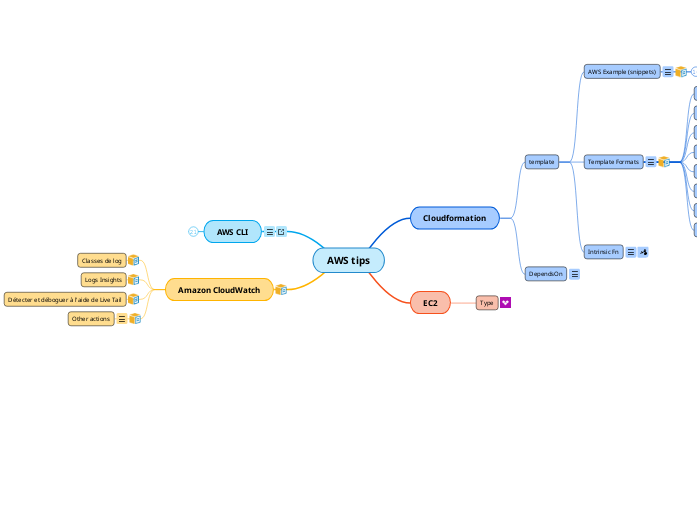
AWS tips
Amazon CloudWatch
Other actions
- Surveillez les journaux des instances Amazon EC2 : vous pouvez utiliser les CloudWatch journaux pour surveiller les applications et les systèmes à l'aide des données des journaux. Par exemple, CloudWatch Logs peut suivre le nombre d'erreurs qui se produisent dans les journaux de vos applications et vous envoyer une notification chaque fois que le taux d'erreurs dépasse un seuil que vous spécifiez. CloudWatch Logs utilise les données de vos journaux à des fins de surveillance ; aucune modification de code n'est donc requise. Par exemple, vous pouvez surveiller les journaux des applications pour détecter des termes littéraux spécifiques (tels que NullReferenceException « ») ou compter le nombre d'occurrences d'un terme littéral à une position donnée dans les données des journaux (tels que les codes d'état « 404 » dans un journal d'accès Apache). Lorsque le terme que vous recherchez est trouvé, CloudWatch Logs rapporte les données selon une CloudWatch métrique que vous spécifiez. Les données des journaux sont chiffrées, pendant le transit et pendant le repos. Consultez Commencer à utiliser CloudWatch Logs pour démarrer.
- Surveiller les événements AWS CloudTrail enregistrés : vous pouvez créer des alarmes CloudWatch et recevoir des notifications concernant une activité d'API particulière telle qu'elle est capturée, CloudTrail et utiliser la notification pour résoudre les problèmes. Pour commencer, consultez la section Envoyer CloudTrail des événements aux CloudWatch journaux dans le guide de AWS CloudTrail l'utilisateur.
- Auditez et masquez les données sensibles : si vos journaux contiennent des données sensibles, vous pouvez les protéger grâce à des politiques de protection des données. Ces politiques vous permettent d'auditer et de masquer les données sensibles. Si vous activez la protection des données, les données sensibles correspondant aux identifiants de données que vous sélectionnez sont masquées par défaut. Pour plus d’informations, consultez Aider à protéger les données sensibles des journaux grâce au masquage.
- Conservation des journaux : par défaut, les journaux sont conservés indéfiniment et n'expirent jamais. Vous pouvez ajuster la stratégie de conservation pour chaque groupe de journaux. Elle peut être indéfinie ou comprise entre 10 ans et un jour.
- Archiver les données du journal : vous pouvez utiliser CloudWatch les journaux pour stocker les données de vos journaux dans un espace de stockage hautement durable. L'agent CloudWatch Logs permet d'envoyer rapidement des données de journal avec ou sans rotation depuis un hôte vers le service de journalisation. Vous pouvez ensuite accéder aux données brutes des journaux lorsque vous en avez besoin.
