por CARMEN MARTINEZ PADILLA 5 anos atrás
496
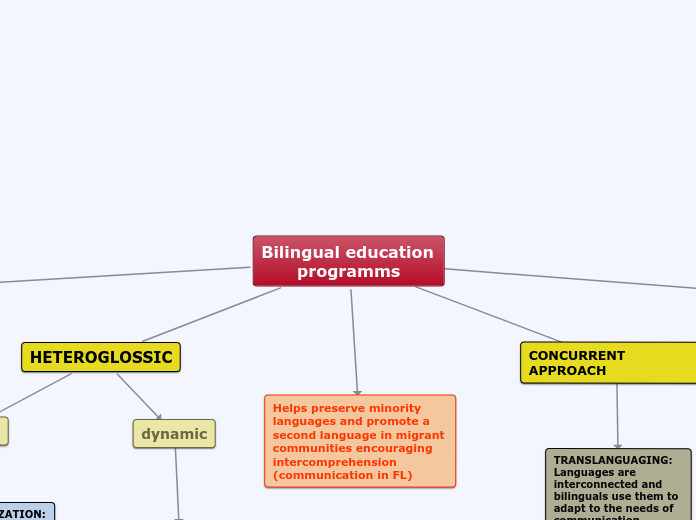
Bilingual education programms
Bilingual education programs play a crucial role in preserving minority languages while promoting second language acquisition, especially within migrant communities. These programs encourage intercomprehension and cognitive engagement through the use of an additional language in non-language subjects, a method often referred to as CLIL.