Enquiry led learning: developing independent thinkers
The process of experimentation, which is
common in science, can also be used to solve technological problems.
Experimenting: Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved.
Student led creative process implementing principles of science, engineering, math and problem solving skills
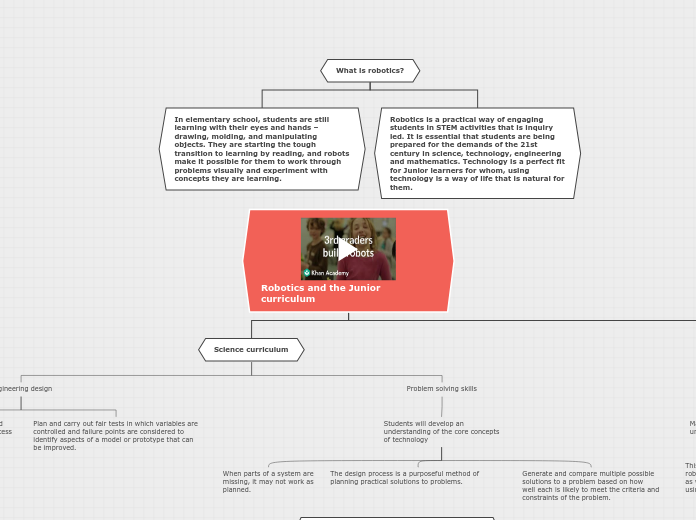
What is robotics?
Robotics is a practical way of engaging students in STEM activities that is inquiry led. It is essential that students are being prepared for the demands of the 21st century in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Technology is a perfect fit for Junior learners for whom, using technology is a way of life that is natural for them.
In elementary school, students are still learning with their eyes and hands – drawing, molding, and manipulating objects. They are starting the tough transition to learning by reading, and robots make it possible for them to work through problems visually and experiment with concepts they are learning.
Robotics and the Junior curriculum
Math curriculum
Useful link to measurement and data
Mathmetics strand: Geometric measurement:
understand concepts of angle and measure angles.
This can be incorporated into the curriculum using robotics by designing a robot incorporating angles, as well as coding a pathway or pattern for a robot using the measurement of angles.
Science curriculum
Problem solving skills
Students will develop an
understanding of the core concepts
of technology
Generate and compare multiple possible
solutions to a problem based on how
well each is likely to meet the criteria and
constraints of the problem.
The design process is a purposeful method of planning practical solutions to problems.
When parts of a system are
missing, it may not work as
planned.
Engineering design
Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are
controlled and failure points are considered to
identify aspects of a model or prototype that can
be improved.
Define a simple design problem reflecting a need
or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints on materials, time, or cost.