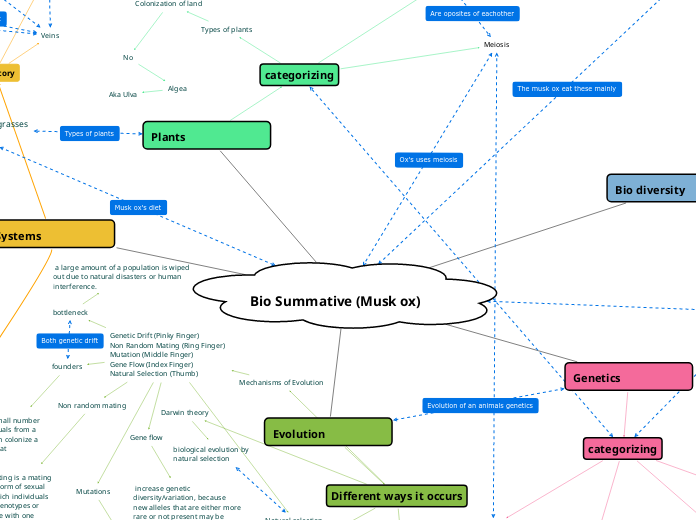
Bio Summative (Musk ox)
Plants
Types of plants
Colonization of land
Yes
vascular
Bryophytes
Aka mosses
Is it a seed plant
Pteridophytes
Aka ferns
Is it flowering
yes
Angiosperm
Aka flowering plant
Gymnosperm
Aka conifers
No
Algea
Aka Ulva
meitosis
Genetics
Chromosomes
X and Y
Non disjunction
Examples: Down's syndrome, Edwards syndrome,Patau syndrome , Etc
failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I, failure of sister chromatids to separate during meiosis II, and failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis.
categorizing
Mitosis vs meiosis
Meiosis
New cells are gametes
New cells are haploid
4 new cells
8 phases
Crossing over occurs
Mitosis
Makes diploid cells
new cells are somatic daughters
2 cells created
4 phases
Blood type
AA, Aa, BB, Bb AB, O
Traits
Recessive
Dominant
Bio diversity
categorizing + Taxonomy
life, domain, kingdom, phylum, clss, order, family, genus, species
Domains
Eukaryote
Kingdoms
Protists
Plantae
Fungi
Animalia
Phylums
Chordate
Prokaryote
Kindoms
Bacteria
Archea
Evolution
Different ways it occurs
Evedince
Embryology
focuses on early stages of cell development
Comparative anatomy
wings and fins have a very similar bone structures to hands and arms because of comparative anatomy
DNA
comparing the DNA of 2 animals
Biogeography
patterns of geographic distribution of organisms and the factors that determine those pattern
Artificial selection
Seen in someting like dogs and cats, this is a proccess of someone or something making two animals mate.
Fossils
Bones of dead animals
Gene pools
All alleles for a particular gene/trait within a population.
Alleles are one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome.
Darwin theory
biological evolution by natural selection
Mechanisms of Evolution
Genetic Drift (Pinky Finger)
Non Random Mating (Ring Finger)
Mutation (Middle Finger)
Gene Flow (Index Finger)
Natural Selection (Thumb)
Natural selection
Gene flow
increase genetic diversity/variation, because new alleles that are either more rare or not present may be introduced into the population.
Mutations
it generates the genetic variation on which the evolutionary process depends.
Non random mating
Assortative mating is a mating pattern and a form of sexual selection in which individuals with similar phenotypes or genotypes mate with one another more frequently than would be expected under a random mating pattern.
founders
when a small number of individuals from a population colonize a new habitat
bottleneck
a large amount of a population is wiped out due to natural disasters or human interference.
Systems
Respatory
Pharynx
Larynx
Diaphragm
Trachea
Alveoli
Diseases
asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, sleep apnea and occupational lung diseases
Bronchioles
Bronchi
Epiglottis
Nose
lungs
Digestive
Accessory Organs
Liver
filters all of the blood in the body and breaks down poisonous substances,
Pancrease
produces enzymes that help to digest food, particularly protein. The endocrine pancreas makes the hormone insulin, which helps to control blood sugar levels.
Gall bladder
Stores Bile that was produced by liver
Salivary glands
Makes saliva to break down food
GI track
Esophagus
Transports food from the mouth to the stomach
using a process called peristalsis to move food
Stomach
Both mechanical and chemical digestion occur
Large intestine
Contains bacteria that help to break down waste
Small intestine
Digests food and absorbs nutrients into the blood stream via diffusion
Sections
Jejunum (second section)
Ileum (third/final section)
Duodenum (first section)
Mouth
physically breaks down food
Eats plants such as mosses, grasses sedges, forbs etc
Ciculatory
Heart
parts of heart
Aorta
pulmonary
2 pulmonary arteries
2 pulmonary vens
valves
Atrioventricular Valves
Semilunar Valve
ventricles
septum
atriums
Vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Superior vena cava
Veins
Arteries
Blood
Plasma
Carries a number of dissolved ions such as Na+,
K+, and Ca2+
Protein-rich liquid in which blood cells are
suspended
Platelet
When a blood vessel is broken, platelets will
stick together to seal the hole so the vessel can
rebuild
A cell fragment that helps the blot clot, seal
wounds and stop bleeding
White blood cells
Fight disease-causing bacteria and viruses
Red blood cells
contain proteins called hemoglobin that allow
them to pick up oxygen and carbon dioxide