- Consigner les requêtes DNS de Route 53 : vous pouvez utiliser CloudWatch les journaux pour enregistrer les informations relatives aux requêtes DNS reçues par Route 53. Pour plus d'informations, consultez Consignation des requêtes DNS dans le Guide du développeur Amazon Route 53.
Détecter et déboguer à l'aide de Live Tail
Logs Insights
Classes de log
AWS CLI
AWS CLI est une interface de ligne de commande qui permet aux utilisateurs d'interagir avec les services Amazon Web Services (AWS) via la ligne de commande au lieu d'utiliser l'interface utilisateur graphique. Avec AWS CLI, les utilisateurs peuvent gérer efficacement les ressources, configurer les services et automatiser les tâches dans AWS. Fournit des commandes pour accéder et gérer une large gamme de services AWS, tels que EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, etc. Avec l'AWS CLI, les utilisateurs peuvent écrire des scripts et des commandes personnalisés pour automatiser des tâches répétitives ou complexes dans AWS.
commandes
Configure
sans l'option list, permet de reconfigurer pref et credentials:
aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]:
AWS Secret Access Key [None]:
Default region name [eu-west-1]:
Default output format [None]: ^C
par def:
aws configure list
Name Value Type Location
---- ----- ---- --------
profile D********** manual --profile
access_key ****************7LYG assume-role
secret_key ****************rqi7 assume-role
region eu-west-1 config-file ~/.aws/config
set
EXAMPLES
Given an empty config file, the following commands:
$ aws configure set aws_access_key_id default_access_key
$ aws configure set aws_secret_access_key default_secret_key
$ aws configure set default.region us-west-2
$ aws configure set default.ca_bundle /path/to/ca-bundle.pem
$ aws configure set region us-west-1 --profile testing
$ aws configure set profile.testing2.region eu-west-1
$ aws configure set preview.cloudsearch true
add-model
ADD-MODEL() ADD-MODEL()
NAME
add-model -
DESCRIPTION
Adds a service JSON model to the appropriate location in ~/.aws/models.
Once the model gets added, CLI commands and Boto3 clients will be imme-
diately available for the service JSON model provided.
See 'aws help' for descriptions of global parameters.
SYNOPSIS
add-model
--service-model <value>
[--service-name <value>]
OPTIONS
--service-model (string) The contents of the service JSON model.
--service-name (string) Overrides the default name used by the service
JSON model to generate CLI service commands and Boto3 clients.
See 'aws help' for descriptions of global parameters.
EXAMPLES
Add a model
The following command adds a service model from a file named ser-
vice.json:
aws configure add-model --service-model file://service.json
Adding a model replaces existing commands for the service defined in
the model. To leave existing commands as-is, specify a different ser-
vice name to use for the new commands:
aws configure add-model --service-model file://service.json --service-name service2
get
Suppose you had the following config file:
[default]
aws_access_key_id=default_access_key
aws_secret_access_key=default_secret_key
[preview]
cloudsearch=true
[profile testing]
aws_access_key_id=testing_access_key
aws_secret_access_key=testing_secret_key
region=us-west-2
The following commands would have the corresponding output:
$ aws configure get aws_access_key_id
default_access_key
$ aws configure get default.aws_access_key_id
default_access_key
$ aws configure get aws_access_key_id --profile testing
testing_access_key
