Quantitative approach in education generalities
Quantitative approach is suitable to answer more precisely some fundamental questions.
Quantitative research is principally objective
For instance, to measure an aspect of interest of research study by using numbers.
like who, how much, what, where, when, how many, and how.
Main advantages of quantitative approach.
simplifies the possibility of measuring how many and how often “situations”
helps researches to optimize the time and effort invested in analyzing and describing the results gotten.
the information can be more accurately verified, confirmed and checked.
Disadvantages of the quantitative approach
some mistakes may happen if a hypothesis or a method
Quantitative research can be insufficient
measures variables in a particular context at a determined moment
positivism paradigm neither describes how reality is “shaped” nor refers to how persons “interpret” their behaviors.
can also be restrictive.
Quantitative research is practical and useful because it is likely to
Eliminate bias
Extensive range of data analysis
Quick data collection
Collect reliable and accurate data:
permits to observe, count and analyze the information required using statistical techniques.
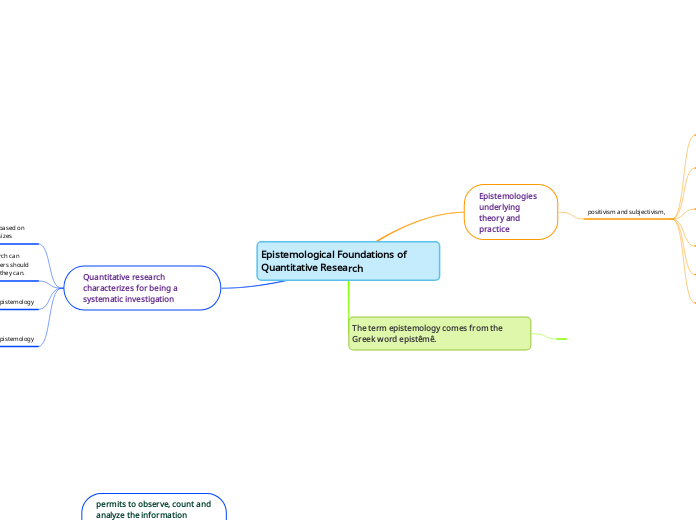
Epistemological Foundations of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research characterizes for being a systematic investigation
The third epistemology
Pragmatism, recommends a mixed methods approach relating quantitative and qualitative
The second epistemology
known as Experiential realism, claims that it is not possible to observe the world from an objective way only
Post-positivists consider that research can never be certain, and that researchers should approximate that reality as best as they can.
the results are based on bigger sample sizes
The term epistemology comes from the Greek word epistêmê.
Epistemologies underlying theory and practice
positivism and subjectivism,
Postmodernism
rejects the idea that science can be regarded as objective.
Criticalism
confronts those predictable knowledge foundations and methodologies.
Interpretivism
incorporates human interest into a study.
Post-positivism
everything that is observed is assumed through a "prior understanding of other theories and concepts."
Subjectivism
gives primacy to subjective experience as fundamental of all measure and law.
Positivism
based on natural phenomena and their properties and relations.