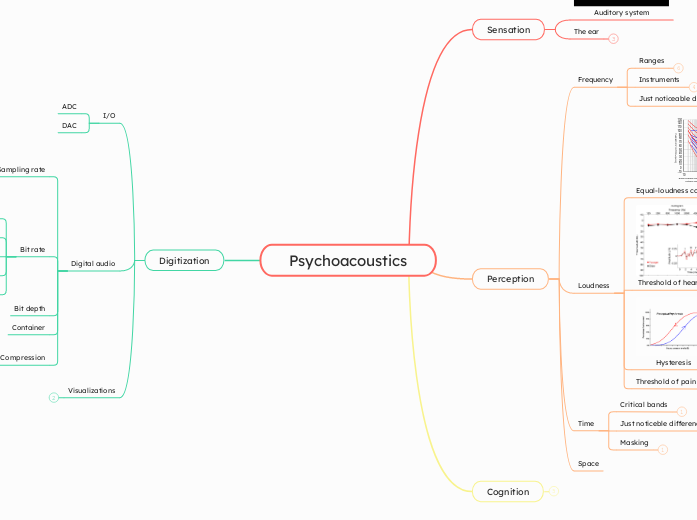
Psychoacoustics
Understanding how humans perceive sound involves examining various components, including the anatomy of the ear and the brain's processing mechanisms. The ear is divided into the outer, middle, and inner sections, each playing a distinct role in sound transmission.