$ aws configure get profile.testing.aws_access_key_id
testing_access_key
List
exemples
aws ec2 describe-instances \
--filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=myapp-api-instance" \
--query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].PrivateIpAddress"
aws ec2 describe-images --owners self \
--filters "Name=name,Values=myapp-server-*" \
--query 'reverse(sort_by(Images, &CreationDate))[*].[CreationDate,Name,ImageId]' \
--output table
aws ec2 describe-images --owners aws-marketplace \
--filters "Name=product-code,Values=aw0evgkw8e5c1q413zgy5pjce" \
--query "sort_by(Images, &CreationDate)[-1].[ImageId]"
aws ec2 describe-images --owners aws-marketplace \
--filters "Name=name,Values=CentOS Linux 7*" \
--query 'reverse(sort_by(Images, &CreationDate))[*].[CreationDate,Name,ImageId]' \
--output table
aws ec2 describe-images --owners aws-marketplace \
--filters "Name=virtualization-type,Values=hvm" "Name=root-device-type,Values=ebs" "Name=product-code,Values=aw0evgkw8e5c1q413zgy5pjce" \
--query 'reverse(sort_by(Images, &CreationDate))[*].[CreationDate,Name,ImageId]' \
--output table
aws s3api list-objects-v2 --bucket "myapp-backup-log-bucket" --query 'Contents[?LastModified >= `2020-12-09`][].Key'
aws ecs describe-services --cluster myapp-global --services SvcECS-myapp-global-discserv-demo --query 'services[0].taskDefinition'
aws deploy get-deployment-target --deployment-id d-KD5KWT432 --target-id myapp-global:SvcECS-myapp-global-discserv-demo --query "deploymentTarget.ecsTarget.status" --output text
ALB_URL=$(aws elbv2 describe-load-balancers \
--names alb-myapp-global-discserv-demo \
--output text \
--query "LoadBalancers[*].DNSName")
LAST_DEPLOYMENT=$(aws deploy list-deployments \
--application-name "${codedeploy_application_name}" \
--deployment-group-name "${codedeploy_deployment_group_name}" \
--query "deployments" \
--max-items 1 \
--output text \
| head -n 1)
DEPLOYMENT_STATE=$(aws deploy get-deployment \
--deployment-id "${LAST_DEPLOYMENT}" \
--query "deploymentInfo.status" \
--output text)
aws elbv2 describe-listeners --output text \
--load-balancer-arn "arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:eu-central-1:123456789012:loadbalancer/app/alb-myapp-global-discserv-demo/85e7d9c4b893b91f" \
--query 'Listeners[?Port==`80`].ListenerArn'
aws elbv2 describe-listeners \
--load-balancer-arn "${LB_ARN}" \
--query 'Listeners[?Port==`443`].ListenerArn' \
--output text
aws elbv2 describe-listeners \
--listener-arns "arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:eu-central-1:123456789012:listener/app/alb-myapp-global-discserv-demo/85e7d9c4b893b91f/02a841099f705adb" \
--query 'Listeners[0].DefaultActions[0].TargetGroupArn' \
--output text
Cheat Sheet
S3
see aws s3 help
s3 — AWS CLI 1.29.82 Command Reference (amazon.com)
lire aussi: AWS CLI: s3 vs s3api (learnaws.org)
website
The following command configures a bucket named my-bucket as a static website:
aws s3 website s3://my-bucket/ --index-document index.html --error-document error.html
website — AWS CLI 1.29.82 Command Reference (amazon.com)
sync
Syncs directories and S3 prefixes. Recursively copies new and updated files from the source directory to the destination. Only creates folders in the destination if they contain one or more files.
rm
rb
presign
Generate a pre-signed URL for an Amazon S3 object. This allows anyone who receives the pre-signed URL to retrieve the S3 object with an HTTP GET request. For sigv4 requests the region needs to be configured explicitly.
