av Nurin Aqilah 4 år siden
265
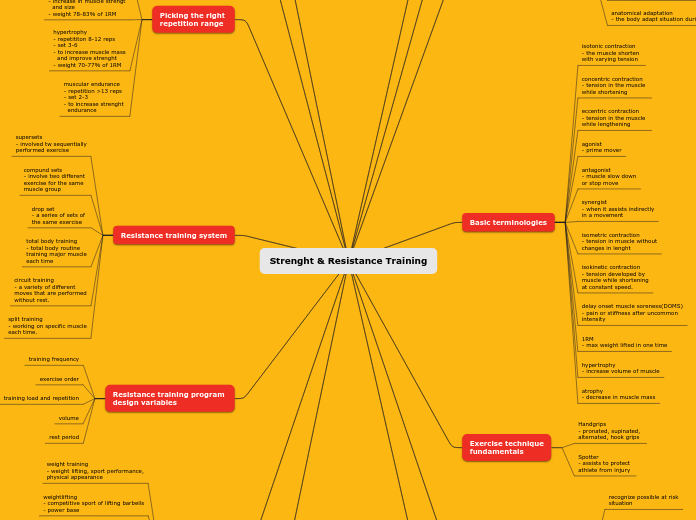
Strenght & Resistance Training
Different training methodologies and terminologies cater to varied fitness goals, such as strength, power, hypertrophy, and endurance. Power and resistance training encompass explosive movements and overall muscle engagement, respectively, while bodybuilding focuses on muscle size without necessarily emphasizing strength.