Cuadro Sinoptico Viviana Bravo GRUPO 152001_19
To name your story, you have to think about the overall message and what you want your audience to understand from the story. Also, make it relevant and easy to remember.
Responsabilidades y obligaciones
Farmacias privadas
10.Informar a la Autoridad Sanitaria competente la ausencia por más de 15 días a través de una nota, indicando el nombre del farmacéutico que lo sustituirá y el período que estará ausente, firmada y sellada por ambos; la cual debe ser presentada con anticipación de su ausencia.
Presentar al término del contrato de regencia, el libro de control de Estupefacientes y Psicotrópicos a la Unidad respectiva, entregando las recetas retenidas hasta la fecha en que se renuncia, verificando la entrega del inventario físico de las existencias al propietario del establecimiento y a la Autoridad competente.
9. Informar a la Autoridad Sanitaria y al propietario del establecimiento con un mes de anticipación la renuncia de la regencia.
8. Vigilar y supervisar que el funcionamiento y las actividades de la farmacia se desarrollen dentro del marco legal vigente.
7. Dar a conocer al personal auxiliar de las farmacias los lineamientos necesarios para el despacho y almacenamiento adecuado de los medicamentos.
6. Preparar fórmulas magistrales y oficinales en áreas y condiciones apropiadas.
5. Supervisar y mantener actualizados los controles y registros de los Estupefacientes, Psicotrópicos, precursores, sustancias y productos químicos y agregados de acuerdo al listado vigente, cuando sea requerido.
4. Supervisar que se cumplan las Buenas Prácticas de Almacenamiento de los medicamentos para asegurar su Calidad.
3. Indicar y advertir por escrito al propietario que no deben expender medicamentos sin registro sanitario, vencidos, alterados, falsificados, muestras médicas, donativos o de propiedad del Instituto Salvadoreño del Seguro Social (ISSS), Ministerio de Salud, MINSAL u otra institución pública o privada.
2. Supervisar el retiro de los medicamentos vencidos a un área separada a la del despacho la sala de venta
1. Supervisar que los medicamentos a comercializar cumplan con el Reglamento de etiquetado vigente de los productos farmacéuticos de uso humano en el país.
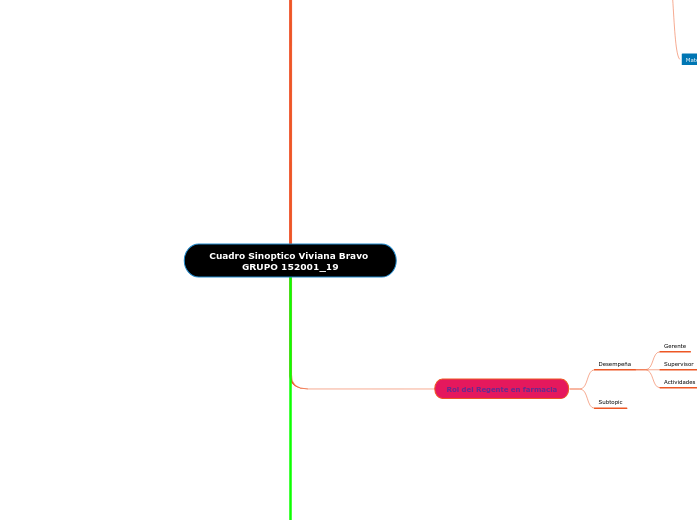
Rol del Regente en farmacia
The ending of a story is essential. We all know that if the ending is weak, what happened before loses its importance. So make it unpredictable, but fair. A resolved ending answers all the questions and ties up any loose threads from the plot.
Subtopic
Desempeña
This is the closure section of the story.
See examples of possible outcomes below:
- all problems have been solved
- it's clear how each one of your characters ends up
- your main character is transformed by the challenge
Actividades de control de calidad
Try answering these questions in order for you to come up with a closure:
- Have all problems been solved?
- Is it clear what happens with all your characters in the story?
- Has the challenged transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Vigilancia
Dispensación de la misma
Supervisor
En la realización
Formulas magistrales no estériles
Uso topico
Gerente
Try answering these questions to come up with a closure:
- Have all the problems been solved?
- Is there a clear picture of what happens with each character in the story?
- Has the challenge transformed your main character?
- How do the characters feel in the end?
Material y equipos usados en las preparaciones
The middle of the story is where you add layers of complications that will lead to the end. Reveal more about the character's journey. Did their personality go through changes? How did they overcome the challenges? And as you build up the story’s central conflict, make it more personal to that character. Also, from the middle act, you have to lead into the final act.
Material general
There wouldn't be any tension and excitement in your story if there weren't any obstacles in your character's way.
Alcoholímetro
Indica de forma cuantitativa la riqueza en alcohol de un líquido o disolución.
Termómetro
Mide la temperatura
Ph metro
Mide la concentración de hidrogeniones de una solución.
Vaso de precipitados
Se prepara disoluciones, contiene productos líquidos.
Vidrio reloj
Se pesa solidos
Espátula
Sirve para separar y recoger sustancias.
Embudos
Se utiliza para liquidos y polvos
Erlenmeyer
Sirve para contener líquidos y calentarlos.
Pipeteo y varilla
Agitar y revolver mezclas
Baño termostático
Calienta el agua a temperatura prefijada
Morteros
Porcelana
...................................