validity 1 hour
mv
mb
cp
ls
aws s3 ls
2023-08-12 10:03:13 xxx-xxx-aiops-repo-for-config
2023-03-17 21:31:32 47896-dependencies
2023-03-02 09:54:20 aws-glue-assets-350822036138-eu-west-1
2023-03-02 09:54:21 cf-templates-1b20l46xpzyab-eu-west-1
2023-03-30 12:56:05 da-xxx-dev-eu-data-bronzebatchdatalake
2023-03-30 12:55:25 da-xxx-dev-eu-data-bronzerawdatalake
2023-03-30 12:54:33 da-xxx-dev-eu-data-bronzerawdatalake-test-cases:s
~
le contenu d'un S3:
aws s3 ls s3://newdep
2023-03-17 18:09:47 788412928 AlertAPI.tar
aws s3 ls s3://aws-glue-assets-350822036138-eu-west-1
PRE notebooks/
PRE scripts/
PRE sparkHistoryLogs/
PRE temporary/
aws s3 ls --recursive s3://aws-glue-assets-350822036138-eu-west-1 |head
2023-03-15 13:40:01 9846 notebooks/da-xxx-pipeline-dev-transformation-v999-do-not-delete.ipynb
2022-11-03 10:57:28 14612 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-000-V2.ipynb
2022-11-02 16:26:31 5603 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-000-V3-test.ipynb
2022-11-04 12:26:15 9759 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-000-V3.ipynb
2022-10-07 08:30:09 5603 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-999-V1-do-not-delete.ipynb
2023-01-30 09:03:30 12138 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-999-V2-do-not-delete.ipynb
2022-10-27 08:15:09 28885 notebooks/xxx-datarepo-glue-script-999-V2.1-do-not-delete.ipynb
2023-02-22 14:23:32 29230 scripts/da-xxx-pipeline-dev-transformation-v1-cmk-test.py
2023-03-03 12:42:25 22904 scripts/da-xxx-pipeline-dev-transformation-v1-test-03-03-2023.py
2023-02-22 12:01:51 29230 scripts/da-xxx-pipeline-dev-transformation-v1-test-forAnil.pyn
fichiers de conf
config
[default]
region=eu-west-1
[profile XXX-PROD]
role_arn=arn:aws:iam::<xxxxxxxxxxx>:role/role-user-administrator-read-only
source_profile=xyz@xyz.com
region=eu-west-1
[profile XXX-NONPROD]
role_arn=arn:aws:iam::<xxxxxxxxxxx>:role/role-user-administrator-read-only
source_profile=xyz@xyz.com
region=eu-west-1
[profile XXX-TEST]
role_arn=arn:aws:iam::<xxxxxxxxxxx>:role/role-user-administrator
credentials
cat .aws/credentials
[christophe.xxx@xxx.com]
aws_default_region = eu-west-1
aws_access_key_id = XXXSDRF
aws_secret_access_key = XXXAZERTYsuetshs
aws_session_token = <XXXXXXXXXXXxxxxxxxxxxx>
EC2
Type
Cloudformation
DependsOn
DependsOn
"DependsOn":"CloudWatchTransformFunctionRole"
This attribute is used to define that the creation of a specific resource follows another. I often use it if a certain resource requires an IAM role or CloudWatch LogGroup created beforehand and I need to ensure the order is followed. Otherwise, the CloudFormation template may fail with an error message that the ARN can not be referenced.
template
Intrinsic Fn
The term "Intrinsic Fn" refers to the intrinsic functions in AWS CloudFormation. Intrinsic functions are built-in functions that allow you to perform various operations within your CloudFormation templates. These functions are used to dynamically define values or conditionally control the resources being created.
There are several intrinsic functions available in CloudFormation, such as `Fn::Ref`, `Fn::Sub`, `Fn::Join`, `Fn::If`, and `Fn::Not`.
- `Fn::Ref` is used to get the value of the specified parameter or resource.
- `Fn::Sub` is used to substitute variables within a string with their corresponding values.
- `Fn::Join` is used to concatenate multiple values together.
- `Fn::If` is used to conditionally create resources or specify values based on a condition.
- `Fn::Not` is used to negate a condition.
These intrinsic functions can be used to make your CloudFormation templates more dynamic and flexible by allowing you to reference and manipulate values based on different conditions or inputs.
Template Formats
skeleton
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/format-version-structure.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/template-description-structure.html
Outputs
The optional Outputs section declares output values that you can import into other stacks (to create cross-stack references), return in response (to describe stack calls), or view on the AWS CloudFormation console. For example, you can output the S3 bucket name for a stack to make the bucket easier to find.
