por Samuel Stephenson 4 anos atrás
371
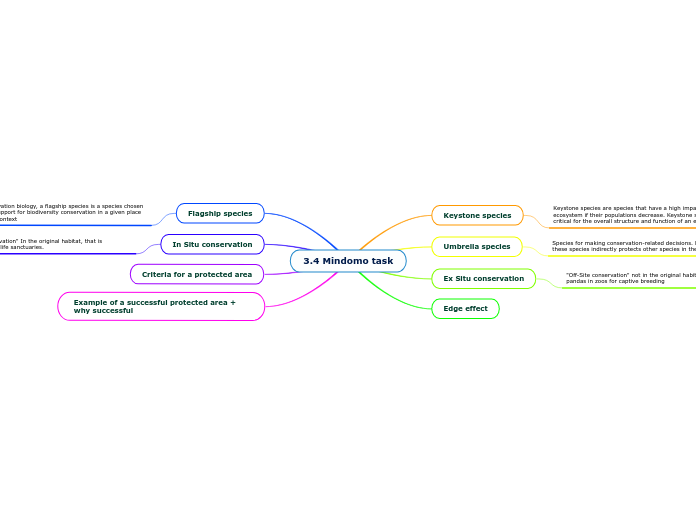
3.4 Mindomo task
In situ conservation involves protecting species within their natural habitats, such as wildlife sanctuaries, to maintain biodiversity. This method contrasts with ex situ conservation, which includes activities like captive breeding in zoos.