Sirve para pulverizar, realizar mezclas homogéneas y amasar.
Vidrio
Balanzas de precisión
Sirve para hallar la masa
Material para medir volumenes
Each story has a main character and that character usually needs to solve a problem or challenge. The character's challenge is the one that creates tension throughout the story.
Entre 1 L
................................................
Type in any other challenges which other characters in the story need to face.
Pipetas graduadas
Transvasar volúmenes exactos de un recipiente a otro.
Matraz aforado
Preparar disoluciones de concentración perfectamente.
Buretras de 25, 50 100 ml
Se utiliza para medir volumetrias
Pipeta automatica
Probetas
Medir volúmenes con un grado de aproximación bastante alto al exacto.
Entre 0.5 ml
In most stories, there are 3 challenges. The number 3 is a mystical number symbolizing completeness. Try to come up with interesting challenges with which your character needs to struggle.
See a few examples below:
- turns into a werewolf at night
- is sent back in time
Operaciones fisicoquímicas usuales en la preparación de medicamentos magistrales no estériles.
In the beginning of the story (or the exposition), you will need to introduce the setting and characters. You might also want to introduce the main conflict. This part of the story is important because it gives the reader necessary background information and maybe even a first insight into a character’s personality.
MEZCLAS
Characters are essential to a good story. Usually, the protagonist(s) is/are the most affected by the plot. Introduce a character by focusing on their actions, interests, and occupation, as the physical appearance doesn't make a difference in most cases.
Combinaciones físicas de las sustancias
Type in the name of your character.
Clases de mezclas
Which traits best describe the character's personality? Choose more if necessary:
introvertedloyalkindindependentquick-thinkingadventuresomeidealisticsweet-naturedcalmrisk-takercreativewittystrictfussyweirdclumsyharshaggressivecarelessclingingcowardlycrueldeceitfulimpulsiveOther
Operaciones basicas
División de solidos
Adición de excipientes
Homogenización
Liquido
Liquido inmiscible
Dispersión heterogénea
Liquido miscible
Disolución homogénea
Solido
Distribución Homogénea
......................................................................
mezcla -
Los componentes tienden a separarse
Rápidamente
mezcla +
Forma espontaneas e irreversible
Mezcla perfecta
Mezclas neutras
No se mezcla espontáneamente y no tiende a separarse.
máxima interposición entre varios componentes
SEPARACIONES
The setting (time & place) of a story can change throughout the plot.
Diferenciar los componentes de una mezcla heterogénea sin alterar el estado de la materia.
Your story can take place wherever your imagination will take you to.
For example: in an elevator, in an enchanted forest, etc. Don't forget to give details of the environment each time the setting changes, otherwise, the story can be confusing. Also, mention the seasons as each of them has unique weather and events.
Disfuncionales
diferenciar de uno o mas componentes de mezcla homogénea ,que modifican el estado físico.
Otras
Granulación
Electroforesis
Sedimentación
Esterilización
Liofilización
Pulverización
Evaporación
Separación un solido de un liquido.
Extracción
Separación de principios activos
Vegetal
Animal
Desecación
Separación total de un liquido contenido en un solido.
Separaciones mecánicas
Decantación
Separación de un solido mezclado heterogéneamente con líquidos en donde es insoluble
Centrifugación
Separación de mezclas
Solidos y líquidos de distinta densidad
Tamización
Separaciones de mezcla pulverulenta en distintas fracciones
Tamizar
Filtración
Separación de un solido que esta disperso en un fluido
Membrana porosa
DISOLUCIONES
Mezclas homogéneas de uno o mas solutos
CONCENTRACION
%v/v, %m/m, %p/v, molaridad, molalidad
Molalidad
Cantidad de masa de soluto con la medida de volumen de una disolución acuosa
M= moles de soluto / 1l de disolución
Molaridad
Cantidad de masa de soluto disuelto en un disolvente
Kg
m=moles de soluto/1kg de disolvente
Unidades concentración
% de masa / volumen %m/v
% de masa/ masa %m/m
% de v/v (%v/v)
Diluido concentrado
Saturada-Insaturada
Diluida insaturada
La cantidad de soluto es mínima al disolvente
Disolución saturada
Soluto y solvente son equilibrados
Disolución sobresaturada
La cantidad del soluto es > que la del solvente
Concentración
Características de una disolución donde muestra la proporción entre un soluto y un disolvente
Disolución concentrada
considerable al disolvente
Dilución
Disminución de concentración de una solución madre
TIPOS
LIQUIDO
Liquido -Solido
Agua + Azucar
Liquido- Gas
Bebidas carbonatadas
Liquido-liquido
Alcohol + Agua
GASEOSO
Gas en solido
Gas - solido
Naftalina
Gas -Gas
Butano
SOLIDO
Gas en solido
Solido-solido
Combinaciones entre dos o mas elementos químicos
Liquido a solido
Mercurio liquido con plata
Odontología, Amalgamas
COMPONENTES
DISOLVENTE
Mayor cantidad
Forma una solución química
SOLUTO
Conocido como solución
Se encuentra en menor cantidad
Solubilidad
Es la cantidad máxima del soluto
Es una propiedad que depende del tipo del soluto, del disolvente y las condiciones ambientales.