####### Outputs #########
Outputs:
KMSArn:
Value: !GetAtt KMSKey.Arn
Description: the KMS Key Arn
KMSId:
Value: !Ref KMSKey
Description: the KMS Key ID
CloudFormationBucket:
Value: !Ref CloudFormationBucket
Description: the CloudFormationBucket source bucket
ApplicationBucket:
Condition: HasBackendBucket
Value: !Ref ApplicationBucket
Description: the Application backend source bucket
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/outputs-section-structure.html
Resources
The required Resources section declares the AWS resources that you want to include in the stack, such as an Amazon EC2 instance or an Amazon S3 bucket.
Resources:
# AWS Service Role for AutoScaling, required as a KMS policy principal (ASG needs KMS symmetric
# key access to launch EBS-encrypted-based EC2s.
# NOTE: contrary to the console, the custom suffix cannot be set to NULL in CloudFormation.
AWSServiceRoleForASG:
Type: AWS::IAM::ServiceLinkedRole
Properties:
AWSServiceName: autoscaling.amazonaws.com
CustomSuffix: !Ref ProjectCode
Description: Allows EC2 Auto Scaling to use or manage AWS services and resources on your behalf.
# KMS key with root, lambda, cloud watch events and asg as principals
KMSKey:
Type: AWS::KMS::Key
DeletionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
Description: !Ref KMSDescription
EnableKeyRotation: true
KeyPolicy:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Id: keypolicy
Statement:
- Sid: keyAdmin
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
Fn::Sub: arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:root
Action:
- kms:*
Resource: "*"
- Sid: S3CryptDecrypt
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: s3.amazonaws.com
Action:
- kms:Encrypt
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:ReEncrypt*
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
Resource: "*"
- Sid: LambdaCryptDecrypt
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: lambda.amazonaws.com
Action:
- kms:Encrypt
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:ReEncrypt*
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
- kms:DescribeKey
Resource: "*"
- Sid: EventsCryptDecrypt
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: events.amazonaws.com
Action:
- kms:Encrypt
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:ReEncrypt*
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
- kms:DescribeKey
Resource: "*"
- Sid: ASGCryptDecrypt
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
Fn::Sub:
- arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/aws-service-role/autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForAutoScaling_${ProjectCode}
- ProjectCode: !Ref ProjectCode
Action:
- kms:Encrypt
- kms:Decrypt
- kms:ReEncrypt*
- kms:GenerateDataKey*
- kms:DescribeKey
Resource: "*"
- Sid: ASG Allow attachment of persistent resources
Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS:
Fn::Sub:
- arn:aws:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/aws-service-role/autoscaling.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForAutoScaling_${ProjectCode}
- ProjectCode: !Ref ProjectCode
Action:
- kms:CreateGrant
Resource: "*"
Condition:
Bool:
kms:GrantIsForAWSResource : true
Tags:
- Key: "Origin"
Value: !Sub Stack_${AWS::StackName}
- Key: "<Cie>:billing"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "<Cie>:environment"
Value: !Ref Environment
- Key: "<Cie>:application_code"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "app:project"
Value: !Ref ProjectName
DependsOn: AWSServiceRoleForASG
KMSAlias:
Type: AWS::KMS::Alias
Properties:
AliasName: !Sub alias/kms-key-${ProjectCode}-${Environment}-${AWS::Region}
TargetKeyId:
Ref: KMSKey
# bucket for ProjectCloudFormation files and sources
CloudFormationBucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
AccessControl: Private
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration:
BlockPublicAcls: true
BlockPublicPolicy: true
IgnorePublicAcls: true
RestrictPublicBuckets: true
# SCO add -${AWS::Region} to the bucket name
BucketName: !Join ["-", ["s3", !Ref ProjectCode, !Ref ProjectName, !Ref Environment, !Ref S3BucketIdentifier, !Ref 'AWS::Region']]
BucketEncryption:
ServerSideEncryptionConfiguration:
