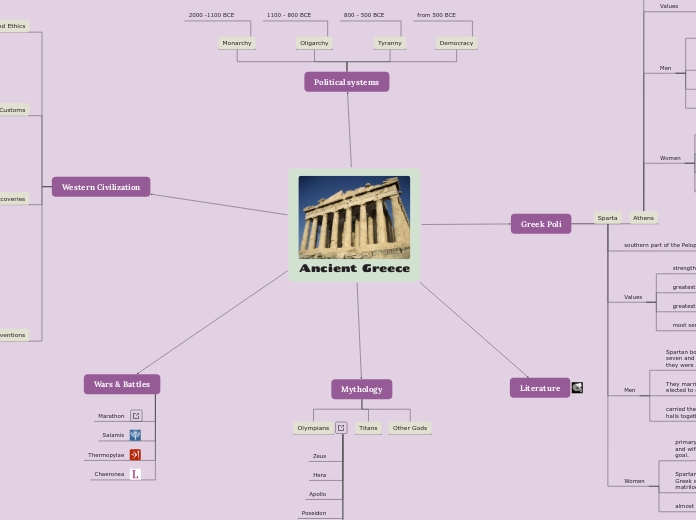
Ancient Greece
Explore Greek's fascinating ancient civilization
Seek to understand how this civilization had evolved into becoming one of the most powerful in history. Learn about Greek values, principles, their scientific breakthroughs, great battles, and mysterious stories with gods and goddesses.
Literature
Literature in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greeks were very prolific in writing. Their traditional literary genres were: epic; poem; play; history; philosophical dialogue and treaty; political and/or legal speech.
Mythology
Greek Mythology
img://149677d8f2044df786ea12fd88e58f5f
was part of the religion in Ancient Greece and it included all the myths and teachings of their gods, the origins of the world and the Greek cult and ritual practices.
Other Gods
Titans
Olympians
Hades
Hades brother of Zeus
was the god of the underworld, ruling over the dead.
Ares
Ares son of Zeus and Hera
was the god of war. He was disliked both by his parents and by the people. Though the god of war, he was considered to be a coward.
Poseidon
Poseidon brother of Zeus
was the god of the sea and protector of all waters. He was also the god of horses. There is amyth about Poseidon creating the first horse in order to impress his beloved Demeter.
Apollo
Apollo son of Zeus and Letto
was the god of the sun, truth, music, poetry, dance and healing.
Hera
Hera queen of gods
was the wife of Zeus. She is the patron of weddings and marriage. Her jealousy is well-known throughout history because she used to take awful revenge on Zues' girlfriends and illegitimate children.
Zeus
Zeus king of the gods
Also, called the 'cloud-gatherer' and 'thunderer' by the Greek poet Hesiod, Zeus was the supreme ruler of the Olympian gods. He controlled the weather, and every time a lightning struck, people thought it was a sign from Zeus.
Wars & Battles
Most important battles in Ancient Greece
img://1effb42f913c4eca996100e576b04894
Already internally warring, Ancient Greece has fought many battles with external enemies, but four of them were extremely significant: Battle of Marathon (490 B.C.), Battle of Salamis (480 B.C.), Battle of Thermopylae (480 B.C.), and Battle of Chaeronea (338 B.C.).
Chaeronea
Thermopylae
Salamis
Marathon
Greek Poli
What is a 'polis'?
A city-state in Ancient Greece was called a 'polis'. The polis consisted of the people who lived within a walled area (the size of a few city blocks) and the crops surrounding this area. Poli (plural of 'polis') were grouped in leagues as a form of alliance in front of enemy invasions. Two of the most important polis in Ancient Greece were Sparta and Athens.
Athens
men entertained, wives were not invited to the dinner
were valued, but had only indirect influence on politics
took care of the home and children
pale skin was in style
Women in Athens
Type in several details that best portray their contribution to the Athenian society.
Only men were engaged in politics and public events
citizens (Athenian-born men) had that the right to vote
Metics (men that were not Athenian-born), had to pay taxes and serve in the military, but these men did not have voting privileges.
dominant role in public life in ancient Greece
Men in Athens
Athenian men are famous for creating the democracy. Type in several details related to their other contribution to the Athenian society.
believed that individuals should be free as long as they acted within the laws of Greece
What did Athenians value the most?
Type in the values promoted in Athens.
on a peninsula that stretches southeastward into the Aegean Sea
Where is Athens located?
Because of its location, Athens was a perfect polis for trade, but also easily accessible for invaders. Type in the geographical position of Athens.
