Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, July 27). Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Retrieved October 17, 2020, from cc.gov: https://www.cdc.gov/co/faqs.htm
Center of Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, Janurary 20). National Center for Enviromental
Helath. Retrieved October 17, 2020, from cdc.gov: https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/features/copoisoning/index.html#:~:text=Every%20year%2C%20at%20least%20430,due%20to%20accidental%20CO%20poisoning.
Enviromental Protection Agency. (2000, January). Preventing Carbon Monoxide Poisoning.
Retrieved October 17, 2020, from www.epa.gov:
https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-08/documents/pcmp_english_100-f-09-001.pdf
Gozubuyuk, A. A., Dag, H., Kacar, A., Karakurt, Y., & Arica, V. (2017). Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation, and treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning in child, infant, and fetus. Northern clinics of Istanbul, 4(1), 100–107. https://doi.org/10.14744/nci.2017.49368
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G. Worldwide epidemiology of carbon monoxide poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2020 Apr;39(4):387-392. doi: 10.1177/0960327119891214. Epub 2019 Dec 1. PMID: 31789062. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31789062/#:~:text=The%20worldwide%20cumulative%20incidence%20and,%25%20and%2040%25%2C%20respectively.
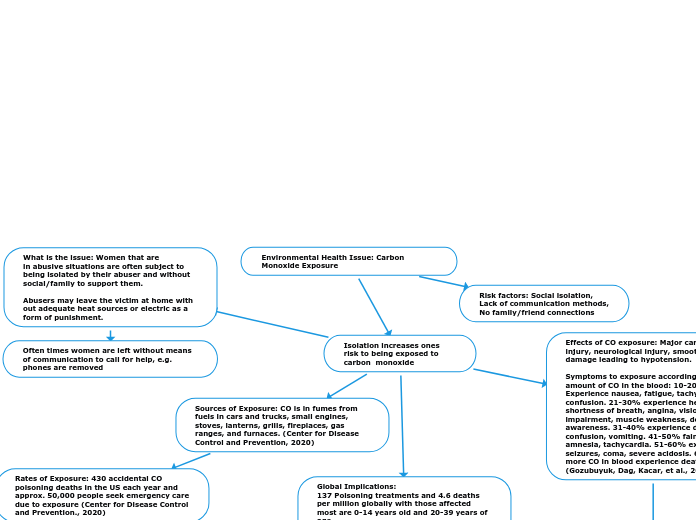
Environmental Health Issue: Carbon Monoxide Exposure
Isolation increases ones risk to being exposed to carbon monoxide
Global Implications:
137 Poisoning treatments and 4.6 deaths per million globally with those affected most are 0-14 years old and 20-39 years of age.
Globally men are 2x as likely to be affected.
(Mattiuzzi & Lippi, 2019)
Sources of Exposure: CO is in fumes from fuels in cars and trucks, small engines, stoves, lanterns, grills, fireplaces, gas ranges, and furnaces. (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020)
Rates of Exposure: 430 accidental CO poisoning deaths in the US each year and approx. 50,000 people seek emergency care due to exposure (Center for Disease Control and Prevention., 2020)
Exposure Pathway
1. Source - Fumes are created from combustion present from fuels of cars, trucks, engines, stoves, lanterns, fireplaces, grills, ranges, and furnaces. (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020)
2. Mechanism - A portable heat source is brought into a home for heat and light.
3. Point of Exposure - A woman and child are being isolated in a home without heat or electricity. Due to the frigid temperatures outside the woman used a portable propane grill left by a previous tenant.
4. Route of Exposure - The woman bring the grill in and lights it because she and the child are freezing. Soon they become warm and fall asleep. While sleeping, carbon monoxide builds up in the small home. The woman and child breath in the gas that have no odor, they lose the ability to breathe and never regain consciousness.
Effects of CO exposure: Major cardiac injury, neurological injury, smooth muscle damage leading to hypotension.
Symptoms to exposure according to the amount of CO in the blood: 10-20% Experience nausea, fatigue, tachypnea, confusion. 21-30% experience headache, shortness of breath, angina, vision impairment, muscle weakness, decreased awareness. 31-40% experience dizziness, confusion, vomiting. 41-50% fainting, amnesia, tachycardia. 51-60% experience seizures, coma, severe acidosis. 60% or more CO in blood experience death. (Gozubuyuk, Dag, Kacar, et al., 2017)
Prevention: Use CO alarms in sleeping areas, do not use non-vented appliances, do not burn fuels indoors, be aware of symptoms.
How can we help from a public health perspective: 1) Identify domestic violence survivors that may be at risk and provide education and support. 2) Distribute CO detectors free of charge in areas where domestic violence has been identified as prevalent. 3) Distribute education packets at health fairs and other ares where women may be seeking health related information.
What is the issue: Women that are
in abusive situations are often subject to
being isolated by their abuser and without
social/family to support them.
Abusers may leave the victim at home with out adequate heat sources or electric as a form of punishment.
Often times women are left without means of communication to call for help, e.g. phones are removed
Risk factors: Social isolation,
Lack of communication methods,
No family/friend connections