Gene Duplication
Paralogs
Two copies of a gene
Selection
Orthologs
Neofunctionalization
Non functional mutation
Drift
Pseudogenes
Tandem Repeats
rrna or histone genes
Gene Clusters
alpha hemoglobin and myglobin genes
fetal hemoglobin
monotremes
Hagfish
Unequal crossing over
Organic MOlecule
Nucleotide Bases
RNA replicate
Acquires a memberane
forms peptides eventually proteins
Co Evolution
Species Interactions
No Covoluiton
Competition why? --
Ammensilism -0
Commensalism +0
Effects Coevolution
Consumer Resource +-
Cyclic Coevolution Arms Race
Viruses
Rabbits and myxoma virus
Avirulent
Mode of transmission Vertical Transmission
Low transmibility
Virulent
High Transmisiblity
Plants and Parasites
Secondary Compounds
Plants and Beetles
Puffins Lice
Mutualsim ++
Ants and Acacia
Coevolution
Cospeciation
Molecular clock??
Synonymous Substitutions
Birds, Lice, and bacteria
Farenholz Rule
Coadaption
Comparitive method
Post evolutionary
Discrete
Concentrated Changes Test
Extinct Species
Environmental Correlation
Genetic Correlation
Continous
Discrete Environments
Pair Wise???
Regression why????
Contrast Regresson
Polytomies
Resolve and see if there's still a relationship
Sunflower
Pre-evolutionary
Adaptation
Process
Trait
Molecular Method
Positional Homology
Out group compariosn
DNA/RNA sequences
Stem Loop structures
Morphological Charecter
Floating topic
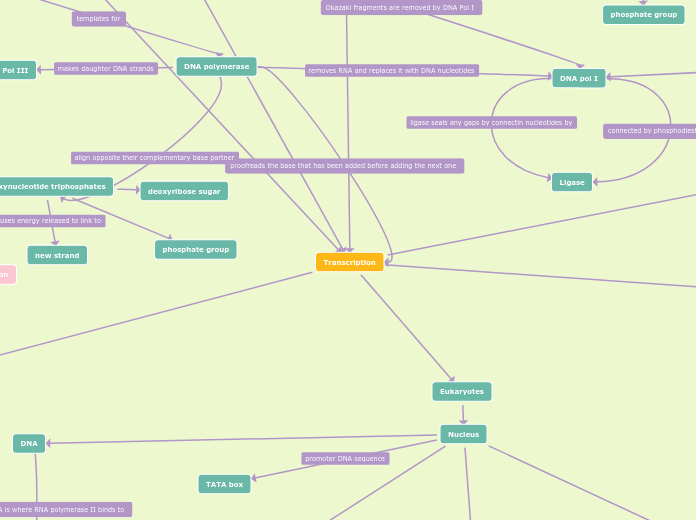
DNA
Promoter sequence
Active Cap
camp
Operator Sequence
Repressor
Allolactose
Transcription Factors
General
Specific
Repressors
Activators
Chromatin 10 nm
30nm and 300 nm
300 nm Metaphase Chromosome
TRANSCRIPTION
promoter binds to 3'-5' template
Elongation
mRNA made to 5'-3' direction
Termination
mRNA synthesis stops at
the terminator sequence
occurs in Nucleus
needs to be modified before
it can be translated
RNA Processing
addition Poly AAA tail
splicing
addition 5' G-CAP
occurs in Cytoplasm
mRNA that is ready
for TRANSLATION
make mRNA
DNA REPLICATION
Semi Conservative
ORI Origin of Replication
separates two strands of DNA
keeps strands separated
primer binding
Elongation
TRANSLATION
starts in Cytoplasm
START only
always in Cytoplasm START+Complete
Ribosomes
Bound Ribosomes
Free Ribosomes
ER
Golgi
Lysosomes, Cell membrane, and Outside the Cell
RNA is used to produce proteins
Polypeptide
Termination
peptide bonds
initiation
elongation
large ribosome
A-Amino Acyl Transferase
adds Codon
continuous Codon cycle added
E-Exit
release Codon
P-peptidyl transferase
5-AUG-3'
small ribosomes
double helix and double stranded
anti-parallel strands
complimentary base pairings
1.holds genetic material 2. provides directions for its own replication 3. directs synthesis RNA(mRNA)
activated through Dimerization
GTP/ATP binds to G-protein receptor> release GDP
binds to enzyme, uses a phosphate from GTP(ATP) to produce cAMP
cAMP
2nd signal molecule messenger
1st protein kinase activated
Subtopic
Protein Kinase 3,4,5
extracellular signals
intracellular signals
the signal to Nuceus
patterns of protein transciptions
mediating cell to cell communication
Cell Growth
metabolism
Cell Signaling
Signaling Molecules
Membrane
Response
Transduction
h
Reception
Proteins
Receptors
Intracellular Receptors
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Membrane Receptors
Ion channel
Signal molecule binds to the receptor
Gate allows specific ions (Na+ and Ca+) through a channel in the receptor
Voltage across the membrane is changed
Action potential is triggered
Tyrosine Kinase /RTK
GCPR
Signal mlcl binds to receptor
Which swaps out GDP for GTP
G-protien
Adenyl Cyclase (enzyme)
Cyclic AMP
AMP
Protein Kinase Cascade
Activates a Cellular Response
Long Distance
Hormonal Signaling
Local Signaling
Paracrine Signaling
Synaptic Signaling
Phosphatase deactivates the protein Kinase by removing a phosphate group.
