What can go into a lesson?
Study skills
The following skills can be taught, learnt and encouraged in a language class
motivating yourself, improving your own confidence, being active by asking questions, tolerating frustrations and difficulties, improving your own memory, clarifying things, developing and organizing your own ideas.
preview, review and overview
knowledge of and flexibility with a range of task, activity and information display types
ways of consulting reference works, and ways of using resource rooms and libraries
organization of time, place and materials
Culture
Culture is about difference and variability and thus contain both the potential for opportunity and for conflict.
Advantages:
the chance to develop the intercultural abilities of getting on with people who are different and learning how to express yourself in a new language
the chance to learn about aspects of the new culture, understand its significance for people in that culture and thus, to learn more about the home culture
the chance to meet the new culture and deal with the interest and/or stress that this involves
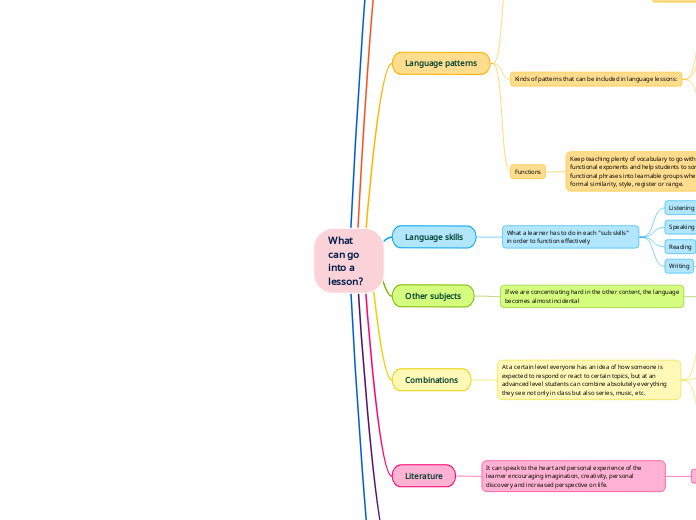
Literature
It can speak to the heart and personal experience of the learner encouraging imagination, creativity, personal discovery and increased perspective on life.
Practical principles for teaching literature
Choose pieces to work on because they are short or funny or match student interest
Start helping students to enjoy the musical and expressive nature of language and literature
Combinations
At a certain level everyone has an idea of how someone is expected to respond or react to certain topics, but at an advanced level students can combine absolutely everything they see not only in class but also series, music, etc.
Practical principles for teaching situations, topics and themes
It is necessary to show the students that they are not seen as something that is only there to teach and only that, it is necessary to show them that everything goes beyond that, that it is for their preparation.
Topics and themes
All activities should be based on and designed for the development of the topic, but they also help to keep the student focused and goal-oriented, they help to keep the student-focused by using topics they like.
Situations
Creating a situation that can be based on the language needed or seen in the lesson can be a great way for the learner to develop in the right way in real life and turn help in the lesson.
Other subjects
If we are concentrating hard in the other content, the language becomes almost incidental
working in real life situations in English
Language skills
What a learner has to do in each "sub skills" in order to function effectively
Writing
make sentences and punctuaction
Reading
Know letters, words and phrases
Speaking
Use different parts of the mouth and body
Listening
Recognise sounds, words and phrases
Language patterns
Functions
Keep teaching plenty of vocabulary to go with the functional exponents and help students to sort all the functional phrases into learnable groups whether by using formal similarity, style, register or range.
Kinds of patterns that can be included in language lessons:
Work on four basic sentence types
exclamative
imperative
Interrogative
declarative
Working on the SVO pattern
entails dealing with noun phrases every bit as much as verb phrases
Normal word order
students whose language has a different normal word order can express their thoughts clearly in English.
Grammar is utterances and sentences
generalizability
meaning
form
look and sound, or indented first lines of new paragraphs and word order
Classes and people
areas that are subject matter for a lesson
Time: how long a lesson
Territory: where staff and students are allowed to go
Clothing: how status is marked by clothing.
Conduct: how to treat students
Resources: which material are available or acceptable at work
Student behaviour alone and in groups: students regulate their own behaviour
Spoken or unspoken ground rules: How to operate the class
The people in the class as the subject matter: the teachers and students form part of the content of lessons in their own right
What there is to teach and learn
Things that could go into a lesson
•classes and people
• language patterns
• language skills
• combinations
• literature
• culture
• study skills