Eastern Approaches to a Unified Reality
Sources
http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/taoism/
Ms. Howlett's Content of U1A5
http://www.religionfacts.com/
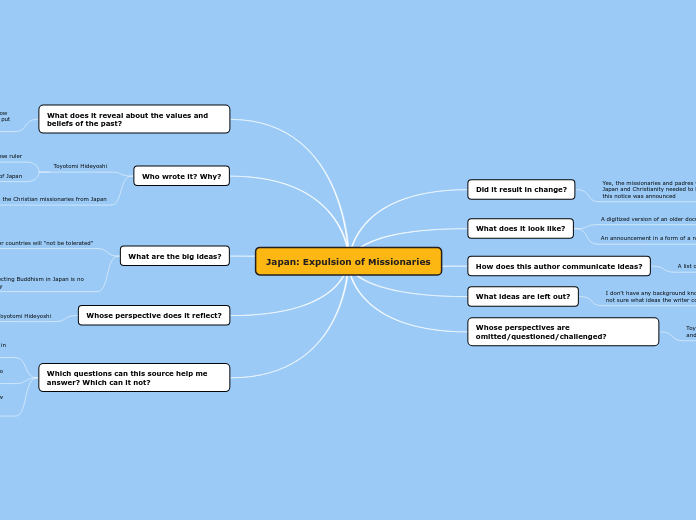
Taoism
Ch'i or Qi
Cosmic Vital Energy
Yin Yang
Complimentary Forces
Wu Wei
Letting the World Take its Natural Course
"When Nothing is Done, Nothing is Left Undone"
- Tao Te Ching
Tzu Jan
"That Which is Naturally So"
Te
Awareness of Tao
Virtue
Wu and Yu
Non-Being and Being
The One
Essence of Tao
Tao
-Source of Creation
-The Ultimate
-Inexpressible and Indefinable
-Unnameable
-Natural Universe as a Whole
-Way of Nature as a Whole
Communist Takeover of China
Religion Banned
142 C.E.
Revelation of the Tao to Zhang Daoling
Popular in Taiwan
Confucianism
Influence
Vietnam
Korea
Japan
Beliefs
Heaven (T'ien)
Optimistic View of Human Nature
"Humans are Teachable, Improvable, and Perfectible Through Personal and Communal Endeavour"
Ren (Humaneness or Benevolence) and De (Virtue)
Xiao (Filial Piety)
Shu (Reciprocity)
Zhong (Loyalty to One's True Nature)
Li (Ritual Norms)
Enlightenment
Revitalization of Nobility and Virtue
Importance of Elders and Ancestors
China
6th-5th Centuries BCE
Supreme Sage K'ung-fu-tsu (Confucius)
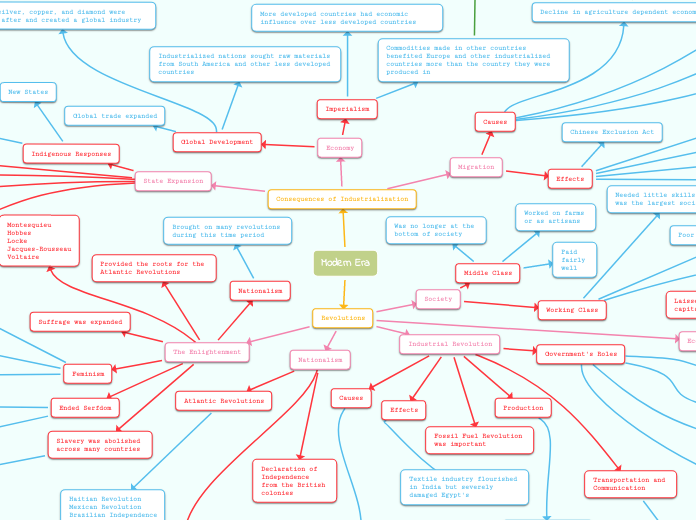
Buddhism
Types of Buddhism
Mahayana Buddhism
Major Forms
Zen, Nichiren, Tendai, and Pure Land
Ways of Worship
Ritual, Devotion, Meditation
Deities, Celestial Beings, Other Traditional Religious Elements
China and Japan
Theravada Buddhism
Focuses on Monastic Life and Meditation
Atheistic, Philosophical in Nature
Southeast Asia
Dominant World Religion in the East
Began in India 2,500 Years Ago
Buddha
Enlightenment and Nirvana
Worship
Rituals
Karmic Acts
Meditation
Reality
Inter-Related
Ever-Changing
Four Noble Truths
Marga
Path to End Suffering
Noble Eightfold Path
Right --> View, Thought, Speech, Conduct, Vocation, Effort, Attention and Meditation
Nirodha
Nirvana
End of Suffering
"One Must Cease All Desires"
Samudaya
Suffering has a cause
Attachment or Misplaced Desire Rooted in Ignorance.
Dukkha
Suffering is Everywhere and a Part of Life
Background
Story
"Sheltered Young Prince Shocked by Suffering he Saw Outside, Left his Life of Luxury to Seek Answers"
Became Buddha ("Enlightened One")
"Taught Dharma (the Path to Liberation from Suffering) and Establishing the Sangha (a Community of Monks)"
Indian Prince Siddharta Gautama, 500 BCE
Hinduism
Fundamental Beliefs
Karma
Reincarnation
Brahmans
Priests
Vedas
Texts
Goal of the Individual
Self-Realization
Seeking Awareness, Understanding and Connection with Ultimate Reality.
Multiple Paths
Brahman
Divine Self
Following Gods
Monist/Dualist
Realize Truth
Ultimate Reality
"Brahman"
Scope
Third Largest Religion
80% of India's Population
World's Oldest Religion
Dates Back to 10,000 BCE