Molecules tend to be large and polar so they can't pass through.
The whole process from after reception to before the cellular response is transduction.
Early life
Panspermia Hypothesis
Life easy to form when
conditions are right
RNA world
LUCA
Stromatalites
LECA
Precambrian
Photosynthesis
Oxygen Produced
First Eukaryotes
Mitochondria from purple line and chloroplast form cyanobacteria
Decrease green house
Creation of ozone layer
Death of anaerobes
A lot of U not a lot of T
Ribozymes
Explosion leading to earth
Meteor strikes
Atmosphere recreated and moom created
Life creaed
The upper bound stops when a virus kills a host before it can switch. Only exception is quiescent state.
Histone core: H1, H2A, H2B,H3, H4. 300 nm Looped domains
Transmisibility
Virulences
Anthrax the example
Trasnmission
ants provid protection
acacia provides food and shelter
These molecules tend to be small and non polar which allows it to go straight through the membrane.
One Parent and Daughter Strand in each copy (Messleson & Stahl)
Complimentary base pairs bonded with hydrogen bonds while base nucleotides bound by phosphodiester bonds
parasites and hosts
should speciate at the
same time
Occurs in the nucleus in Eukaryotic cells & nucleoid region in Prokaryotic cells. Process by which DNA copies itself. (Hershey & Chase)
SRP binds to the signal peptide which stops transcription and allows ribosome to bind to the ER to finish making the protien. Protiens are modified in the ER to determine location
reducing atmosphere
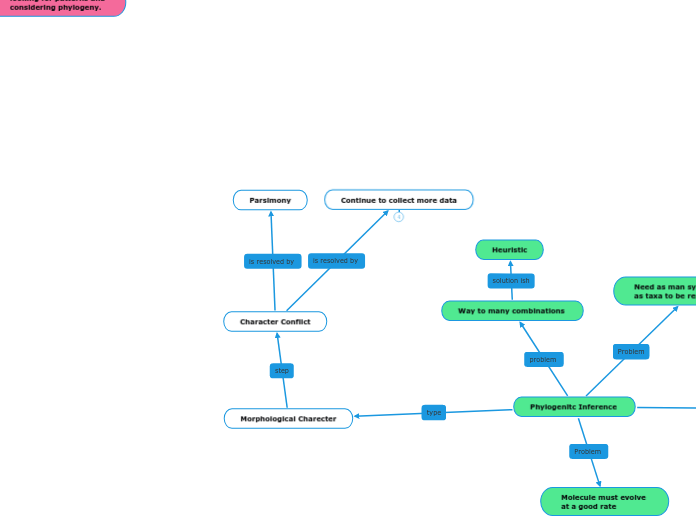
looking for patterns and
considering phylogeny.
Phylogenitc Inference
Molecule must evolve
at a good rate
Need as man synapomorphies
as taxa to be resolved
Way to many combinations
Heuristic
Trasmissibility how easily disease moves transmission how the disease moves
Because we can't determine
homologies/analogies
looking for patterns
Can provide us medicines
C-value paradox
Noncoding proteins
Wrong
Introns and Transposons (MGE)
Slected Against
RNAI
Methlyation
Placental Mammals
Increase levels of gestation
Parasites
Junky Genomes
Bigger genomes escape selection
Bigger genomes are more adaptive
no multicellular
Isn't really a problem won't
be harmful ?????????
Distal Control Element(bind near gene) Activators bring high levels Repressors bring low basal level. Binds to Enhancers
asteroid chemicals helped form life
Protiens made here can end up in any organelle
Proximal Element brings Basal level transcription
Character Conflict
Continue to collect more data
Root the Tree
Embryologonical Criterion
Paleontological Criterion
1. Out group comparison
Parsimony