Sparta
Women
almost as tough as the men
Spartan women had more freedoms and rights than other Greek women. Plutarch wrote that Spartan marriage was matrilocal and that "women ruled over men."
primary duty of Spartan wives was to produce future soldiers and wife swapping was permissible as long as it furthered this goal.
Women in Ancient Sparta
Because their men were mostly in training camps, Spartan women played a very important role in their society. Type in several details that best portray their contribution to the Spartan society. Example: they owned a third of the polis' land.
Men
carried their weapons with them at all times and ate in mess halls together.
They married at any time, but lived with men. At 30 they were elected to citizenship.
Spartan boys were taken from the mothers at the age of seven and moved into barracks and taught to be men until they were aged 20.
Men in Ancient Sparta
Spartan men and their bravery made this polis one of the most famous cities of the ancient civilizations. Type in several details related to the way Spartan men lived and fought. Example: they were constantly training for war.
Values
most serious crime for a Spartan was to retreat from battle
greatest honor was to die fighting in battle
greatest virtue was bravery
strength was admired and weakness was despised
What did Spartans value the most?
Type in the values promoted in Sparta.
southern part of the Peloponnese
Where was Ancient Sparta located?
Sparta had a strategical location, with natural defenses that prevented her from getting sacked.
Type in Sparta's location.
Political systems
Political systems in Ancient Greece
img://83b13cf6633a4f72a3aa889a701056fb
Since Ancient Greece has numerous city-states, the Greek civilization had numerous governments, each city-state with its own political system.
Aristotle categorized these political systems and came up with these main categories: monarchy, oligarchy, tyranny and democracy.
Democracy
from 500 BCE
Tyranny
800 - 500 BCE
Oligarchy
1100 - 800 BCE
Monarchy
2000 -1100 BCE
What is the period
in which this political system was adopted? Type in the answer.
Western Civilization
Ancient Greece as Cradle of Western Civilization
img://b0da26103098452d9526c04c2d0ec5fa
Western civilization, also known as 'Western culture', 'Western lifestyle' or 'European civilization', has its origins in Ancient Greece.
The concept refers to a heritage of social values and norms, political systems, traditional customs, and distinguishing technologies and artifacts that have some origin or association with Europe.
Technologies & Inventions
concept of democracy
modern philosophy
basis of geometry
olympics
cartography
alarm clock
odometer
water mill
Technologies and inventions in Ancient Greece
There are a lot of ancient Greek inventions that have shaped modern technology. Type in the ones that you consider to have a great impact and utility in our everyday life.
Discoveries
Hippocrates
Hippocratic Oath
Discoveries of Hippocrates of Cos (460 - 370 B.C.)
Hippocrates of Cos is among the most remarkable figures in the history of medicine, also being referred to as the 'father of western medicine'. What were his main discoveries? Type them in.
Anaxagoras
1st molecular theory of matter
Discoveries of Anaxagoras of Clazomenae (510 - 428 B.C.)
Anaxagoras was the one who brought philosophy from Ionia to Athens. He is famous for his contributions to astronomy. Type in his most important discoveries.
Pythagoras
The Pythagorean Theorem
Discoveries of Pythagoras of Samos (570 - 495 B.C.)
Pythagoras of Samos was a Greek philosopher, mathematician, astronomer, and the founder of the religious movement called 'Pythagoreanism'. Type in his most important discoveries.
Thales
earthquake theory
Discoveries of Thales of Miletus (620 - 546 B.C.)
Thales of Miletus was one of the Seven Wise Men of Greece, a prolific philosopher, geometer, military engineer, and astronomer. Type in the most important discoveries made by him.
Customs
orphaned daughters were left to an uncle or cousin
dead ones had mouth sealed with a token or talisman
husbands controlled all property
Ancient Greece customs and traditions
Customs and traditions follow us all our lives, and are more prominent on special occasions, such as birth, wedding, death, and/or funeral.
Type in several customs and traditions in Ancient Greece.
Social Values and Ethics
skillful warrior
keeping promises and oaths
hospitality
honoring the gods
exhibit bravery
Social Values and Ethics
Social values refer to the norms or behaviors which are widely acceptable and admirable in a society. Following the social values, one shapes up as a good human being and contributes to society’s development.
Ethics governs the principles of right and wrong within a given society or social group.
Type in the values and ethics of ancient Greeks, some of which still lay at the foundation of today's moral philosophy.
exhibit braveryskillful warriorhonoring the godskeeping promises and oathsloyaltyself-controlhospitalityrespectful of women and elderly peoplemodesty