Psychedelics
Many Psychedelic drugs have been deemed illegal under the UN Convention on Psychotropic substances in 1971.
Injection, oral, inhalation, sublingual (chewing), and Transcutaneous (contact with skin).
Psychedelics are hallucinogenic drugs, the primary function of hallucinogenic drugs are to alter moor, perception, and to alter the state of consciousness.
LSD, Ketamine, Bath salts, Ect.
Abuse of Hallucinogenics can leave the body to be unable to produce the right amount of serotonin.
Speech problem, memory loss, visual disturbances, mental problem, flashback, bladder ulcers, kidney problems, and other mental problems.
Hallucinations, dry mouth, anxiety, paranoia, intense feelings and sensory feedback, fluctuation in heart rate, and distorted sense of time.
Effects brain functionality by prematurely flooding the brain with serotonin. The serotonin neurotransmitter is responsible for mood regulation, sensory perception, sleep cycles, hunger, body temp, sex drive and muscle control.
Psychedelics are made up from certain plants and chemicals, these plants and chemical compounds disrupt communication between chemical systems and the brain.
Hallucinogen
Heroin
Illegal under the 1970 Controlled substances act.
Injected, smoked, snorted
Users use heroin in multiple ways such as by injection, snorting, sniffing or by smoking, some may mix heroin with other drugs such as cocaine. This practice is known as speedballing.
White powder heroin, brown powder, and black tar
Potentiality of contracting HIV, hepatitis C, and other bacterial infections of the skin, heart, and bloodstream. Liver and kidney damage, addiction overdose, and death.
symptoms
Restlessness, severe muscle and bone pain, sleep problem, cold flashes, severe heroine craving, uncontrollable leg movement, and diarrhea and vomiting.
Long Term
Collapsed veins from injection, damaged tissue in the nose from snorting, infection of heart lining and valves, liver and kidney disease, and mental disorders
Short Term
Dry mouth, warm flushed skin, heaving felling of arms and legs, nausea, severe itching of skin, clouded mental consciousness, Going back and fourth between the state of consciousness, and semiconscious.
Heroin enters the brain rapidly, and binds to opioid receptors in areas that are focused on feeling pain and pleasure. This controls the users heart rate, sleeping, and breathing.
Opioid
Alprazolam:
(Xanax)
Available by prescription only in the USA.
Oral consumption of pill
Therapeutic Use
relief of anxiety, relief of panic attacks/panic disorder, relief of anxiety associated with depression
Prescription drug in pill form.
Dependence of the drug, Depression, suicidal tendencies. Long term memory loss, and emotional changes.
seizures, delusion, withdrawal symptoms, drowsiness, vertigo, weakness, dizziness, ataxia, fatigue, constipation, Cardiovascular collapse.
In the brain it cause the GABA Neurotransmitter to be released. The transmitter acts as a release to calm nerves.
Meth
The street drug meth was made illegal in 1970 in the USA.
But there are controlled prescription sales of pharmaceutical drugs that contain ephedrine and pseudoephedrine.
Meth is smoked, injected,
snorted, or taken in pill form.
Is used to give a sense of a eutrophic high, it is used by smoking, snorting, or by injection. Most common is smoked.
Common forms
Powdered meth, crystalized meth, tablets, liquid meth.
Meth causes mass physical change. It changes ones physical appearance, Due to skin rashes, meth mouth, loss of hair. It effects internal organs causing stroke, heart attack, and death.
Increased heart rate and blood pressure, damaged blood vessels, leads to heart attacks and strokes, liver/kidney/ lung damage, and memory loss due to brain damage.
Can make user feel a sense of euphoria, when the drug wears off there is a crass, leads to more use, weight loss, nausea, increased irritability, hallucinations, anxiety, and paranoia.
Meth produces an excessive release of dopamine.
Causes euphoric feeling, followed by a crash, and a need for greater drug use. Damages nerve terminals in the regions of the brain that contain dopamine and serotonin.
Tobacco
12 states have raised the legal age to 21 to purchase tobacco.
