por Austin Evans 2 meses atrás
25
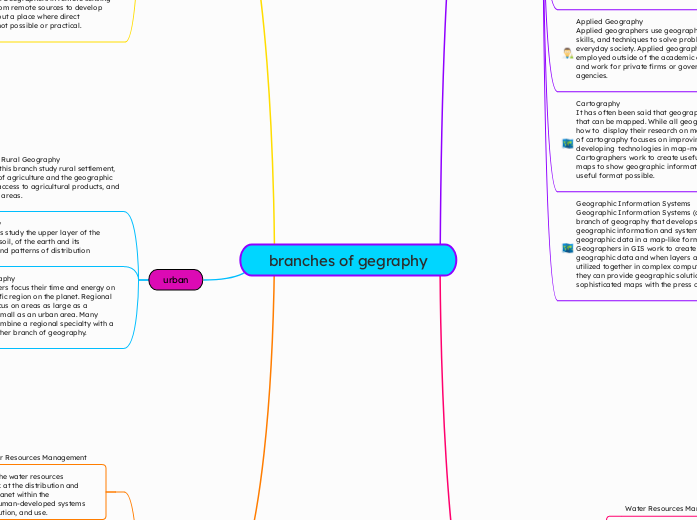
branches of gegraphy
Geography encompasses various specialized branches, each focusing on different aspects of the Earth's features and human interaction with them. Urban geography investigates the development and functioning of cities and towns.