Prometió
2da guerra mundial
Su llegada al poder
Se eligió
Los bolcheviques
Eso produce
Hizo
Por
Generales
Como la
Involucración de
Su situación
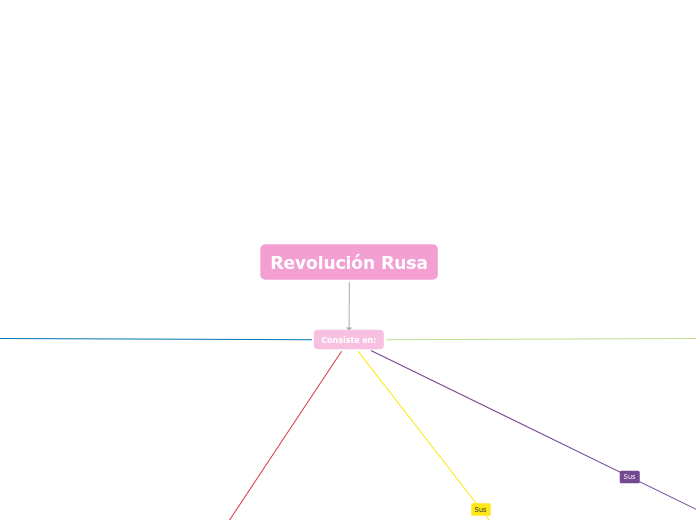
Revolución Rusa
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
Consiste en:
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Antecedentes
Revolución 1905
El zar Nicolás II no acepto las solicitudes para la
revolución de 1905
Y
Esa solicitud la reprimió con fuego y sangre, resultando como el Domingo Sangriento
Las malas cosechas provocan revueltas
campesinas
Se produce
La guerra ruso- japonesa
Enojo del pueblo y demanda de cambios
Gana japón
1881-1917
Régimen zarista
Alejandro III y Nicolás II
Autocracia que trae represión, pero también
orden social
1867-1914
Ligeras reformas
De
Abolición, incertidumbre e industrialización
Etapas
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
Octubre de 1917
Toman el poder
Marzo de 1917
Un gobierno provisional
Kerensky
Hizo fracasar el golpe de Kornílov
Movimiento obrero
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
Malas condiciones de trabajo y largas jornadas de trabajo
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Huelga de los trabajadores
Caracteristicas
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
Dos poderes
Por el otro
Soviéts
Asambleas de obreros y campesinos
Ocurrió la revolución de octubre la cual tuvo la instalación de el comité militar de Petrogrado el cual era controlado por los bolcheviques
Menos poder en el gobierno provisional
Los bolcheviques tuvieron el plan de tomar el país durante el 2do congreso de los sovients, catalogando cualquier intento contrarevolucionario
Por un lado
Gobierno Provisional
Dirigido por Kerensky y apoyado por la burguesía
También los mencheviques los apoyaron en su decisión de continuar la guerra, pero también perdieron apoyo.
San Petersburgo
Fue llamado "Domingo sangriento"
Indignación de la población
La reacción
La guardia del zar abrió fuego contra los manifestantes
MOVIMIENTO REVOLUCIONARIO DETONANTE
Grupos políticos
Contra el zarismo
Populistas
Esteristas
Cadetes
Partidos obrero social demócrata Ruso
Bolcheviques
Dictadura de propietario
Lenin
Mencheviques
Había que pasar por una revolución burguesa
antes de la socialista
Yuli Martov
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Perdidas de muchas personas por derrotas constantes
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
El zar aumento el reclutamiento de soldados
Produjo
Crisis por falta de mano de obra en el campo
Consecuencias
Decide on the second point of view
Name the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view you are presenting.
Example: Miss Edmunds, Jesse's music teacher.
Joseph Stalin (1878- 1953)
No tuvo reparos en firmar un pacto de no agresión con la Alemania nazi
Tranquilidad en sus fronteras, el reparto de Polonia y la anexión de Estonia, Letonia y Lituania
En 1922 fue nombrado Secretario General del Partido Comunista Panruso
Convirtió a la Unión Soviética en una potencia mundial
Purgas políticas y envió a millones de detractores a los gulags
Su obsesión persecutoria contra todo aquel que le contradijera
Fin del régimen zarista
Etapa de hambruna y la petición popular
Represión política
Crisis de los gobiernos del zar
Influencia de Rasputín
URSS
Type in a quote that points out the character's position about the issue.
Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'She said he was unusually talented, and she hoped he wouldn't let anything discourage him.' (Paterson, 2. 8)
Fin
Dejó de existir en 1991, cuando Rusia, Bielorrusia y Ucrania declararon su disolución y fue reemplazada por la Coalición de Estados Independientes.
Inició
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of viewSecond person point of viewThird person point of viewOmniscient point of view
1922
Se aprobó el Tratado de Creación de la Unión Soviética y la Declaración de la Creación de la Unión Soviética.
1917
Lennin derrocó el régimen del zar Nicolás II, quien tuvo que abdicar y se instaló un gobierno provisional.
Causas
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Régimen del zar
Nobleza con toda la tierra
Altos cargos de la administración del ejército y policía secreta
Iglesia ortodoxa
1era guerra mundial
Intentando mantener ritmo de producción.
What type of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Demasiadas derrotas
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
1era guerra mundial.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Invierno muy duro y con las peores condiciones para Rusia.
Pobreza
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Consiste en:.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)