The other 38 states have 18 years old as the legal age of purchase.
Smoked tobacco, or smokeless tobacco is placed on the inside of the lip.
How its used
Smoked, sniffed or chewed, giving a sense or relaxation from the nicotine.
Smoked tobacco: Cigarettes and cigars.
Smokeless tobacco: Chewing tobacco.
Vaporized tobacco.
Lung, lip, mouth, and throat cancer. Can lead to stroke and heart attacks.
pregnancy issues, such as stillbirth, premature births, children functioning issues.
Lung cancer, heart disease (heart attacks), strokes (caused by blood clots), mouth and throat cancer, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, stomach cancer
Lung damage from tar build up. damage air sacks. Leads to shortness of breath, lung infections. Leads to emphysema.
How it Works
Nicotine stimulates neurotransmitters in brain, leading to more brain activity.
Nicotine is the main chemical in tobacco;
Nicotine is classified as a stimulant.
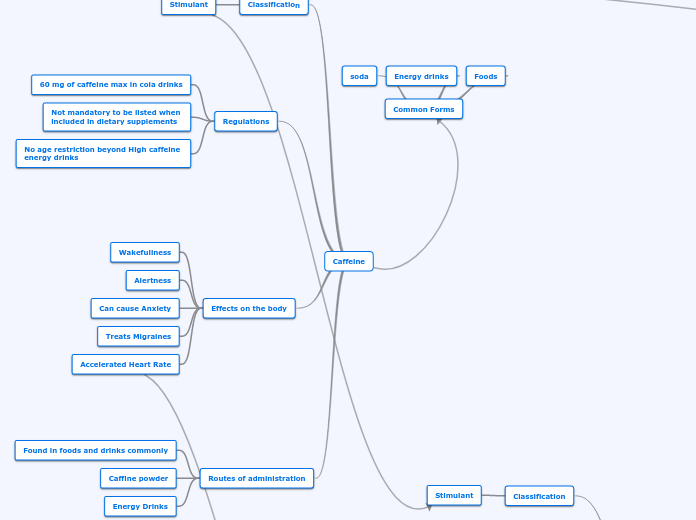
Caffeine
Age regulation in certain states of purchasing energy drinks
Caffeine is used as a quick source of energy. Many people use caffeine to a sense of feeling awake and more alert, but also used as a form of migraine medication.
In specific foods and beverages.
Common forms are coffee, tea, chocolate. But also can be found in pill form.
Physiological concerns
increase incidence of heart attacks, increase risk of coronary artery disease, ulcers, fluctuations in women's hormone levels affects pregnancy
aggravation of anxiety disorders
side effects: nervousness, irritability, insomnia, fatigue
caffeine intoxication
physiological effects
relaxes smooth muscle, especially bronchi
dilates blood vessels in body
constricts blood flow in brain
increase HR and BP
increase gastric acid secretion and GI motility
diuresis
increase metabolism
caffeine is a signal molecule and must bind to a receptor protein associated with the cell.
Caffeine acts in different ways in different tissues because it interacts with different receptors.
Stimulant
Marijuanna
Legal for recreation use in Alaska, Colorado, Oregon, and Washington, as well as in the District of Columbia. Must be 21 years of age to use.
23 states have laws legalizing marijuana in some form.
Routes of Administration
Smoked or consumed.
How it's Used
smoking it as a cigarette, in a pipe or a bong, or eating it in baked goods.
Slang terms of forms: Joint, blunt, edibles, dope.
Leaf form rolled up to smoke, or grinder down to use in a bong, and baked into edibles.
Can also lead to Cancer, lungs & airways, immune system issues.