- ServerSideEncryptionByDefault:
#SSEAlgorithm: AES256
KMSMasterKeyID: !Ref KMSKey
SSEAlgorithm: aws:kms
Tags:
- Key: "Origin"
Value: !Sub Stack_${AWS::StackName}
- Key: "<Cie>:billing"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "<Cie>:environment"
Value: !Ref Environment
- Key: "<Cie>:application_code"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "app:project"
Value: !Ref ProjectName
DeletionPolicy: Delete
# bucket for Project application sources
ApplicationBucket:
Condition: HasBackendBucket
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
AccessControl: Private
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration:
BlockPublicAcls: true
BlockPublicPolicy: true
IgnorePublicAcls: true
RestrictPublicBuckets: true
# SCO add -${AWS::Region} to the bucket name
BucketName: !Join ["-", ["s3", !Ref ProjectCode, !Ref ProjectName, !Ref Environment, !Ref S3BucketIdentifier, 'application', !Ref 'AWS::Region']]
BucketEncryption:
ServerSideEncryptionConfiguration:
- ServerSideEncryptionByDefault:
#SSEAlgorithm: AES256
KMSMasterKeyID: !Ref KMSKey
SSEAlgorithm: aws:kms
Tags:
- Key: "Origin"
Value: !Sub Stack_${AWS::StackName}
- Key: "<Cie>:billing"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "<Cie>:environment"
Value: !Ref Environment
- Key: "<Cie>:application_code"
Value: !Ref ProjectCode
- Key: "app:project"
Value: !Ref ProjectName
DeletionPolicy: Delete
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/resources-section-structure.html
Rules
The optional Rules section validates a parameter or a combination of parameters passed to a template during a stack creation or stack update. To use template rules, explicitly declare Rules in your template followed by an assertion. Use the rules section to validate parameter values before creating or updating resources.
Each template rule consists of two properties:
- Rule condition (optional) – determines when a rule takes effect.
- Assertions (required) – describes what values users can specify for a particular parameter.
Rule-specific intrinsic functions
To define a rule condition and assertions, use rule-specific intrinsic functions, which are functions that can only be used in the Rules section of a template. You can nest functions, but the final result of a rule condition or assertion must be either true or false.
You can use the following rule-specific intrinsic functions to define rule conditions and assertions:
Examples
Conditionally verify a parameter value
In the following example, the two rules check the value of the InstanceType parameter. Depending on the value of the environment parameter (test or prod), the user must specify a1.medium or a1.large for the InstanceType parameter. The InstanceType and Environment parameters must be declared in the Parameters section of the same template.
Rules:
testInstanceType:
RuleCondition: !Equals
- !Ref Environment
- test
Assertions:
- Assert:
'Fn::Contains':
- - a1.medium
- !Ref InstanceType
AssertDescription: 'For a test environment, the instance type must be a1.medium'
prodInstanceType:
RuleCondition: !Equals
- !Ref Environment
- prod
Assertions:
- Assert:
'Fn::Contains':
- - a1.large
- !Ref InstanceType
AssertDescription: 'For a production environment, the instance type must be a1.large'
Transform
optionnel et spécifique, permet d'utiliser des macros dans l'IaC:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/template-macros.html
permet aussi d'appeler des macros définies par AWS : https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/transform-reference.html
Conditions
permet de définir une action à partir de critéres, ex:
Conditions:
CreateProdResources: !Equals
- !Ref EnvType
- prod
...
MountPoint:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::VolumeAttachment'
Condition: CreateProdResources
Properties:
InstanceId: !Ref EC2Instance
VolumeId: !Ref NewVolume
Device: /dev/sdh
NewVolume:
Type: 'AWS::EC2::Volume'
Condition: CreateProdResources
Properties:
Size: 100
AvailabilityZone: !GetAtt
- EC2Instance
- AvailabilityZone
fonctions possibles:
Condition intrinsic functions
You can use the following intrinsic functions to define conditions:
For the syntax and information about each function, see Condition functions.
Mappings
similaire au dico de python, ex:
YAML
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Mappings:
RegionMap:
us-east-1:
HVM64: ami-0ff8a91507f77f867
HVMG2: ami-0a584ac55a7631c0c
us-west-1:
HVM64: ami-0bdb828fd58c52235
HVMG2: ami-066ee5fd4a9ef77f1
eu-west-1:
HVM64: ami-047bb4163c506cd98
HVMG2: ami-0a7c483d527806435
ap-northeast-1:
HVM64: ami-06cd52961ce9f0d85
HVMG2: ami-053cdd503598e4a9d
ap-southeast-1:
HVM64: ami-08569b978cc4dfa10
HVMG2: ami-0be9df32ae9f92309
Resources:
myEC2Instance:
Type: "AWS::EC2::Instance"
Properties:
ImageId: !FindInMap [RegionMap, !Ref "AWS::Region", HVM64]
InstanceType: m1.small
Parameters
Use the optional Parameters section to customize your templates. Parameters enable you to input custom values to your template each time you create or update a stack.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/parameters-section-structure.html
####### Parameters #########
Parameters:
KMSDescription:
Description: The Description of the KMS
Type: String
Default: KMS symetric Key used for EBS, RDS and S3 encryption
S3BucketIdentifier:
Description: Lowercase Name to identify your bucket for infrasctructure code
Type: String
Default: infra
ProjectCode:
Description: Lower case Project Aspire Code
Type: String
ProjectName:
Description: A Lowercase friendly name of the service (i.e OneSearch)
Type: String
Environment:
Description: Solution Environment
Type: String
Default: prod
AllowedValues:
- dev
- int
- val
- prod
- prod2
BackendBucket:
Description: To use a backend s3 bucket to store application file
Type: String
AllowedValues:
- enable
- disable
Default: disable
Metadata
AWS::CloudFormation::Interface is a metadata key that defines how parameters are grouped and sorted in the AWS CloudFormation console. When you create or update stacks in the console, the console lists input parameters in alphabetical order by their logical IDs. By using this key, you can define your own parameter grouping and ordering so that users can efficiently specify parameter values. For example, you could group all EC2-related parameters in one group and all VPC-related parameters in another group.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-resource-cloudformation-interface.html
####### Metadata #########
Metadata:
AWS::CloudFormation::Interface:
ParameterGroups:
-
Label:
default: "KMS Key Information"
Parameters:
- KMSDescription
-
Label:
default: "Project Information"
Parameters:
- S3BucketIdentifier
- ProjectCode
- ProjectName
- Environment
Conditions:
HasBackendBucket: !Equals [!Ref BackendBucket, 'enable']
AWS Example (snippets)
This section provides a number of example scenarios that you can use to understand how to declare various AWS CloudFormation template parts. You can also use the snippets as a starting point for sections of your custom templates.
Topics
Threats
Users may rely too heavily on the provided code snippets without fully understanding the underlying concepts or best practices
Code snippets may become outdated over time as AWS services and CloudFormation features evolve
Other resources or websites may offer more comprehensive and up-to-date examples of CloudFormation templates
Opportunities
Can incorporate user feedback and suggestions to improve the quality and usefulness of the examples
Could provide more detailed explanations or documentation for each code snippet
Can be expanded to include more code snippets for a wider range of AWS services and resources
Weaknesses
Lack of detailed explanations or documentation for the code snippets
Code snippets may not cover all use cases or configurations
May not provide a comprehensive overview of all possible CloudFormation features and services
Strengths
Helps users understand the syntax and structure of CloudFormation templates
Gives examples of how to use AWS services in CloudFormation
Provides code snippets for AWS CloudFormation templates