Affects memory, judgement, decision making and perception; timing, movements & coordination
Effect
Behavioral Effects
-Euphoria
-Relaxation "mellowness"
-Hunger-munchies
-Stimulation
-Mild paranoia
-Hallucinations (high doses)
-Decreased verbal exchange
-Cognitive impairment
Psychological effects
-Increased heart rate--dose dependent effect (different time course of effects depending on how you take drug)
-Red eyes
-Dry mouth
-Bronchiodialation
-Heavy marijuana smoking could lead to pulmonary dysfunction
THC the main chemical in marijuana. THC binds to receptors in the brain "Receptors known as cannabinoid receptors (CBr) or THC receptors.
a depressant and hallucinogen
By Kale Heth
References
National Institute on Drug Abuse. (n.d.). National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Retrieved from https://www.drugabuse.gov/
Nichols, H. (2017, October 16). Caffeine: Benefits, risks, and effects. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/285194.php
Marijuana and Cannabinoids. (2018, October 25). Retrieved from https://nccih.nih.gov/health/marijuana
Smoking: What are the effects? (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.mydr.com.au/addictions/smoking-what-are-the-effects
How Does Alcohol Work? (n.d.). Retrieved from https://alcohol.addictionblog.org/how-does-alcohol-work/
Alcohol's Effects on the Body. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/alcohols-effects-body
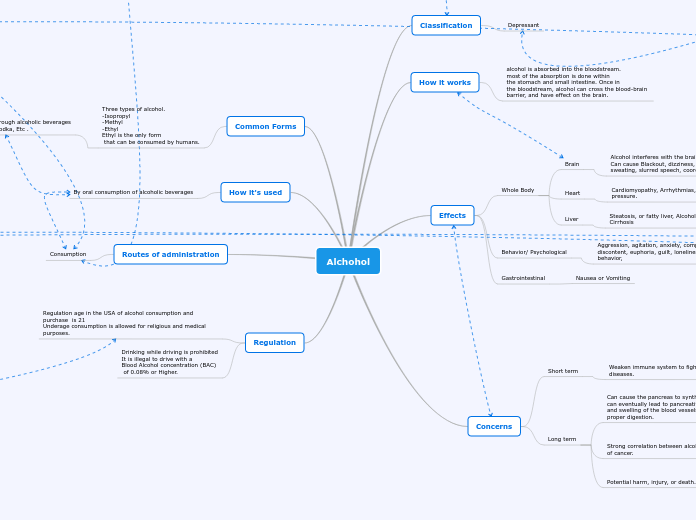
Alchohol
Regulation
Drinking while driving is prohibited
It is illegal to drive with a
Blood Alcohol concentration (BAC)
of 0.08% or Higher.
Regulation age in the USA of alcohol consumption and purchase is 21
Underage consumption is allowed for religious and medical purposes.
Routes of administration
Consumption
How it's used
By oral consumption of alcoholic beverages
Common Forms
Three types of alcohol.
-Isopropyl
-Methyl
-Ethyl
Ethyl is the only form
that can be consumed by humans.
Most common form is through alcoholic beverages
Examples: Beer, Wine, vodka, Etc .
Concerns
Long term
Potential harm, injury, or death.
Strong correlation between alcohol drinking and several types of cancer.
-Head and neck cancer
-Esophageal cancer
-Liver Cancer
-Breast Cancer
-Colorectal Cancer
Can cause the pancreas to synthesize toxic substances that can eventually lead to pancreatitis, a dangerous inflammation and swelling of the blood vessels in the pancreas that prevents proper digestion.
Short term
Weaken immune system to fight off infections, illnesses, and diseases.
Effects
Gastrointestinal
Nausea or Vomiting
Behavior/ Psychological
Aggression, agitation, anxiety, compulsive behavior, discontent, euphoria, guilt, loneliness, or self destructive behavior,
Whole Body
Liver
Steatosis, or fatty liver, Alcoholic hepatitis, Fibrosis, and Cirrhosis
Heart
Cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmias, stroke, and high blood pressure.
Brain
Alcohol interferes with the brain's communication pathways. Can cause Blackout, dizziness, shakiness, craving, or sweating, slurred speech, coordination problems
How it works
alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream.
most of the absorption is done within
the stomach and small intestine. Once in
the bloodstream, alcohol can cross the blood-brain
barrier, and have effect on the brain.
Classification
Depressant